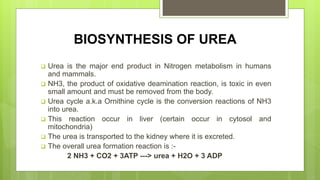
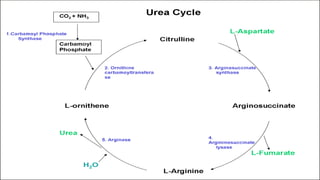
The document discusses the urea cycle, which is the process by which ammonia is converted to urea in the liver and excreted by the kidneys. The urea cycle occurs in both the cytosol and mitochondria of liver cells. One amino group used in urea formation comes from glutamic acid through deamination, while the other comes from aspartic acid generated through a portion of the citric acid cycle. Arginase, the fifth and final enzyme in the urea cycle, cleaves arginine to yield urea and ornithine, regenerating ornithine for continued use in the urea cycle.