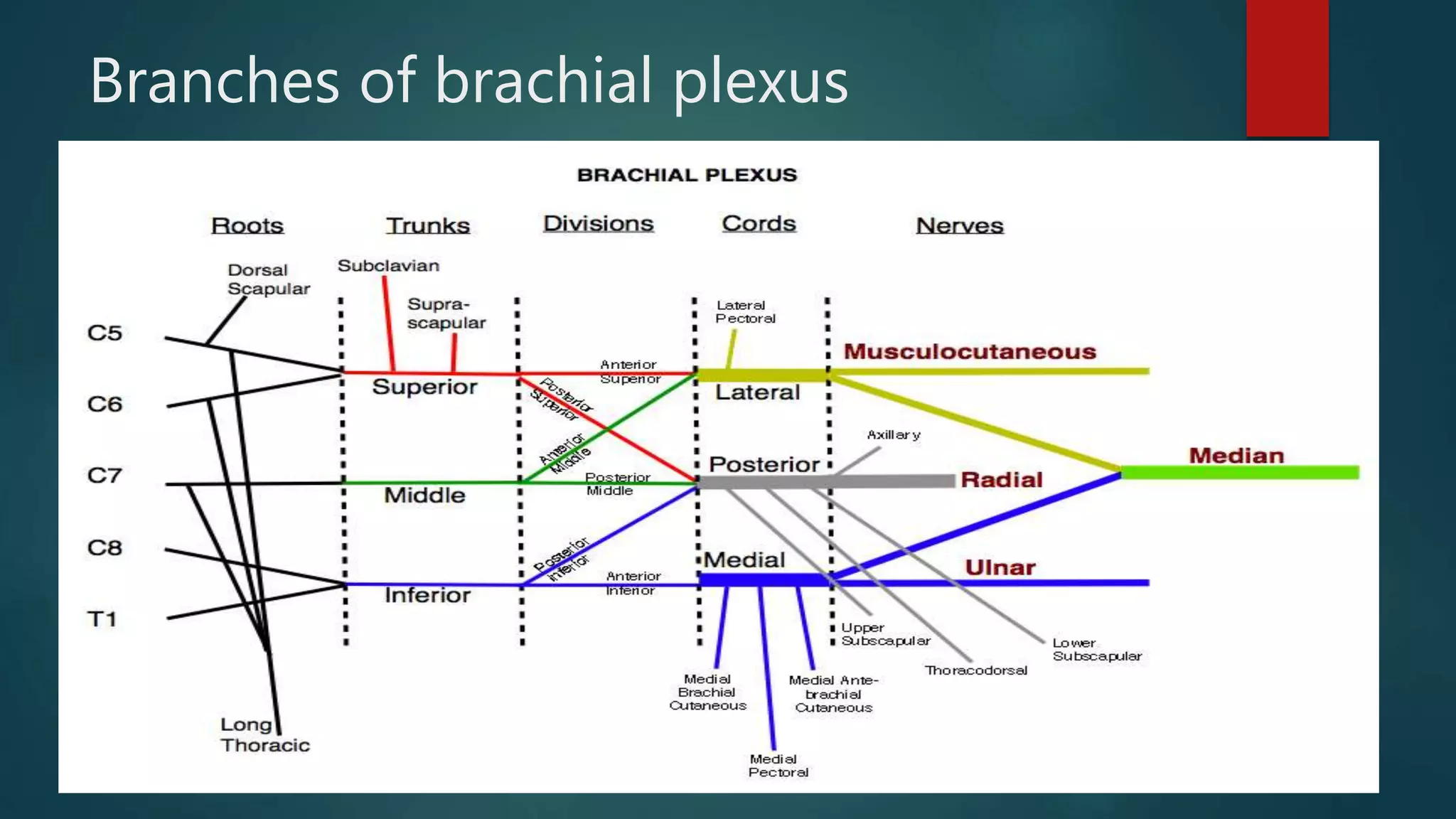
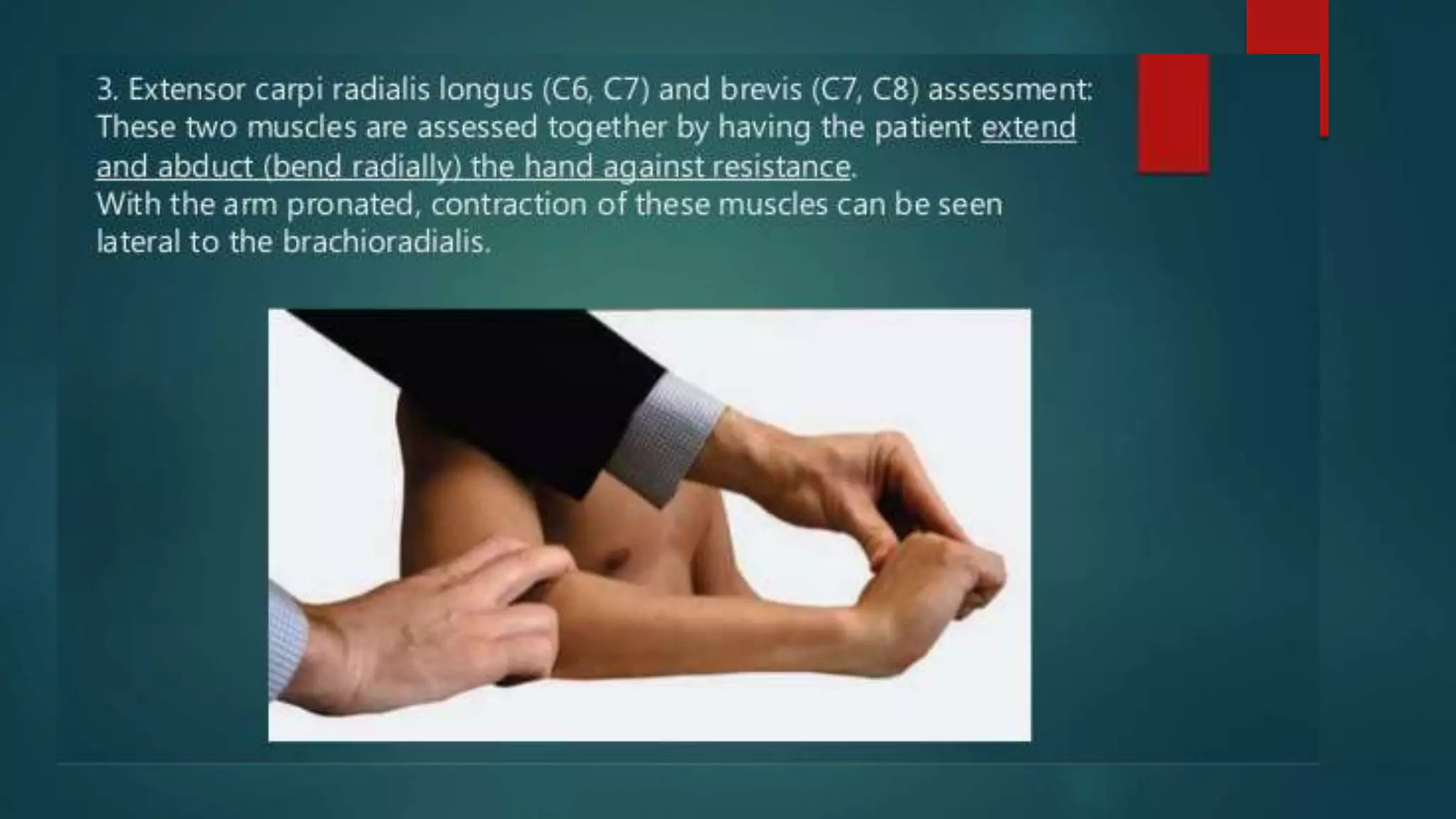
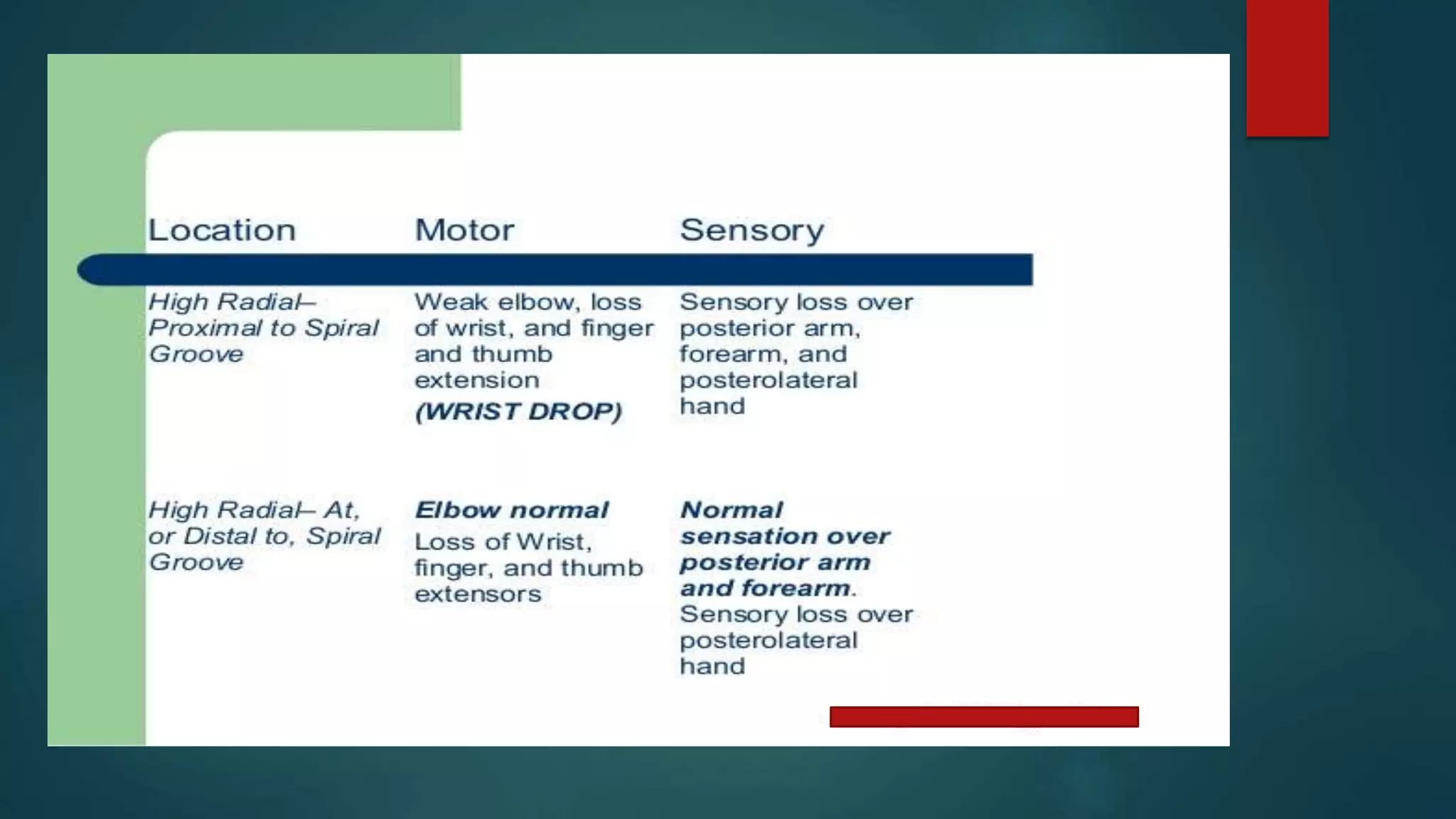
