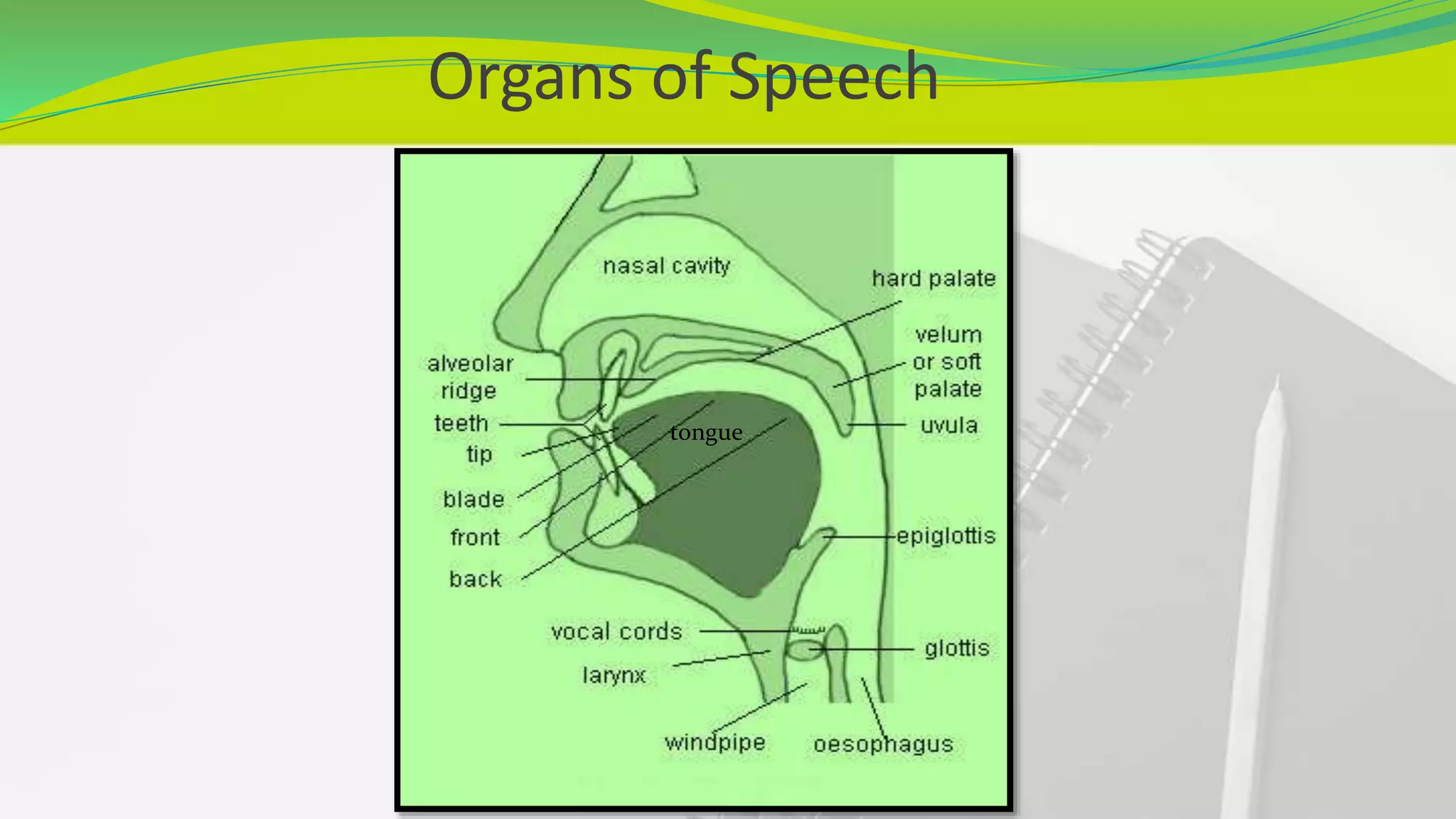
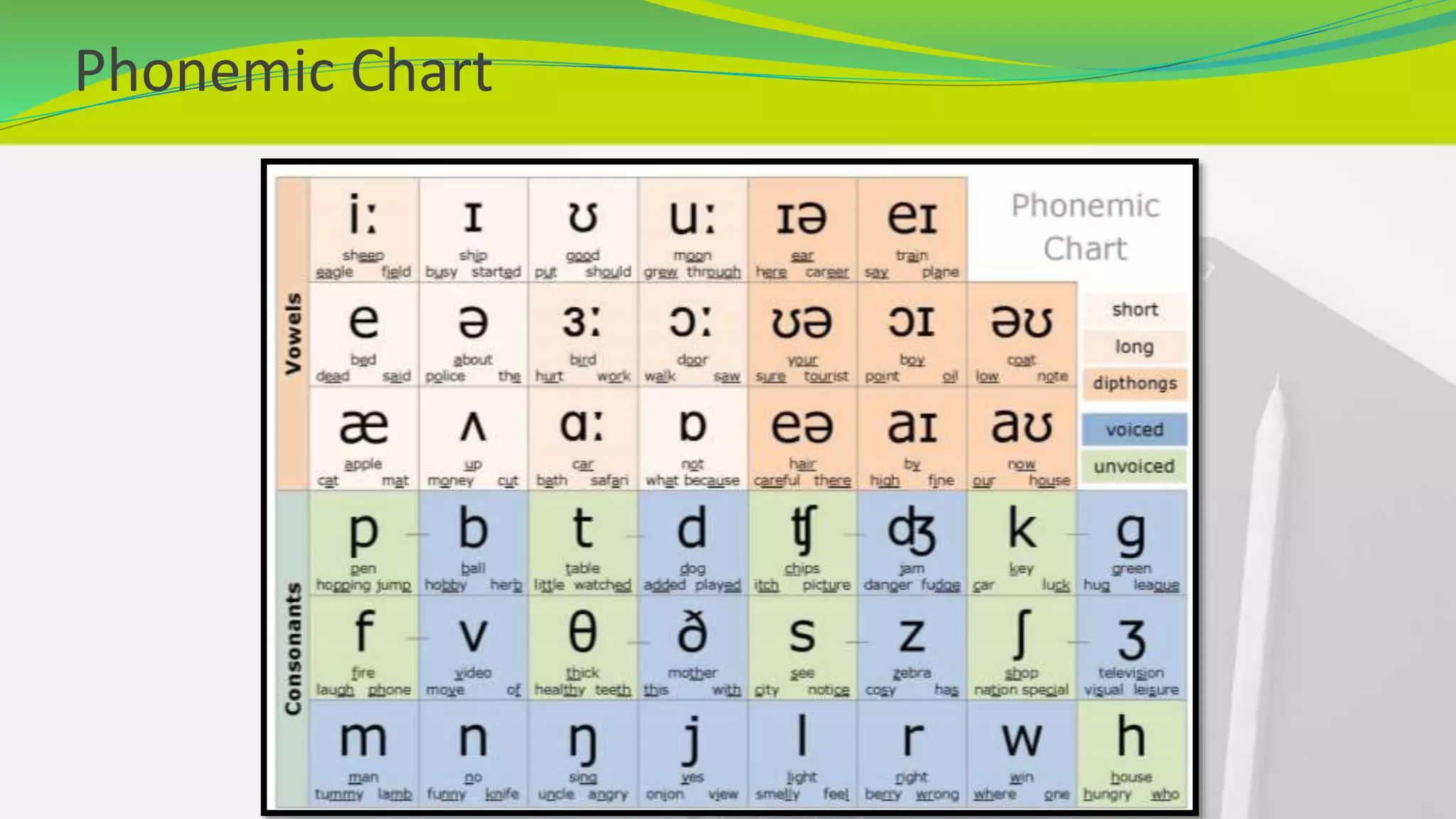
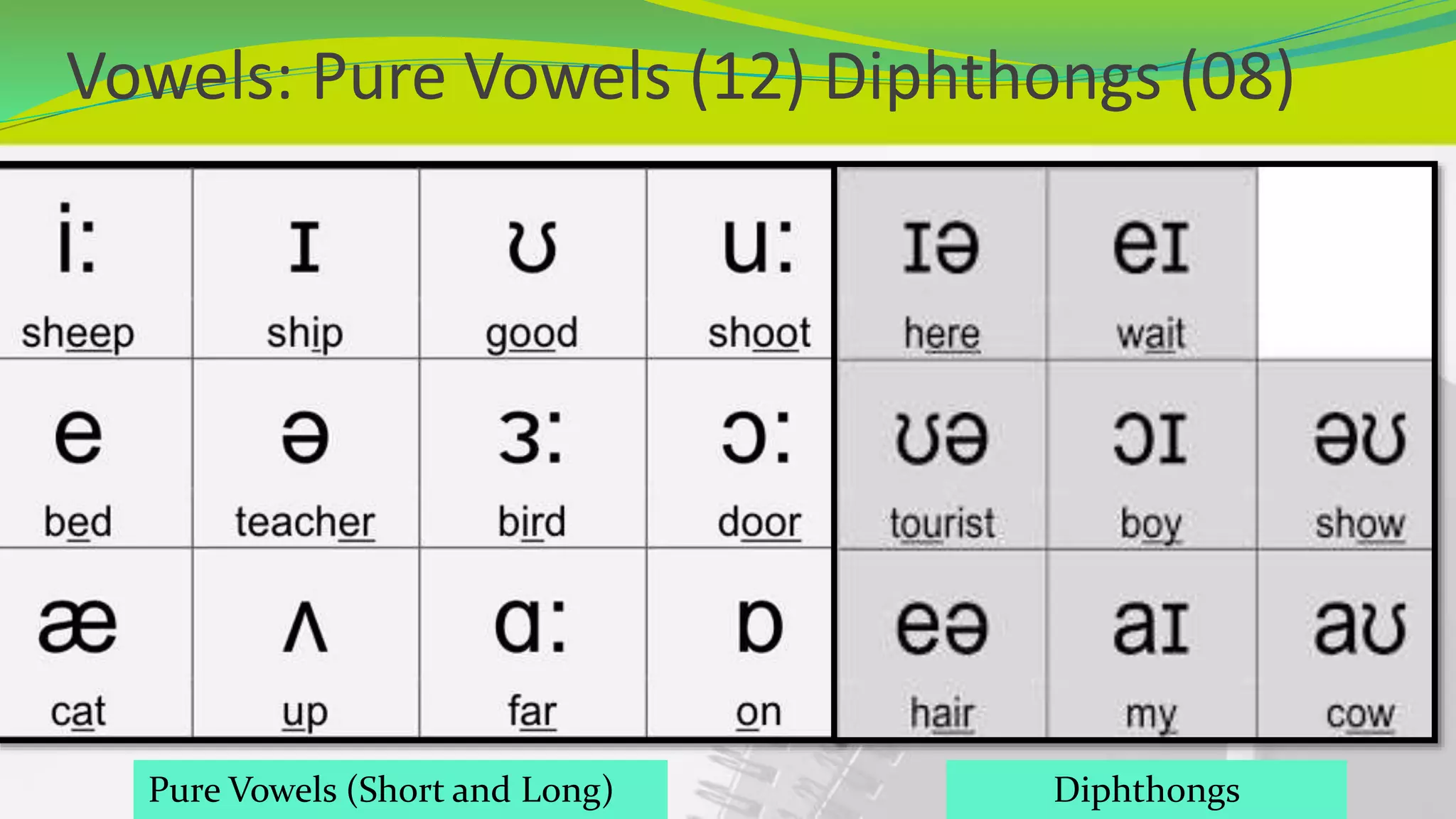
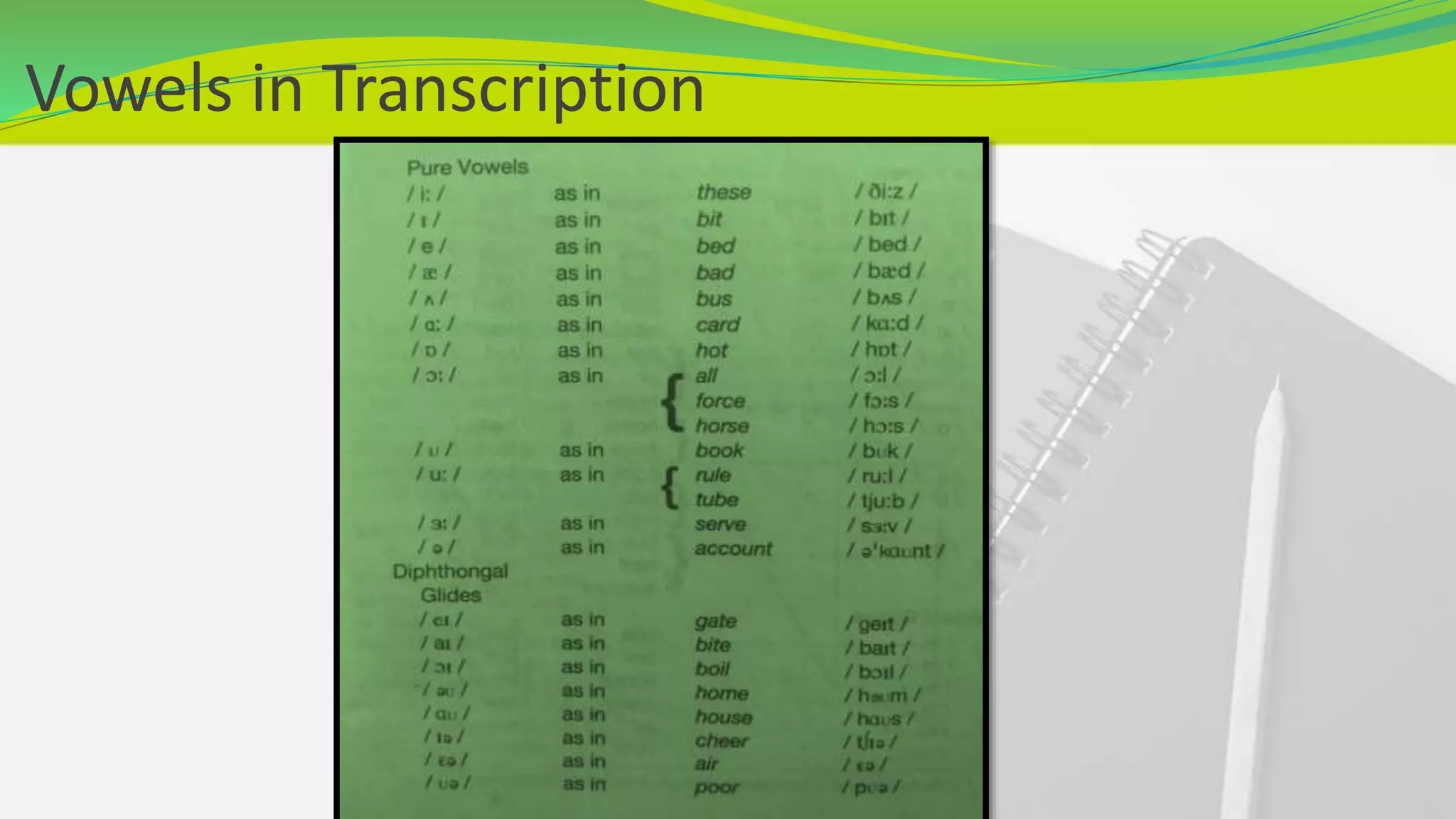
This document provides an introduction to phonetics. It defines phonetics as the study of speech sounds and explains that it involves the complex process of conceptualizing an idea, transmitting it through the nervous system to speech organs, and producing sound waves to communicate. It describes the key organs involved in speech production and defines a phoneme as the smallest unit of phonetics. The document outlines that there are 44 phonemes in English, including 20 vowel phonemes divided into pure vowels and diphthongs. It provides a phonemic chart and discusses vowels in more detail, explaining the categories of pure vowels and diphthongs and providing examples.