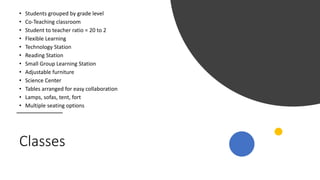
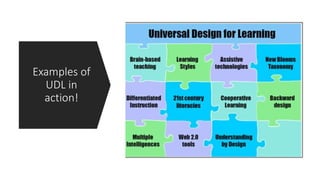
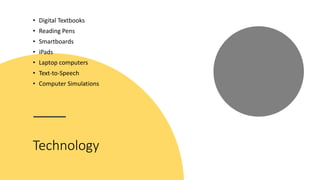
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is an educational framework that provides equal opportunities for all students to learn by removing barriers. A UDL school has accessible classrooms with adjustable furniture, technology supports, and flexible grouping. Teachers receive ongoing training and support collaborative planning. Instruction uses multiple formats and media, feedback, and adjustable levels of challenge. Assessments are frequent, formative, and flexible to support learner variability.