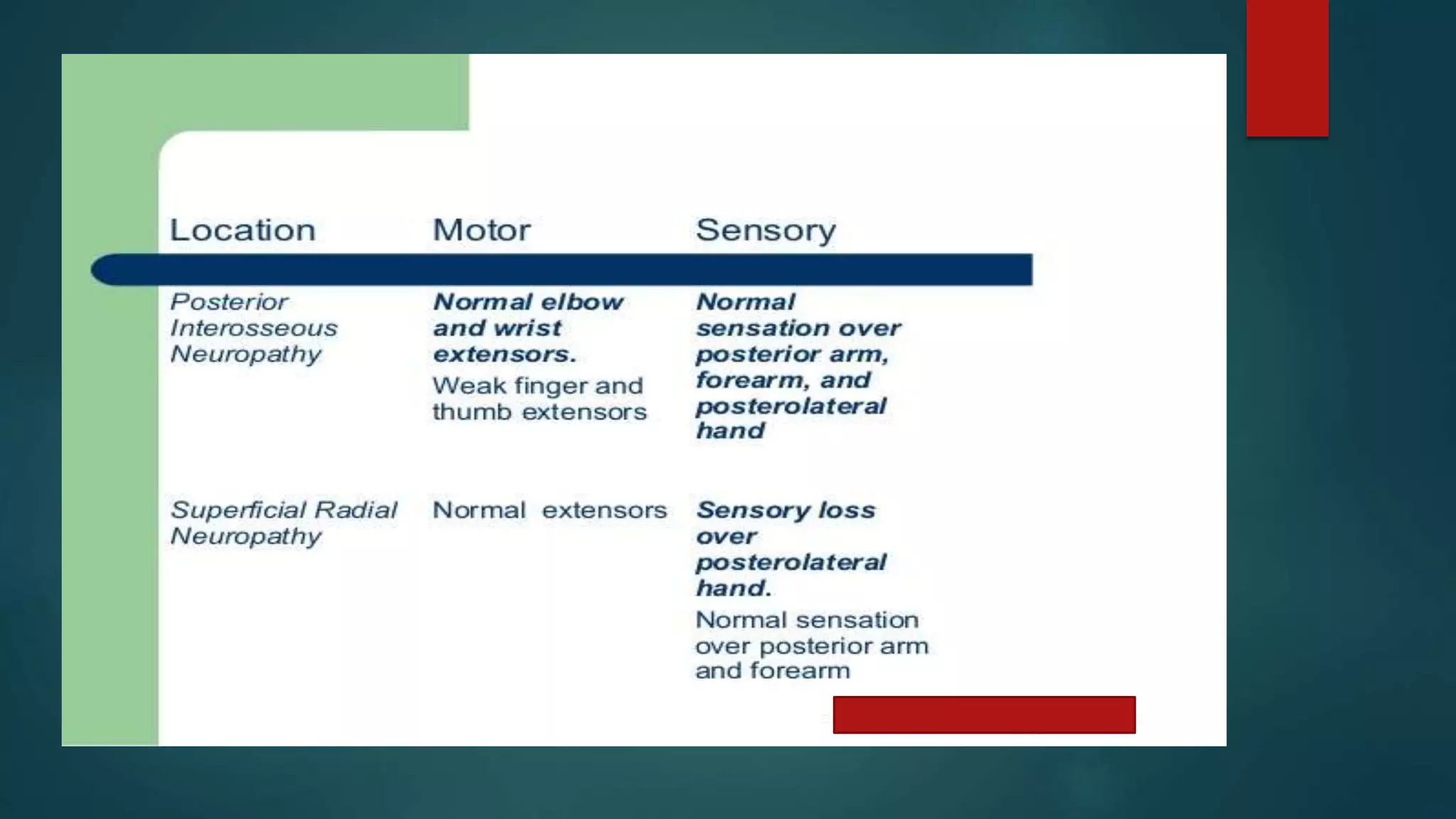
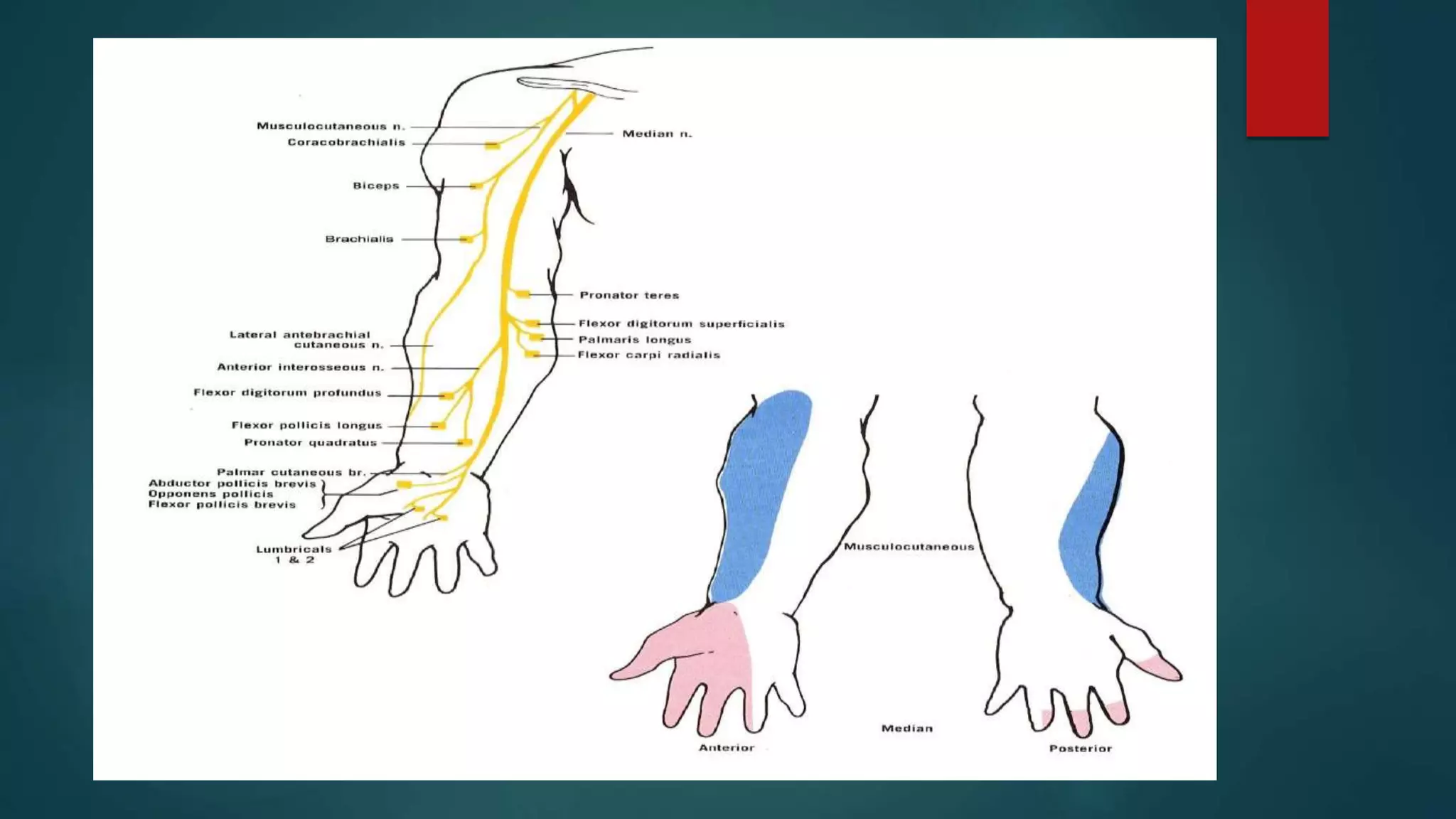
