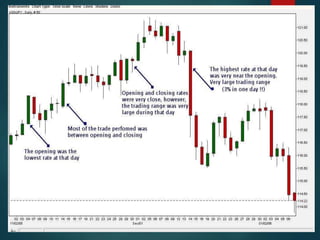
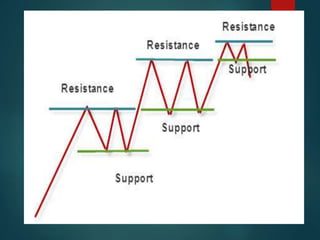
This document provides information on technical analysis and its key concepts. It defines technical analysis as using past and current price and volume movements to predict future market direction. It discusses the assumptions of technical analysis and compares it to fundamental analysis. It then describes various charting methods used in technical analysis like bar charts, line charts, point and figure charts, and Japanese candlestick charts. It also covers chart patterns, efficient market theory, Dow theory, and random walk theory as related concepts in technical analysis.