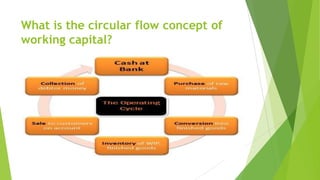
Working capital refers to the capital required to meet the day-to-day operational expenses of a business like wages, raw materials, utilities etc. It consists of current assets like inventory, receivables, cash etc. Proper management of working capital involves determining the optimal level of current assets and liabilities and arranging sources to finance them. The key components of working capital to be managed are inventory, receivables and cash. Firms use various short-term financing options like bank finance, trade credit, commercial paper etc. to manage their working capital requirements.