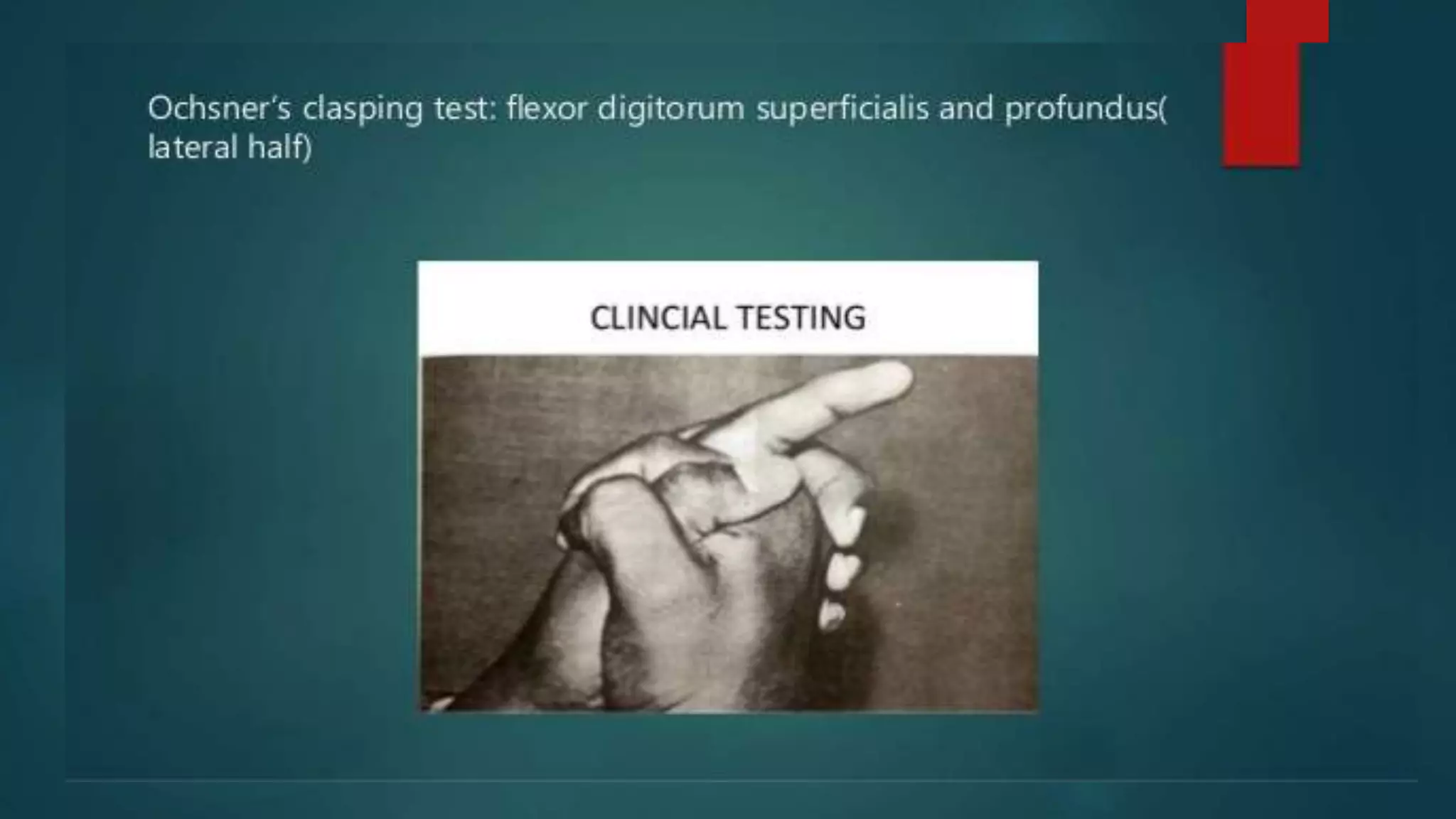
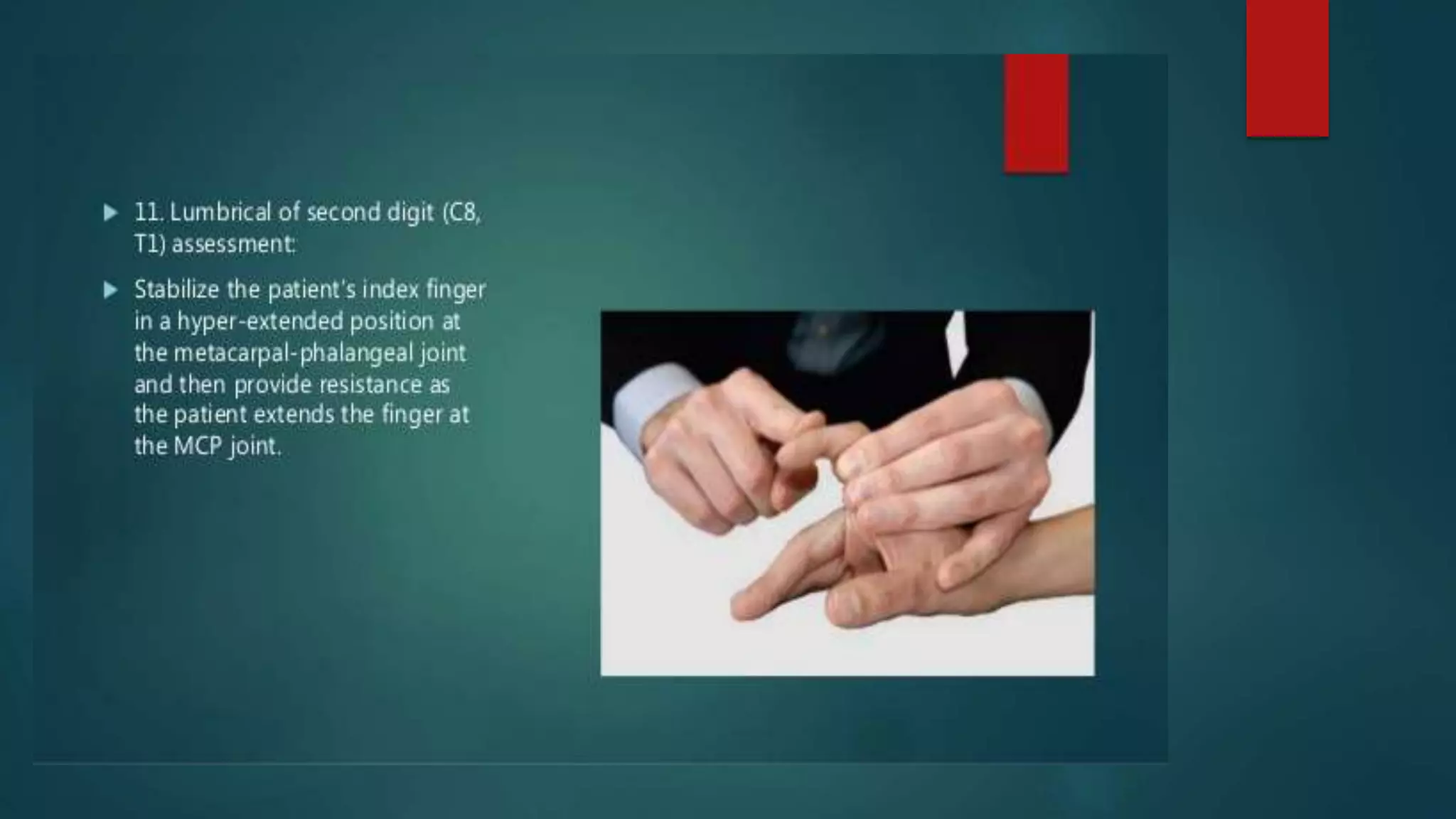
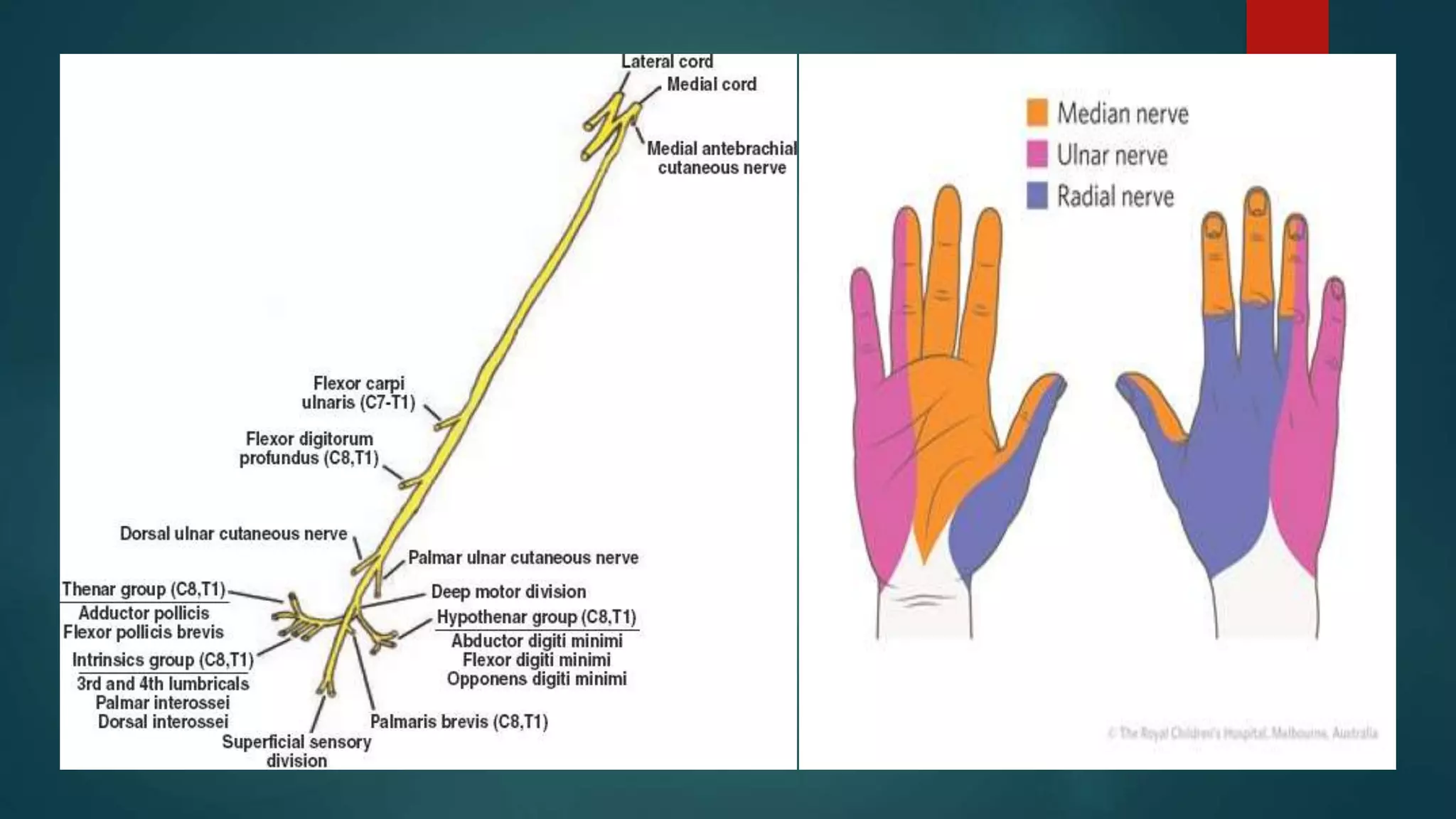
