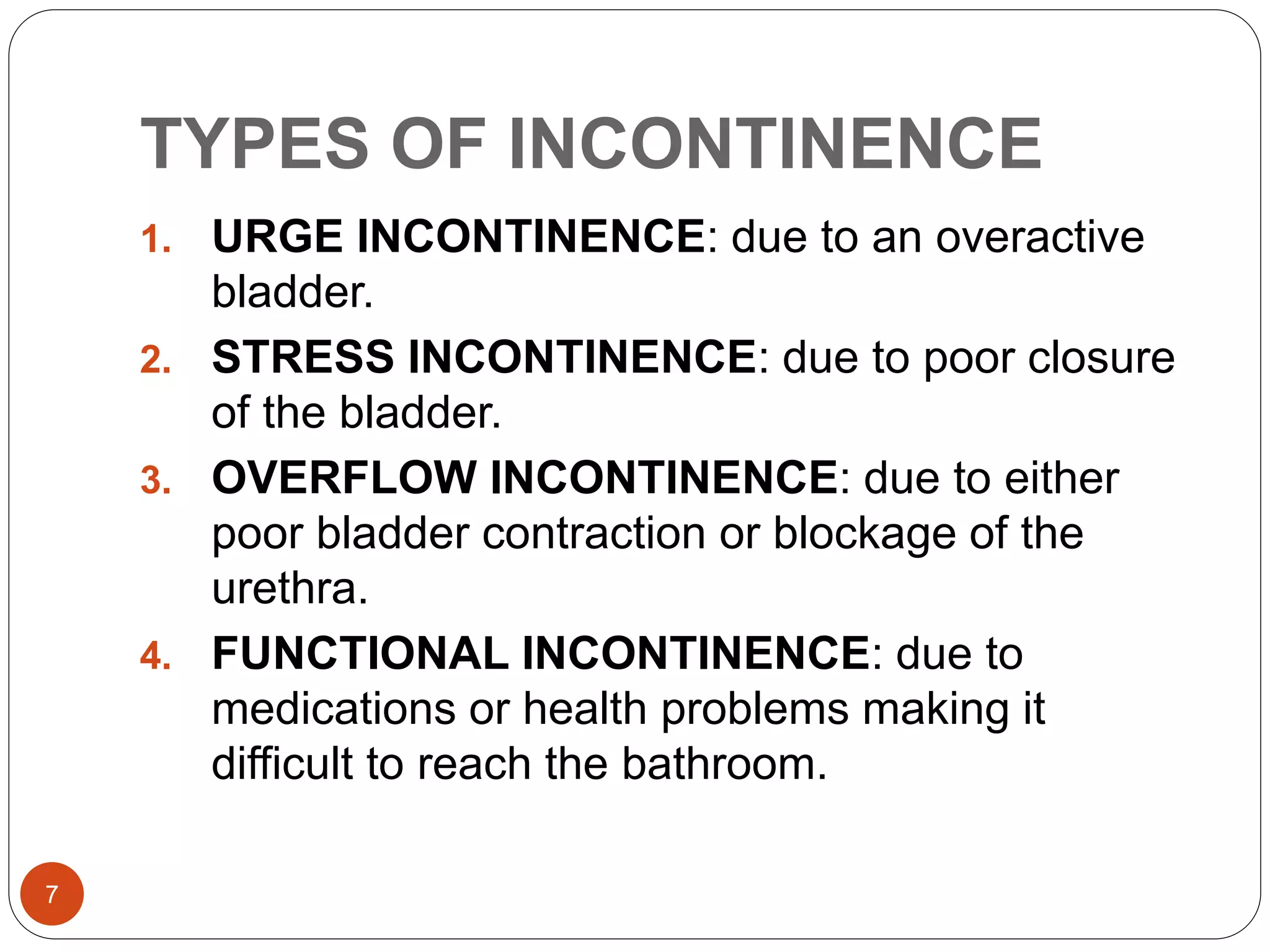
The document discusses the urinary system and three main topics: frequency, urgency, and incontinence. Frequency refers to how often one urinates and normal ranges vary by age. Common causes of increased frequency include urinary tract infections, diabetes, and prostate problems. Urgency is a sudden urge to urinate and is often caused by irritation or inflammation of the bladder wall. Incontinence, or involuntary urination, can be stress-related, urge-related, overflow, or functional due to medications/health issues. It is more common in women and risks include pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause.