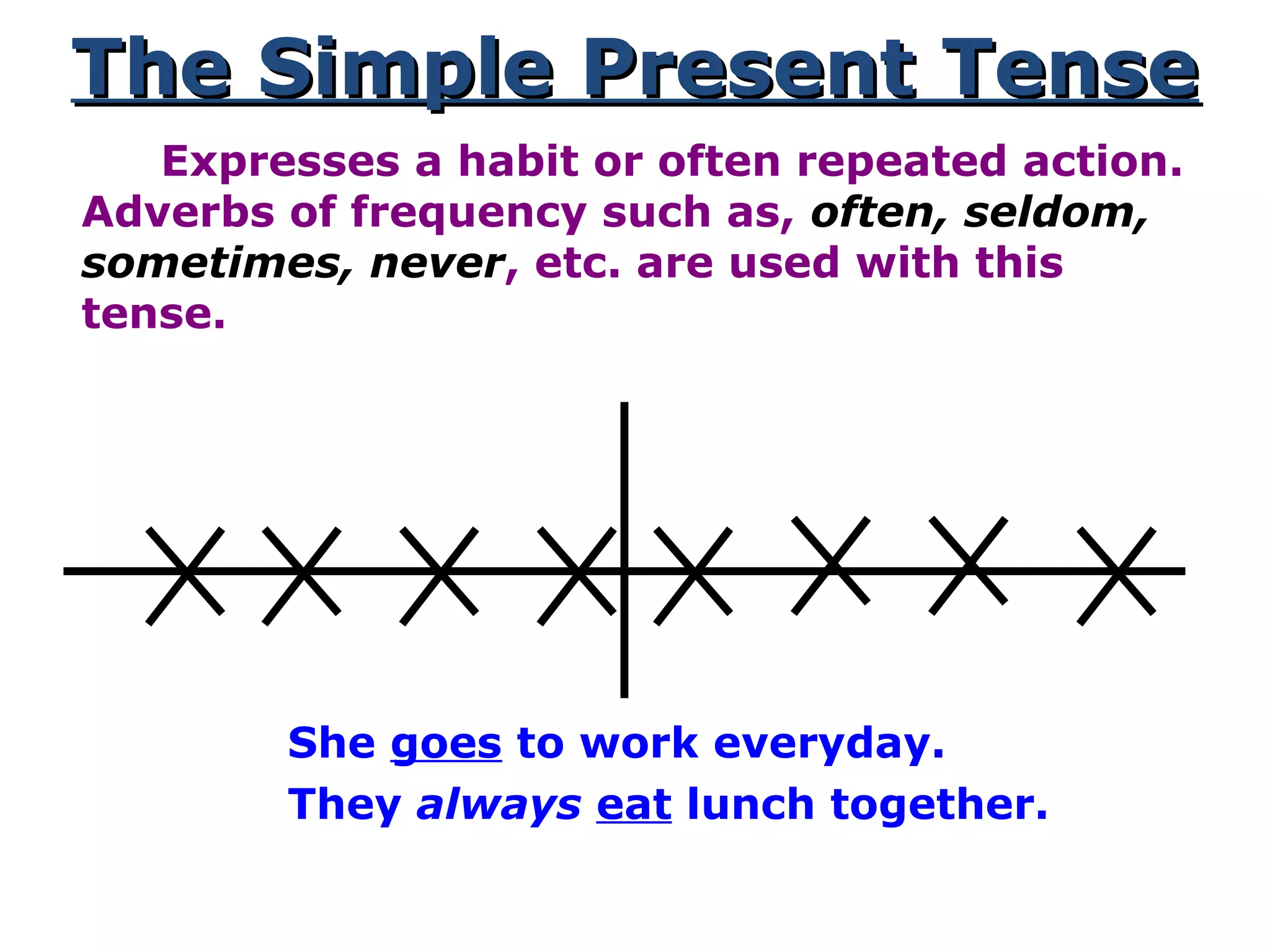
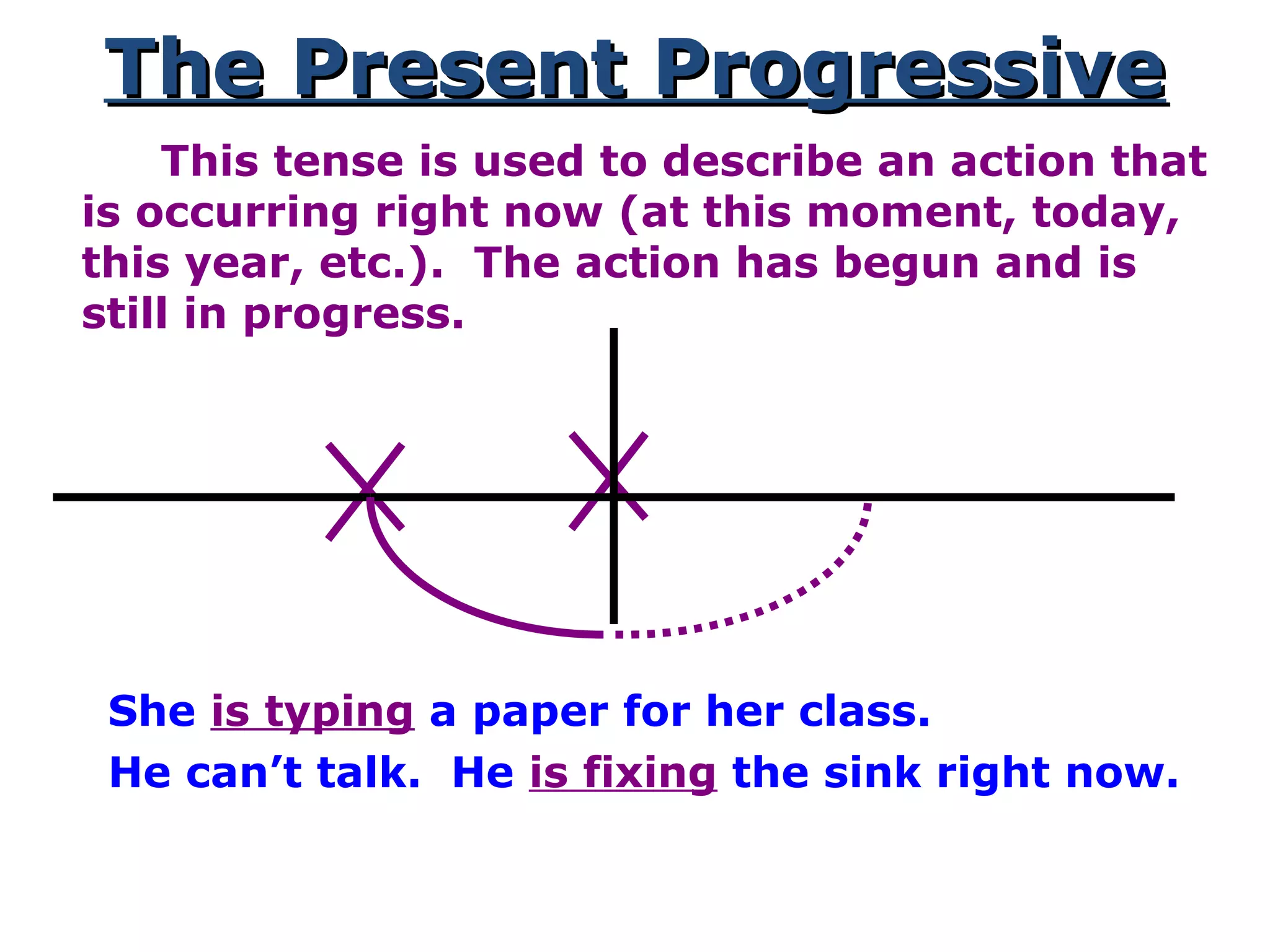
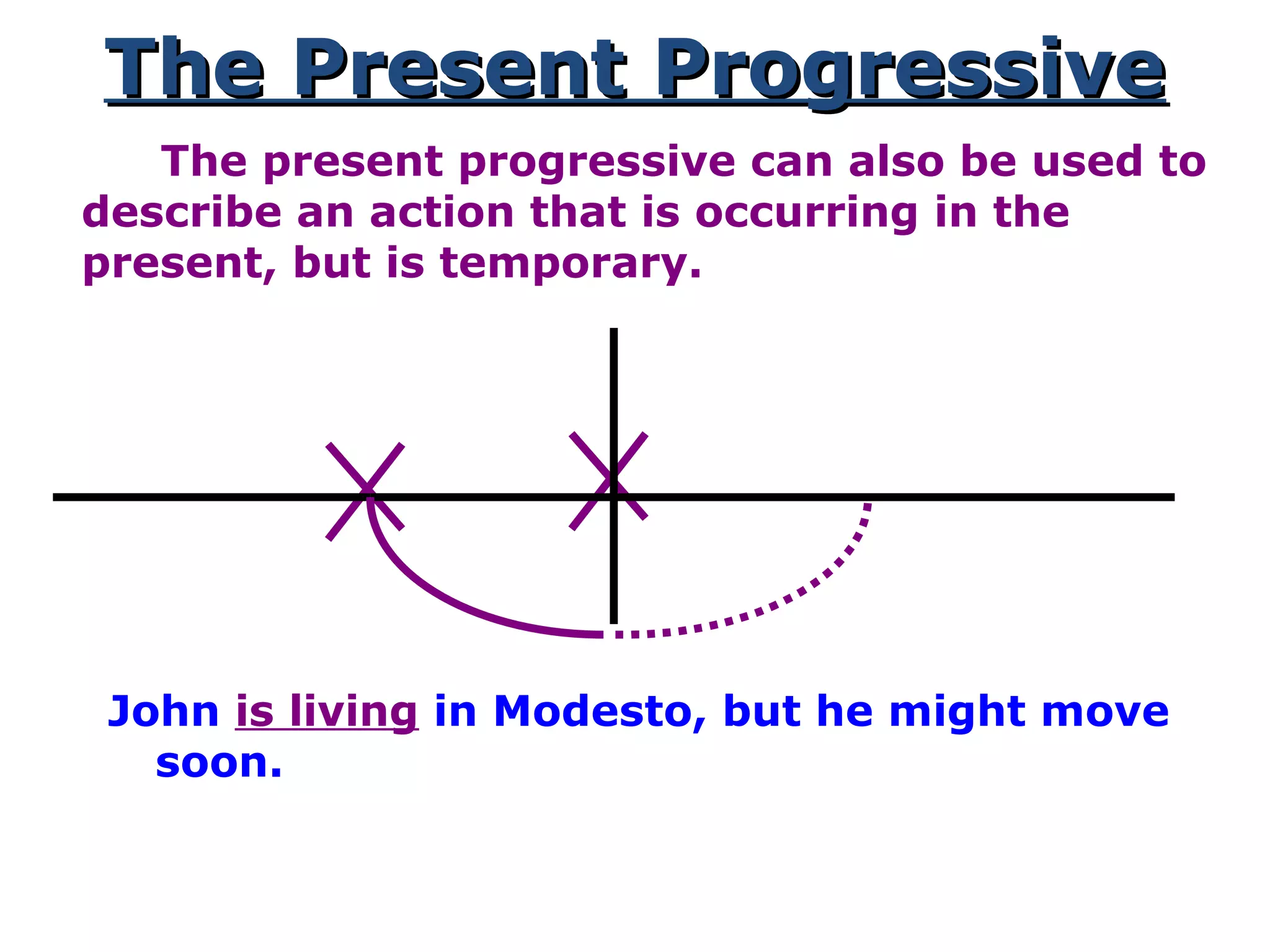
