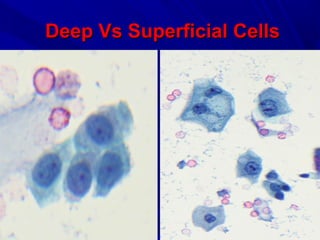
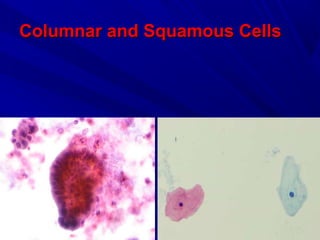
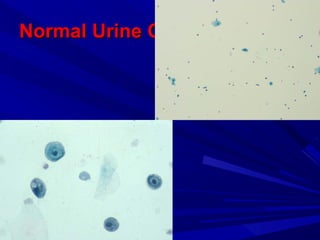
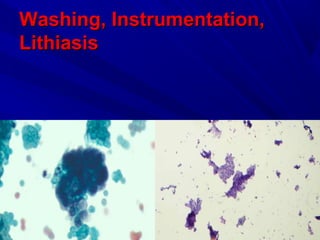
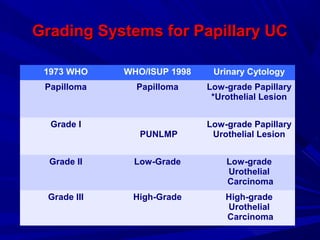
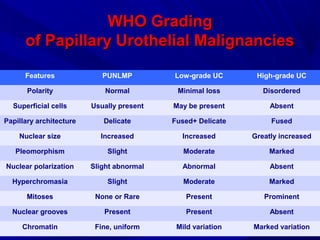
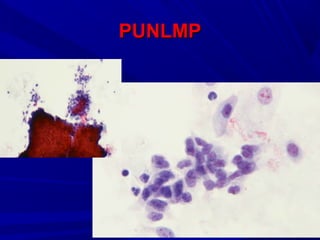
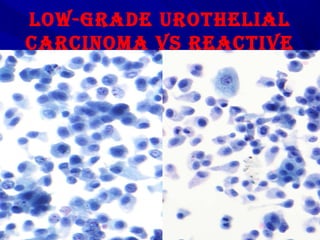
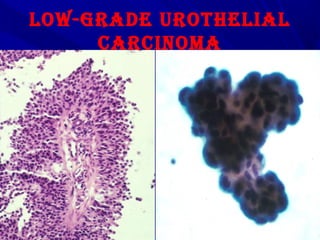
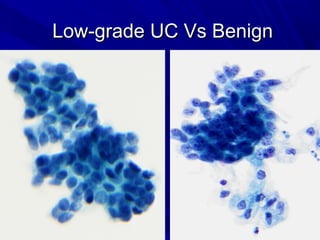
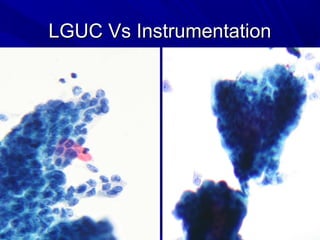
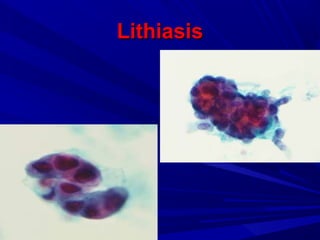
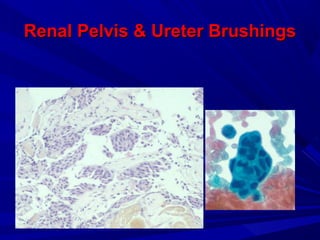
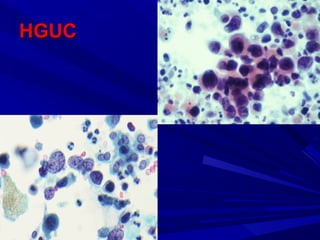
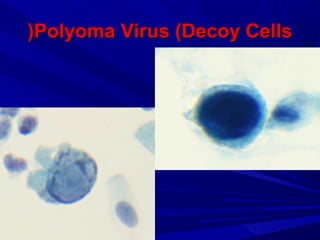
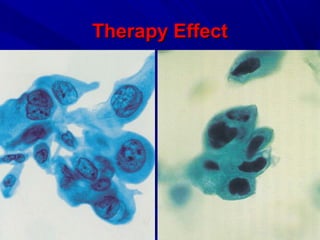
Urine cytology is useful for diagnosing urothelial carcinoma (UC), especially high-grade UC. It has high sensitivity for detecting high-grade lesions but is less reliable for low-grade UC and papillary urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential (PUNLMP) due to their more subtle cytological features and lower shed cell numbers. Cytology is best at detecting high-grade UC, which has a high mortality rate, but is less helpful for monitoring and detecting low-grade neoplasms, which are rarely aggressive. While this limits cytology for low-grade lesions, cystoscopy can readily identify them.