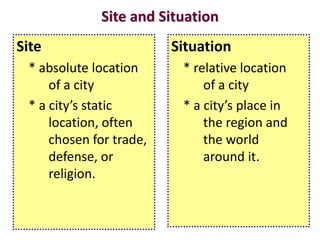
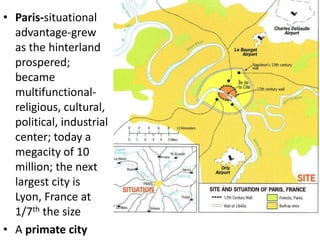
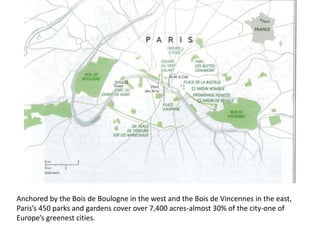
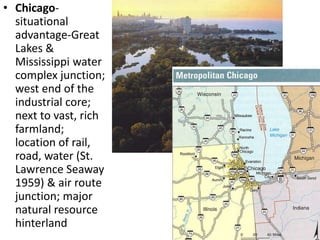
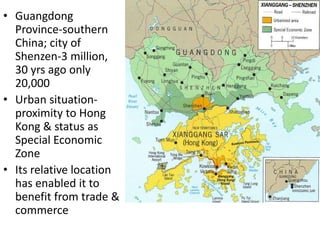
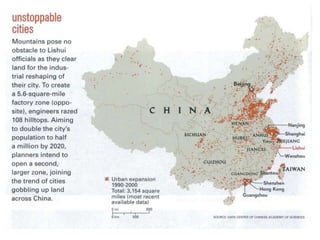
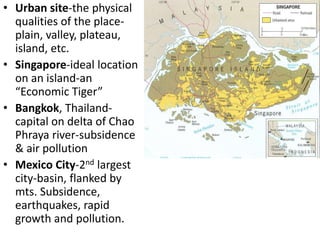
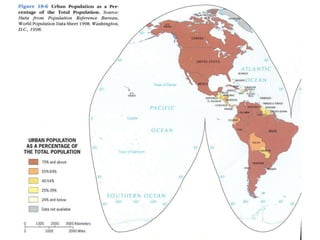
This document discusses urbanization and the factors that influence the location and growth of cities. It examines site (the physical attributes of a location) and situation (the relative location compared to other places). Key points include how urbanization has increased globally with 50% of the world now living in urban areas, and how a city's situation can impact its growth - for example Shenzhen growing due to its proximity to Hong Kong. Site and situation can both help and hinder a city - while prime locations prosper, others may decline if bypassed or lose advantages.