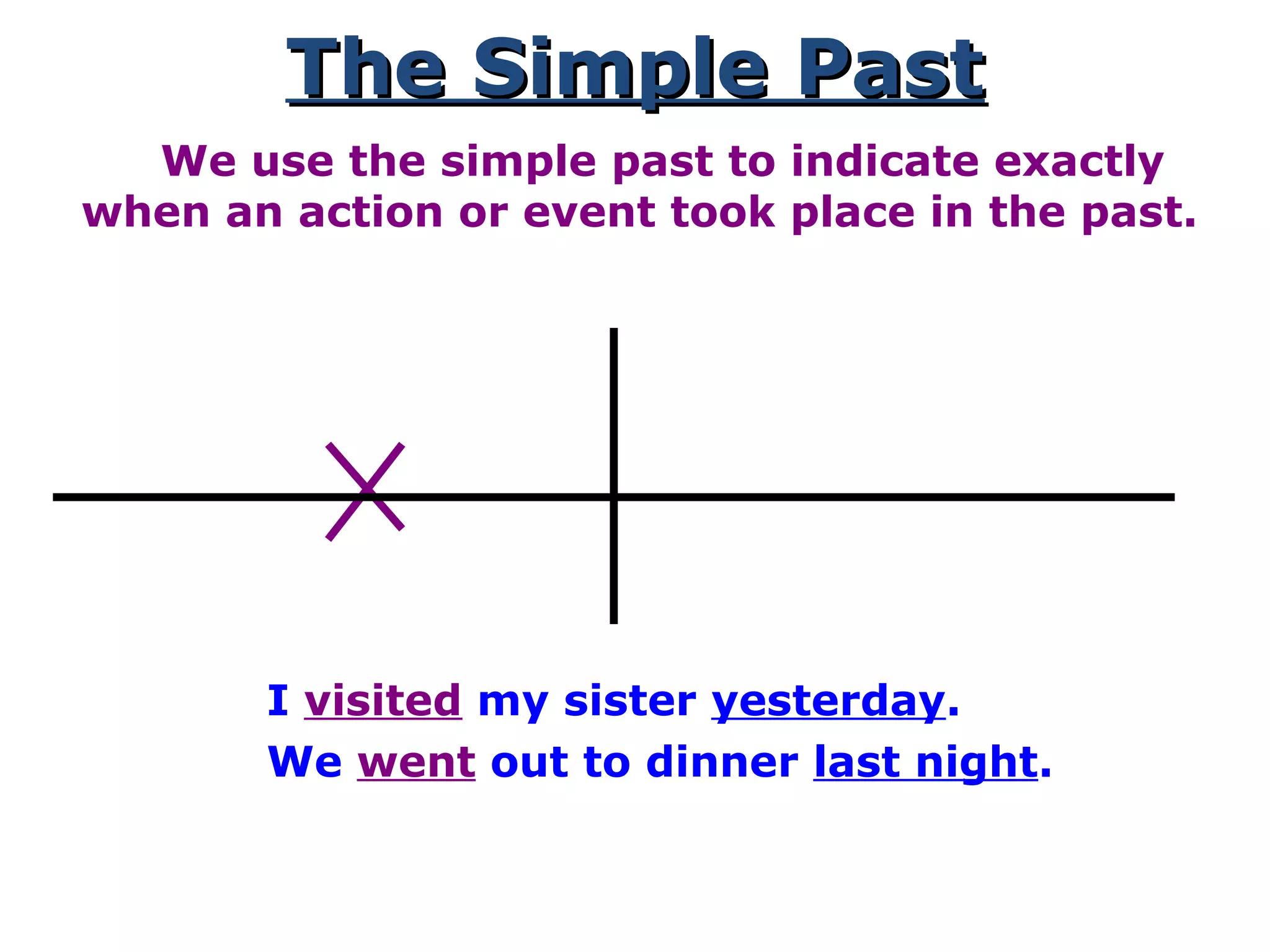
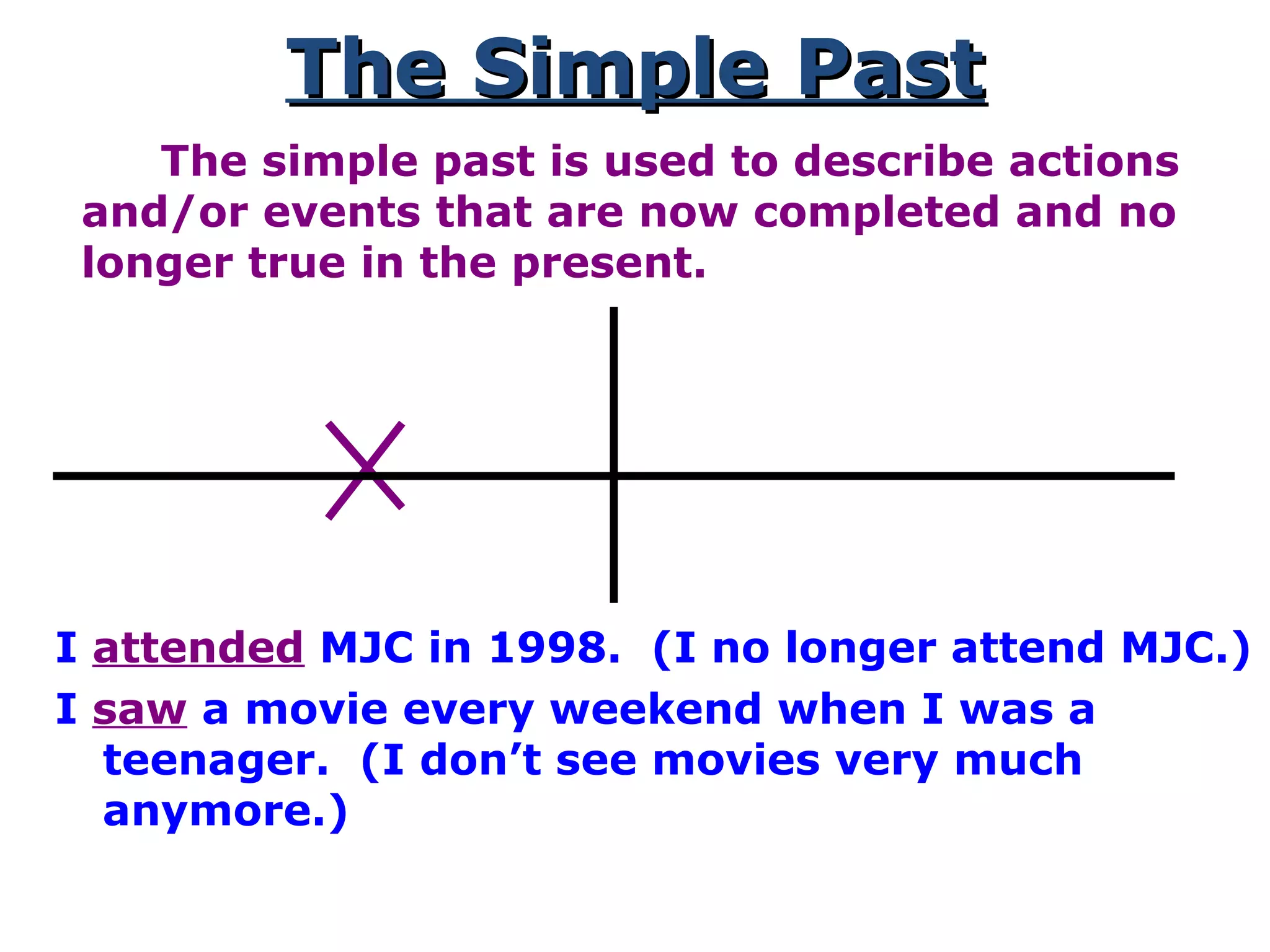
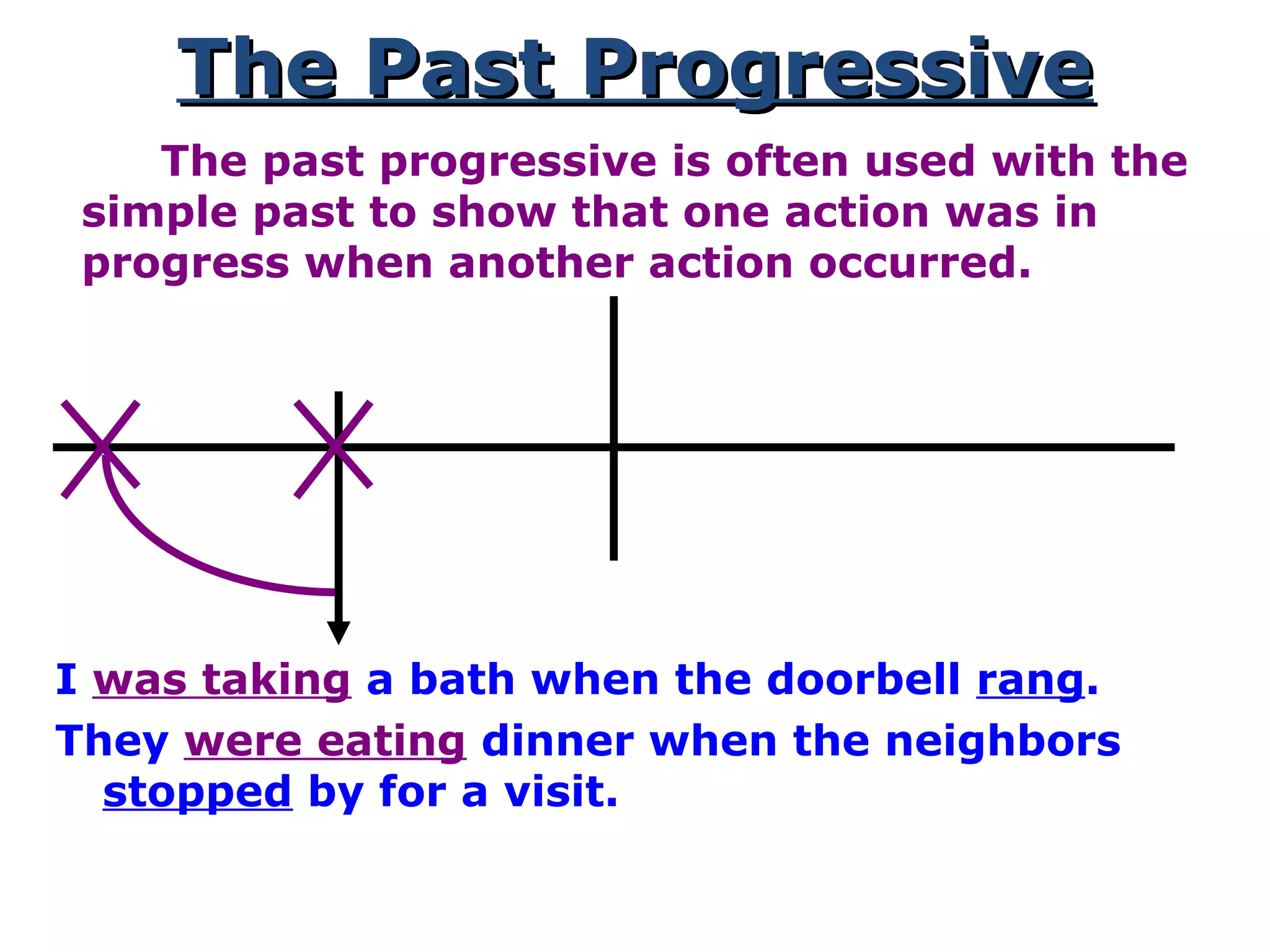
