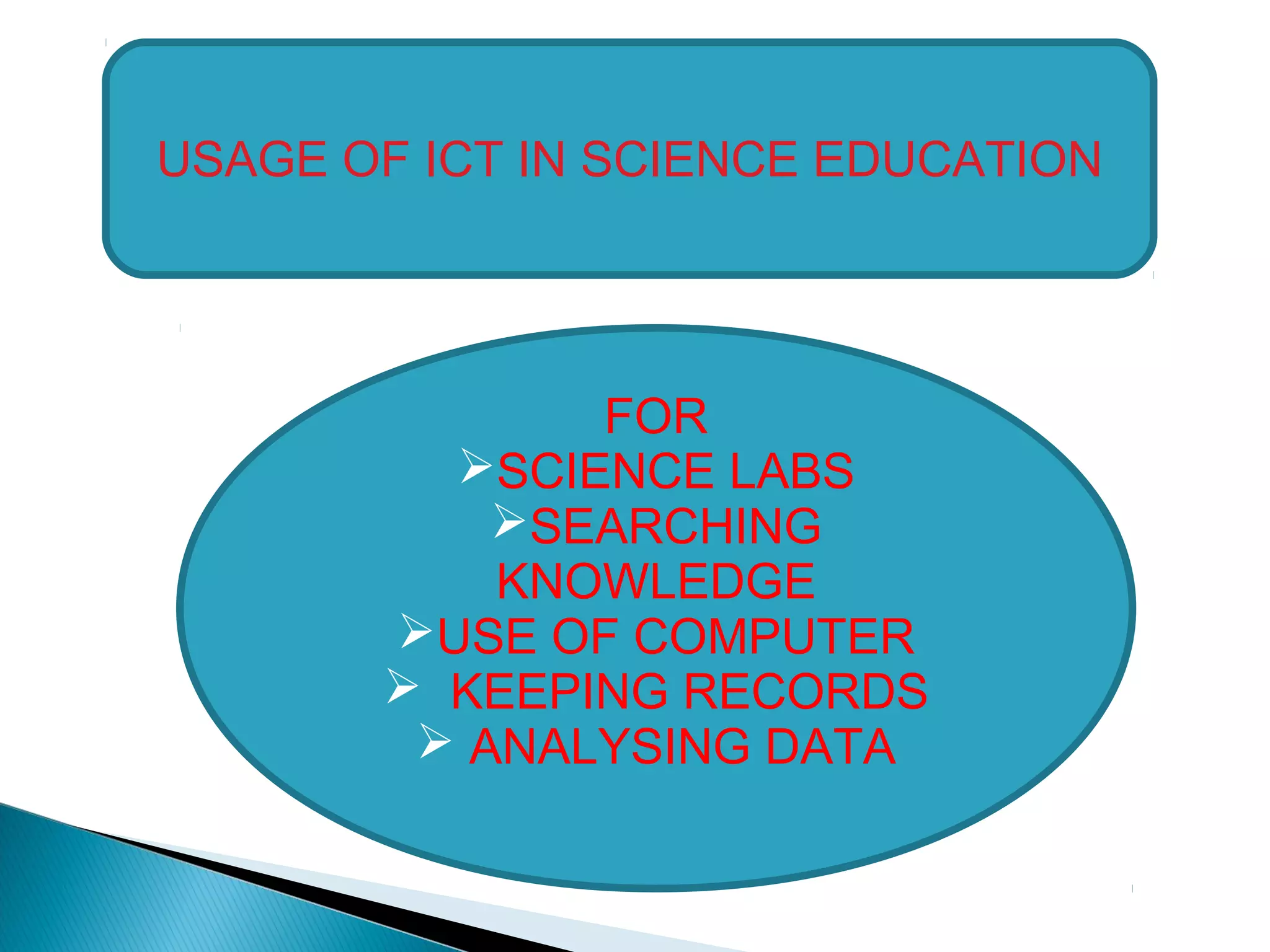
This document discusses the importance of information and communications technology (ICT) in science education. It defines ICT and discusses four common rationales for science education, including the utilitarian, economic, cultural, and democratic rationales. The document outlines benefits of using ICT in science education such as removing problems of space and time, allowing students to access and share knowledge globally, and making learning interactive. It emphasizes that ICT makes serving and sharing knowledge easier and allows students to create records and presentations to track their progress. Finally, the document stresses the importance of ICT in promoting higher-order thinking skills, creating supportive learning environments, and ensuring effective interactive learning.