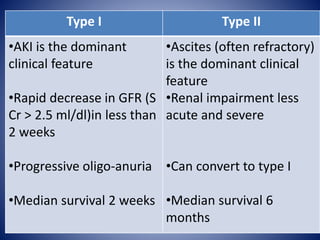
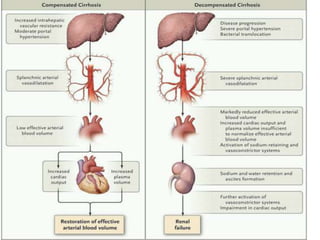
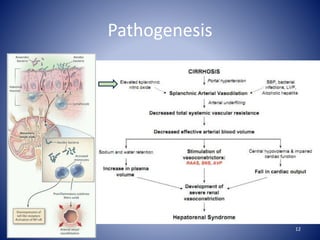
Hepatorenal syndrome is a type of kidney failure seen in patients with cirrhosis or acute liver failure. It occurs due to severe vasodilation in the splanchnic circulation leading to renal hypoperfusion. There are two types - type 1 is characterized by a rapid decline in kidney function over less than 2 weeks, while type 2 is less severe but still associated with refractory ascites. Treatment involves volume expansion with albumin and vasoconstrictors like terlipressin or midodrine to increase renal blood flow. Dialysis or liver transplantation may be needed for patients who do not respond to medical therapy. The prognosis is poor without treatment or liver recovery/transplantation.

































![Not critically ill patient:
• Terlipressin in combination with albumin:
Vasopressin analogues: Terlipressin is given as an
intravenous bolus (1 to 2 mg every four to six hours),
act via splanchnic V1 receptors ↓ serum creatinine,
↑ urine output, ↑ MAP and improved early survival.
Side effects: Ischemia cardiac, digital and
mesenteric.
Albumin is given for two days as an intravenous bolus (1
g/kg per day [100 g maximum]), followed by 25 to 50
grams per day until terlipressin therapy is discontinued.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrspresentation-180629153441/85/Hepatorenal-syndrome-presentation-38-320.jpg)

![• Albumin is given for two days as an
intravenous bolus (1 g/kg per day [100 g
maximum]), followed by 25 to 50 grams per
day until midodrine and octreotide therapy is
discontinued.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrspresentation-180629153441/85/Hepatorenal-syndrome-presentation-40-320.jpg)
![Critically ill patient:
Norepinephrine in combination with
albumin:
• Norepinephrine is given intravenously as a
continuous infusion (0.5 to 3 mg/hr) with the
goal of raising the mean arterial pressure by
10 mmHg
• Albumin is given for at least two days as an
intravenous bolus (1 g/kg per day [100 g
maximum]).
• Intravenous vasopressin may also be
effective, starting at 0.01 units/min and
titrating upward as needed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrspresentation-180629153441/85/Hepatorenal-syndrome-presentation-41-320.jpg)






![Hepatorenal syndrome regularly
develops in patients with systemic
bacterial infection (eg, spontaneous
bacterial peritonitis [SBP]) and/or severe
alcoholic hepatitis. The following
therapies may prevent the development
of hepatorenal syndrome in these
patients:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrspresentation-180629153441/85/Hepatorenal-syndrome-presentation-49-320.jpg)