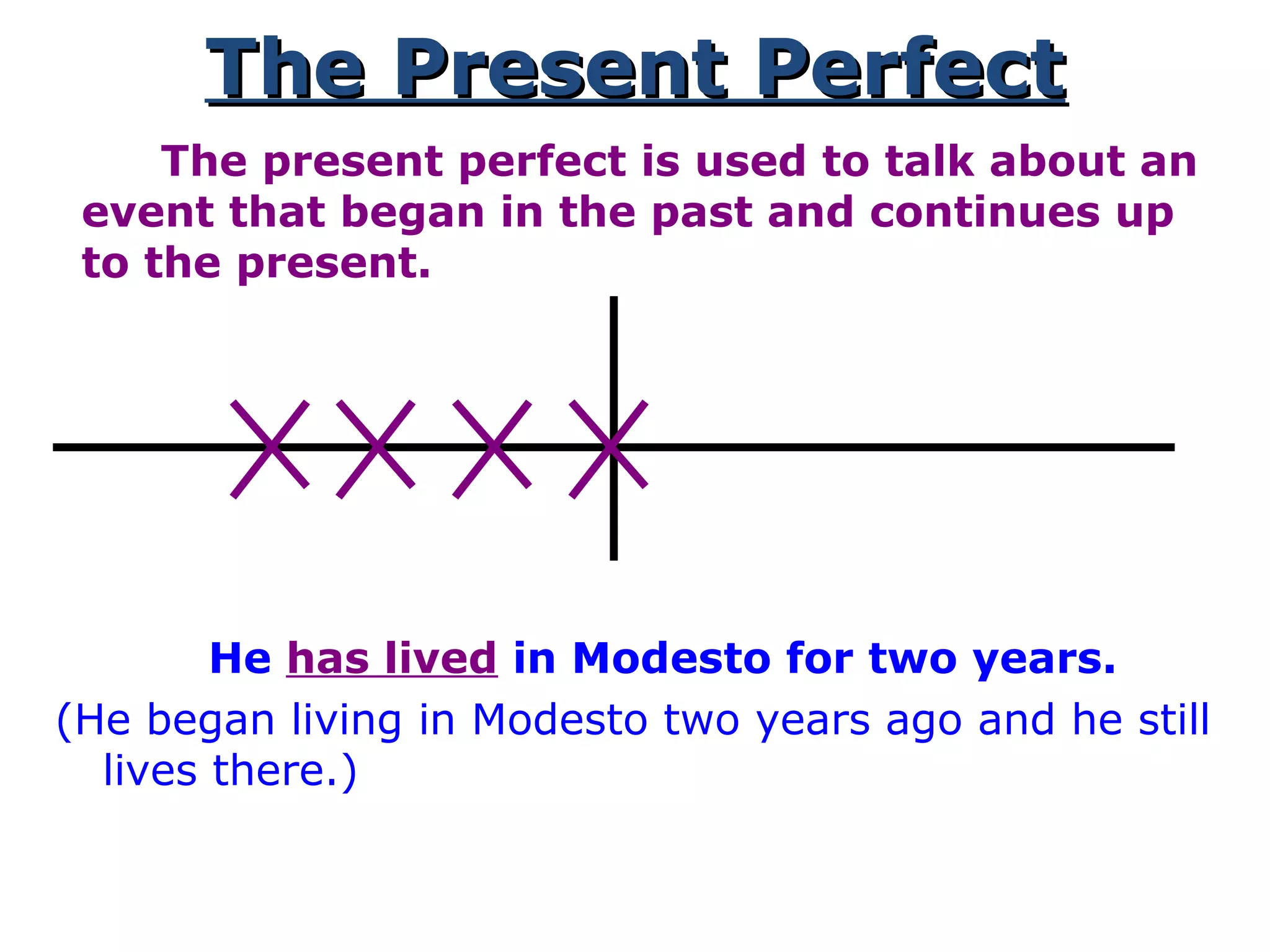
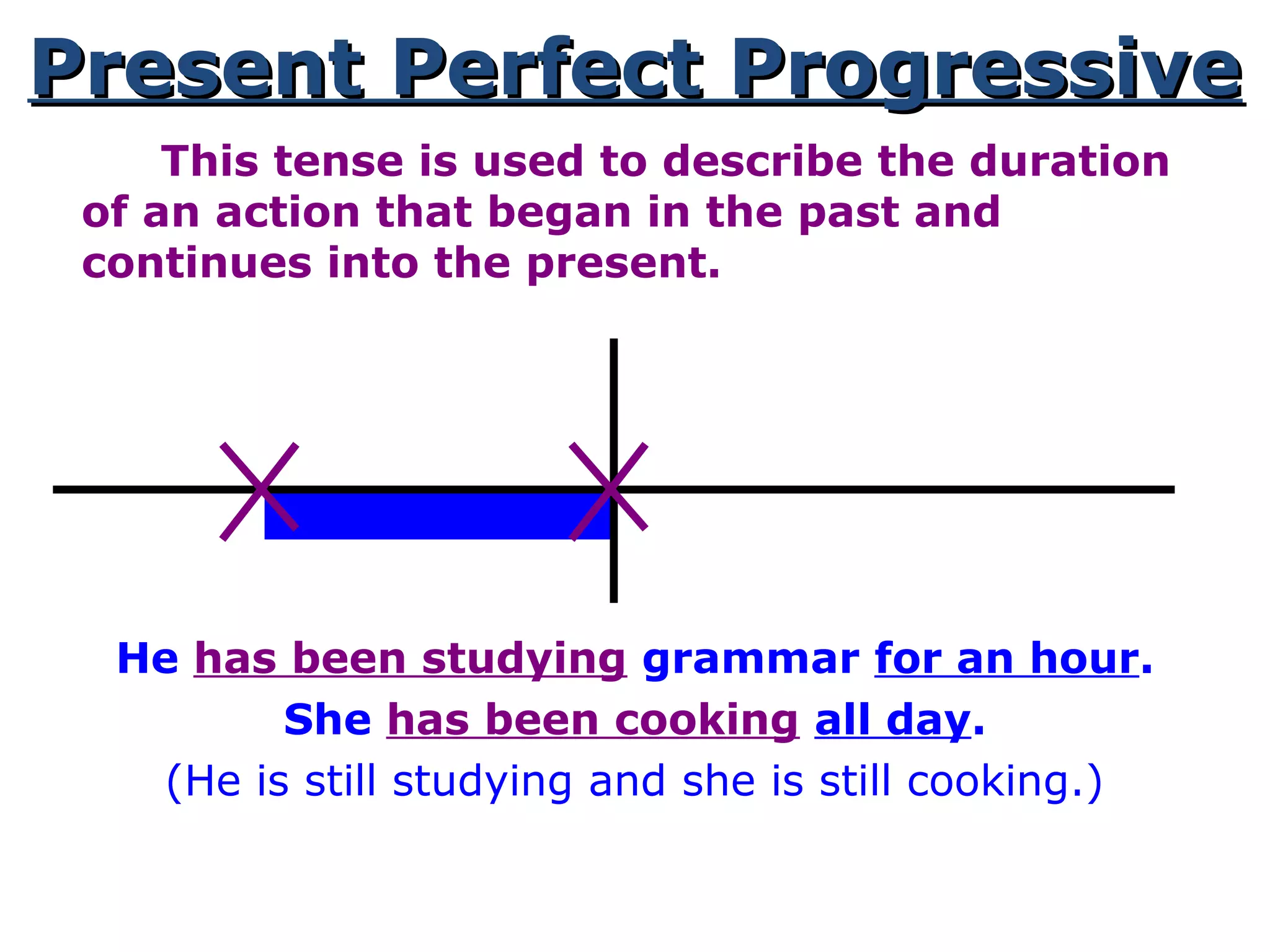
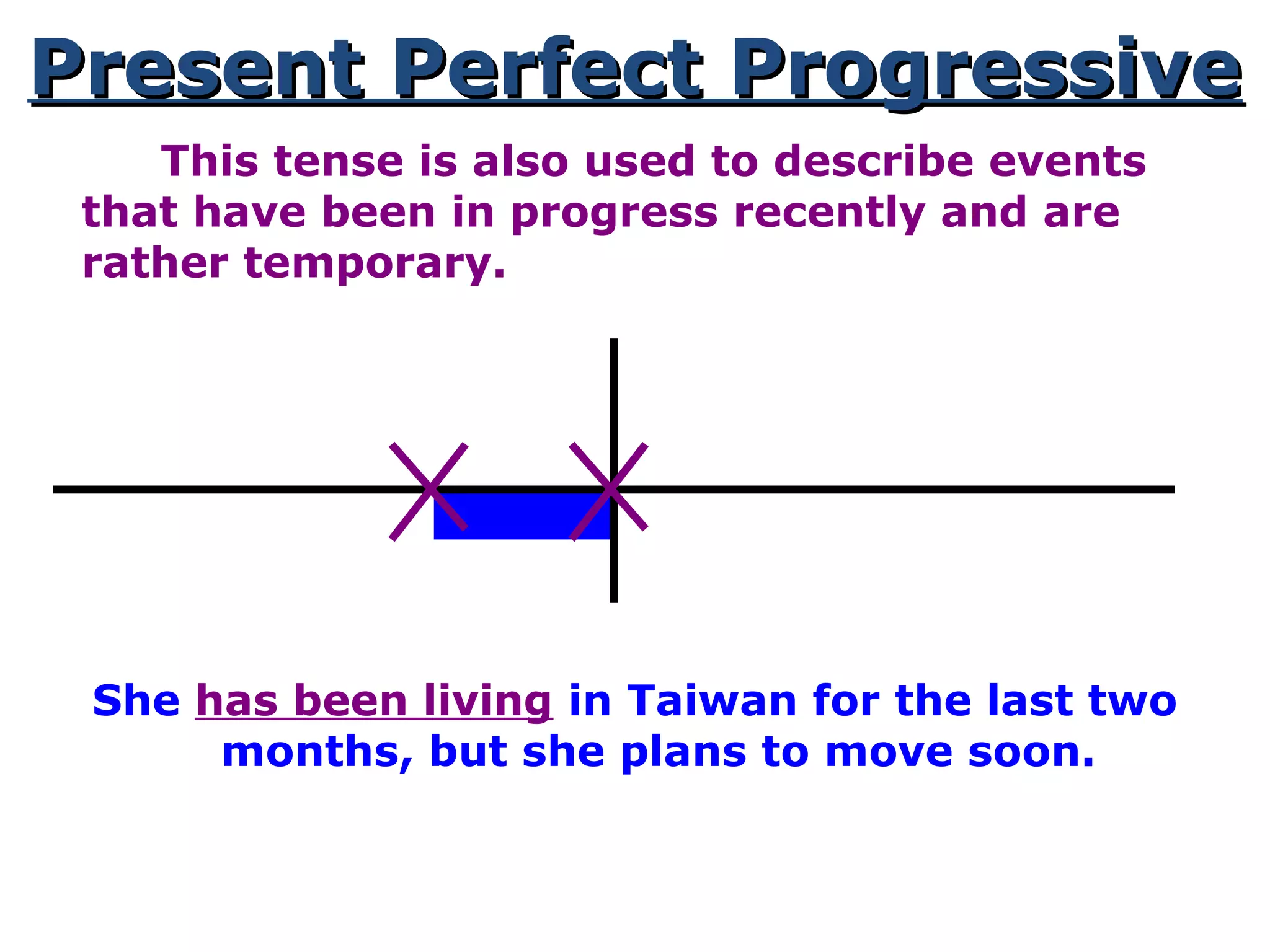
