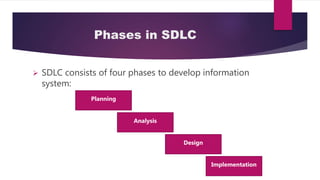
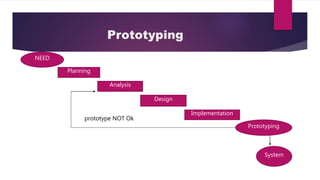
The document outlines the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) as a systematic method for organizations to implement change through phases of planning, analysis, design, and implementation. It emphasizes the importance of feasibility studies and stakeholder involvement, with additional focus on prototyping as a technique for iterative development with immediate user feedback. Maintenance and support activities post-implementation are also highlighted to ensure ongoing system effectiveness.