1. Substations receive power transmitted at high voltages from generating stations and transform the voltage to appropriate levels for local use while providing facilities for switching.
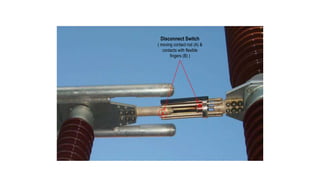
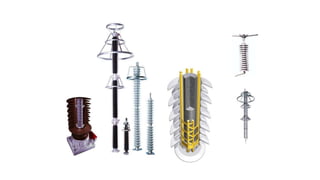
2. Typical components of a power plant substation include busbars, disconnectors, circuit breakers, current transformers, voltage transformers, earthing switches, and surge arrestors.
3. Substations are classified based on their function and location as generating, grid, secondary, distribution, and special purpose substations and based on physical features as indoor, outdoor, pole mounted, and underground substations.