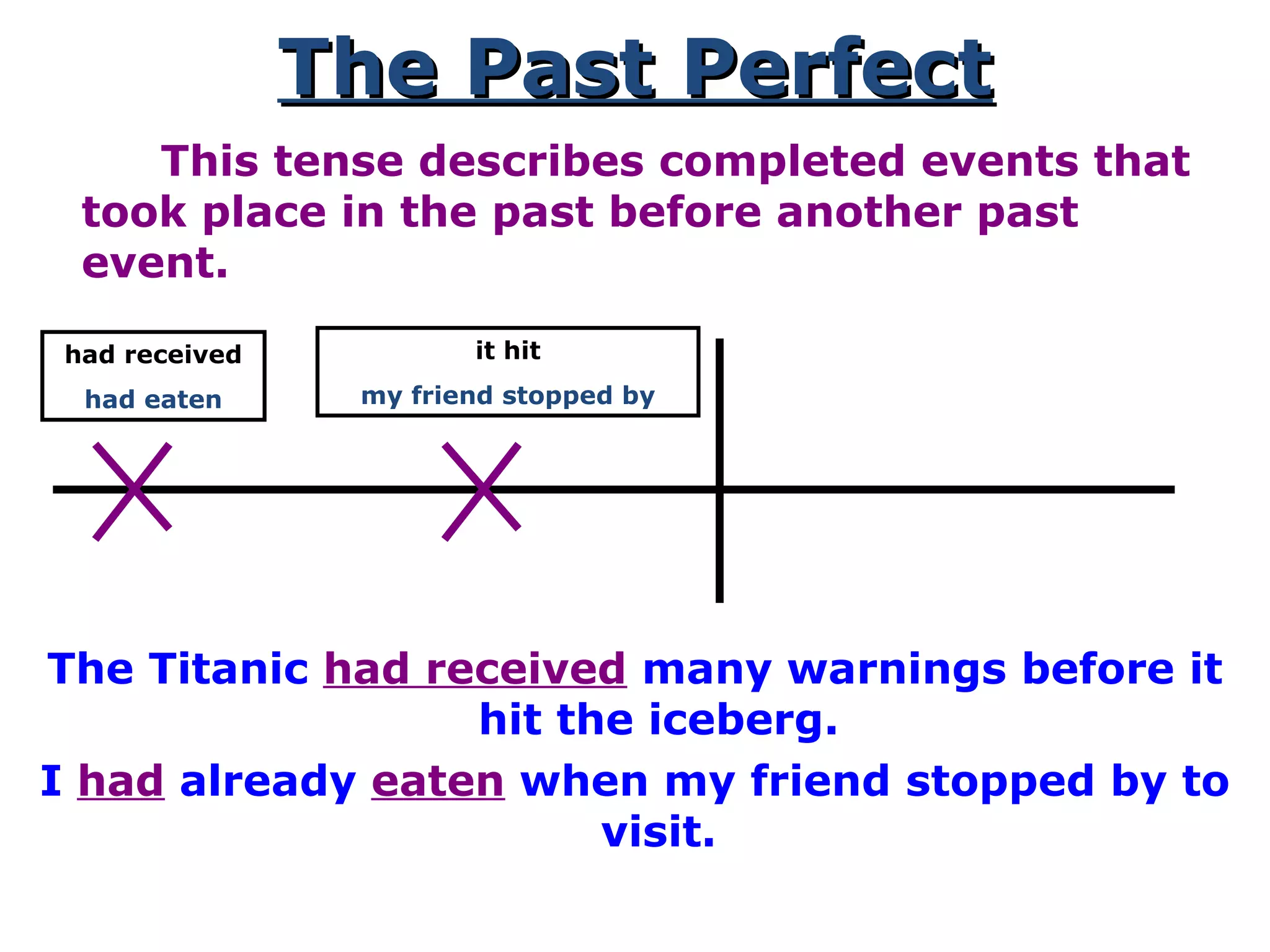
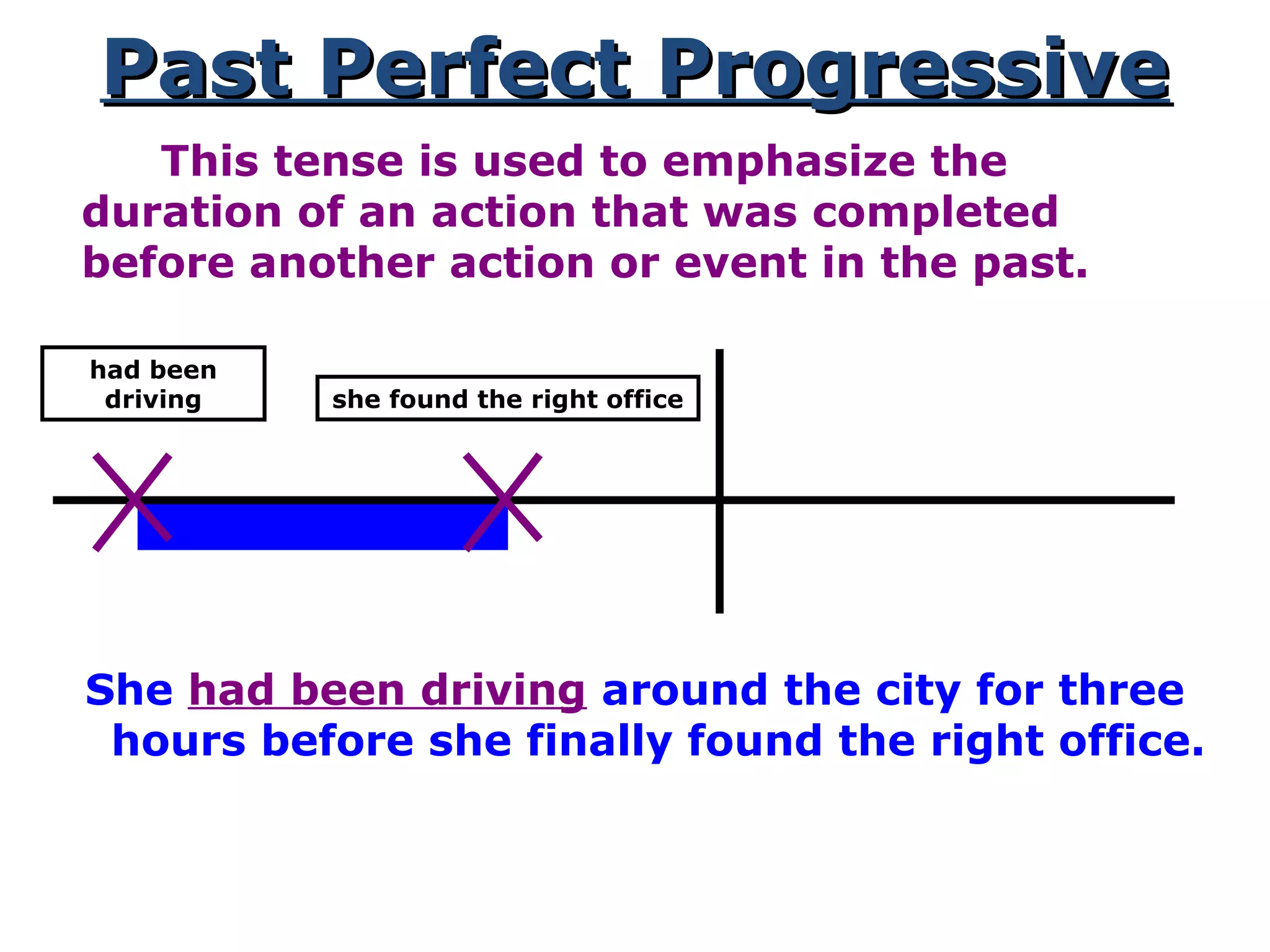
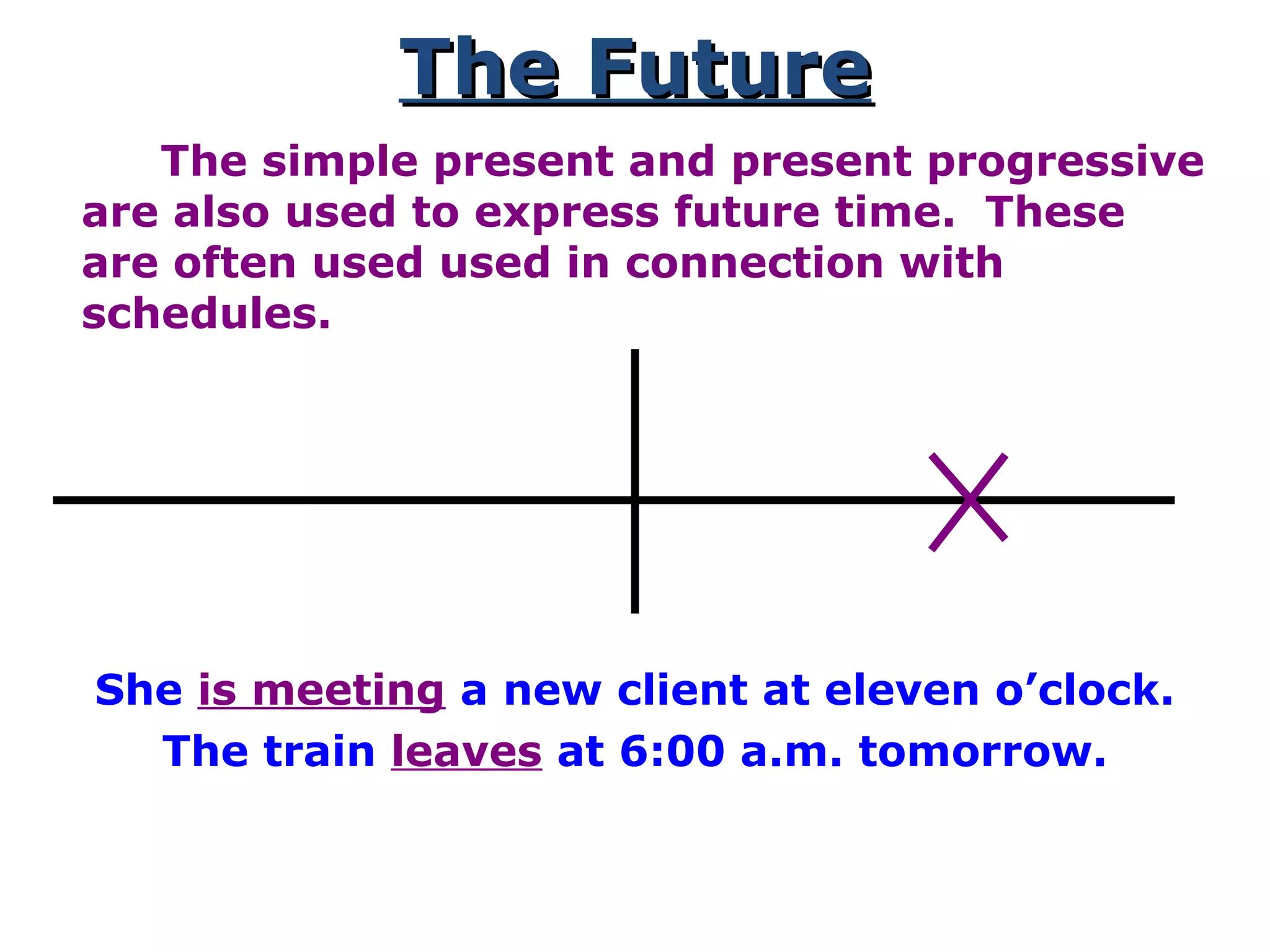
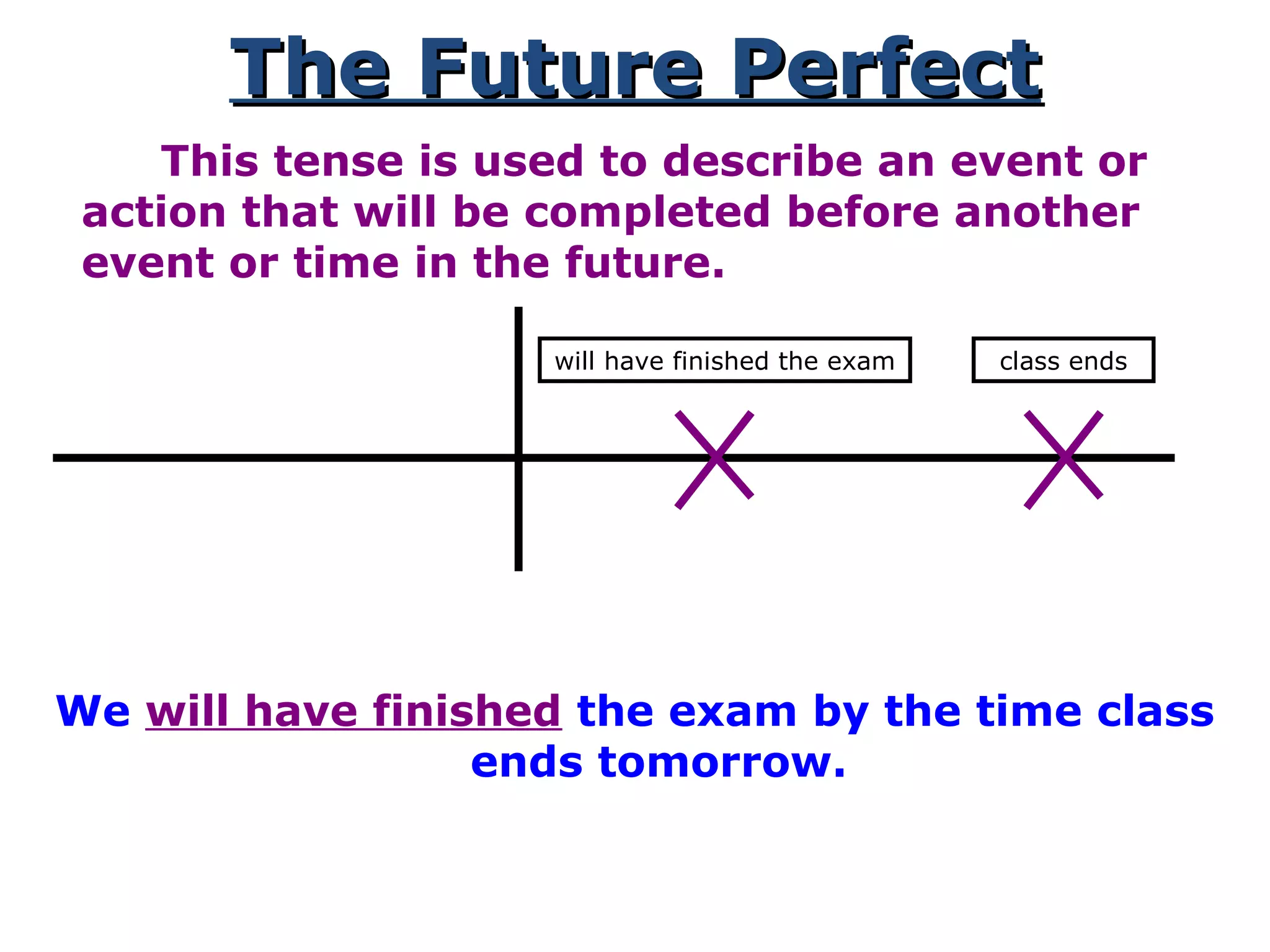
