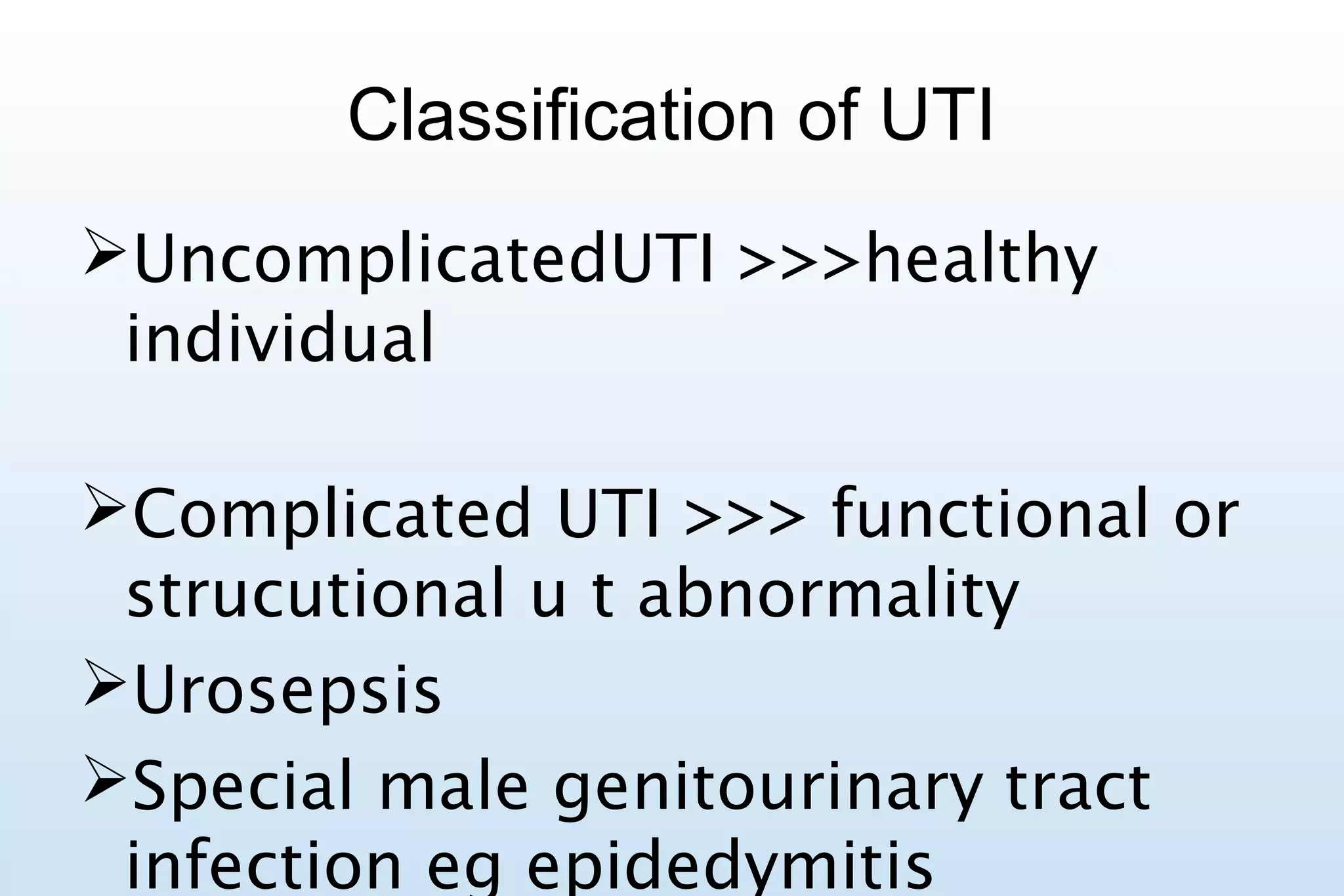
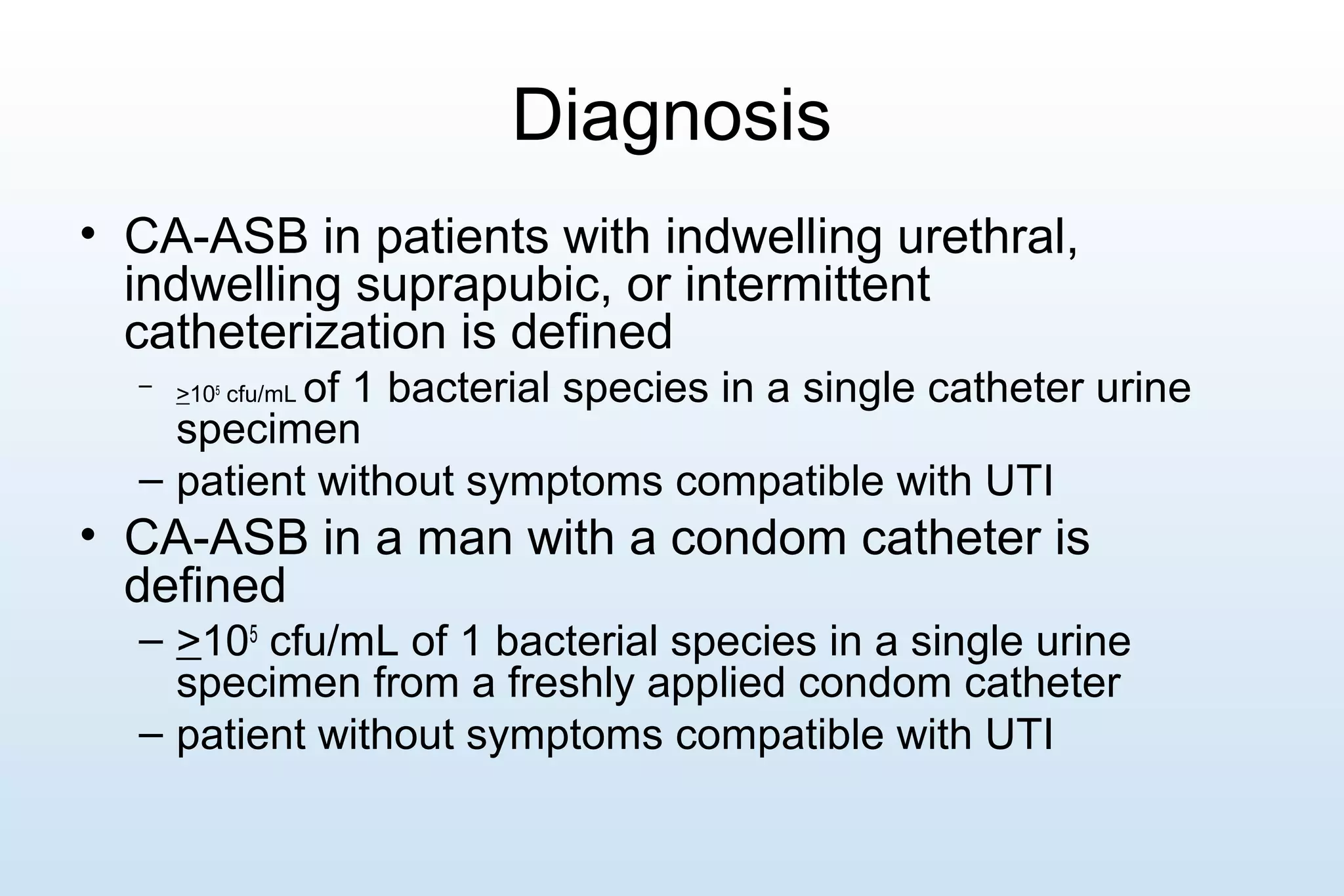
This document provides guidelines for the treatment of nosocomial catheter-associated urinary tract infections (NCUTI) and urosepsis. It discusses the microbiological causes, risk factors, evaluation, diagnosis and treatment recommendations. The most common causative organism is E. coli. Risk factors include advanced age, diabetes, immunosuppression and indwelling catheters. Treatment involves supportive care and targeted antibiotic therapy based on culture and sensitivity results, with durations typically between 14-21 days. Catheter removal is also recommended when possible prior to antibiotic treatment.