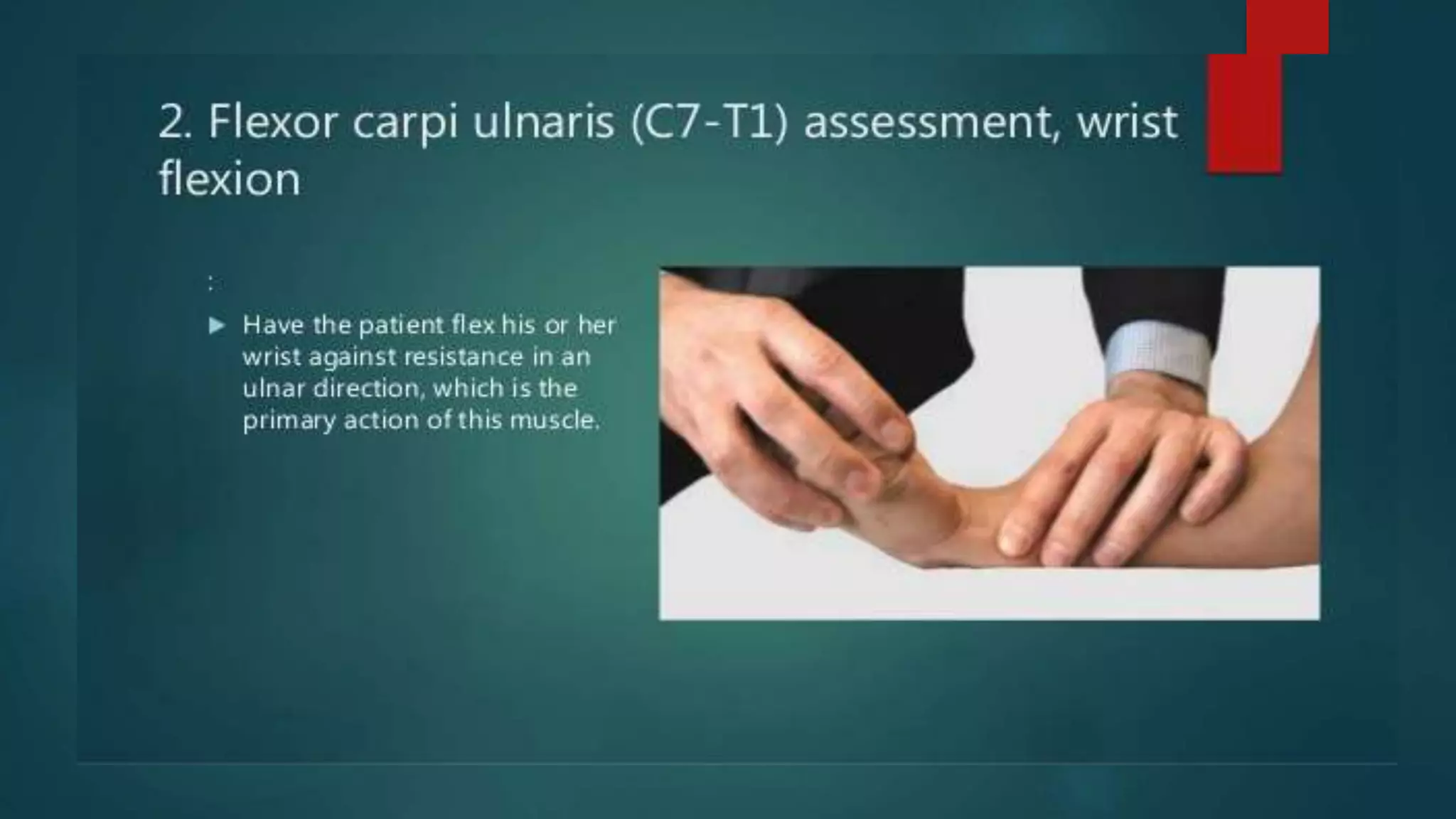
The document summarizes the anatomy and clinical presentations of injuries to the radial, median, and ulnar nerves. It describes the formation and branches of the brachial plexus. The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord and innervates the triceps and muscles of the posterior forearm. Median nerve injury can cause pointing of the index finger. Ulnar nerve injury results in a claw hand deformity due to paralysis of the intrinsic hand muscles.