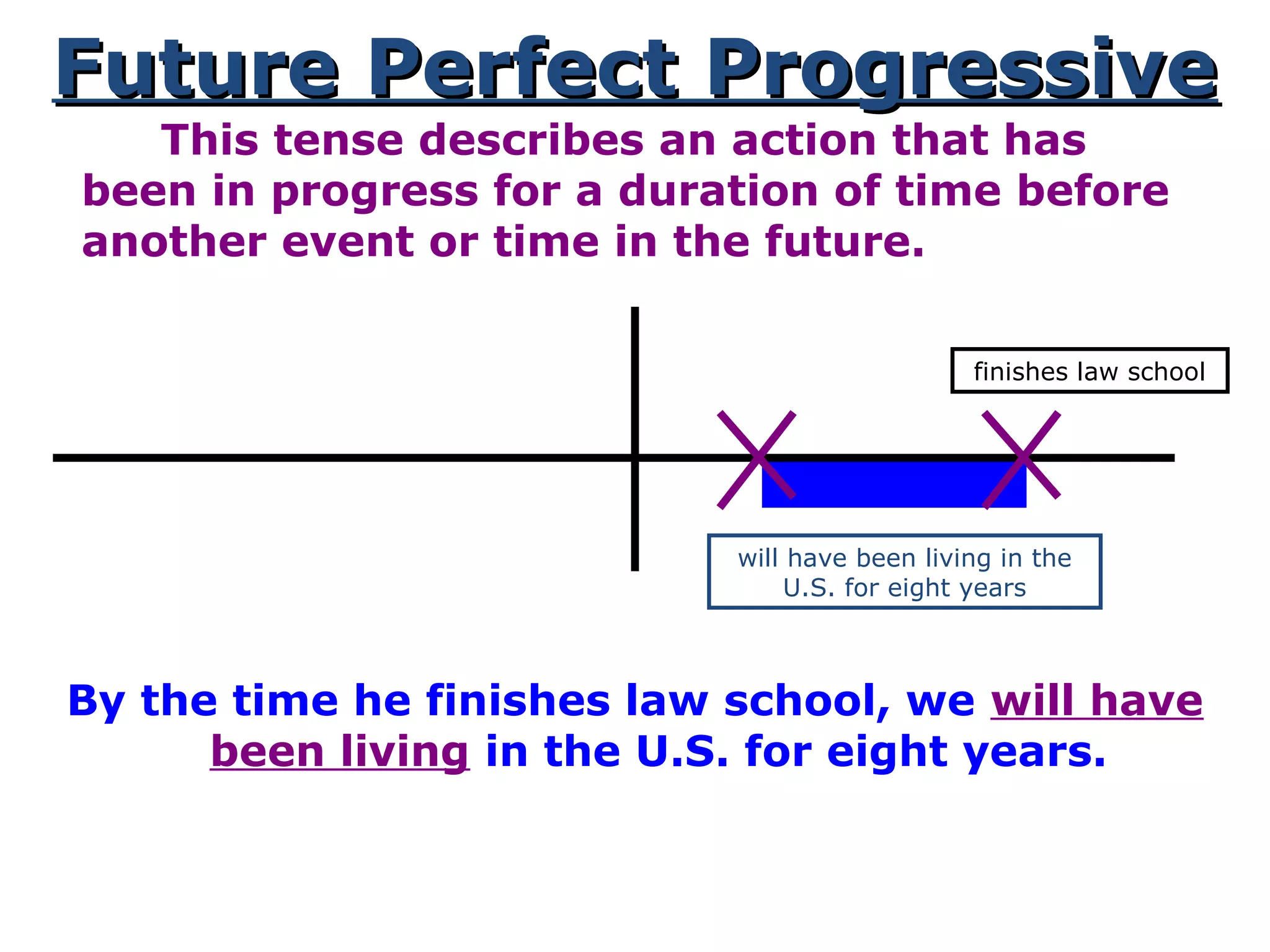
This document provides information about verb tenses in English grammar. It defines what a verb is and explains several common verb tenses including the simple present, present progressive, simple past, past progressive, present perfect, present perfect progressive, past perfect, future, and future progressive tenses. Examples are given for how each tense is used. The document concludes with exercises for the reader to practice identifying verb tenses.