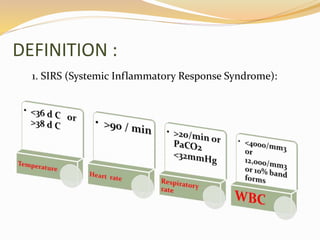
This document defines sepsis and related terms like SIRS, severe sepsis, and septic shock. It discusses the etiology (causes) of sepsis as various infections. It lists risk factors and potential clinical manifestations such as metabolic acidosis, decreased systemic vascular resistance, and organ dysfunctions. Nursing diagnoses are identified like presence of infection, ineffective airway clearance, ineffective breathing, and imbalanced nutrition related to the disease process. Complications of sepsis can include low blood pressure leading to septic shock, ARDS, tissue death, and multiorgan failure.