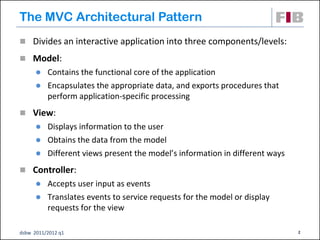
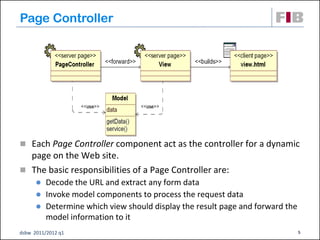
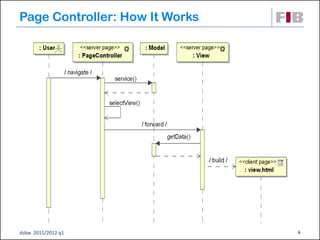
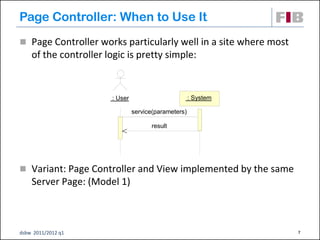
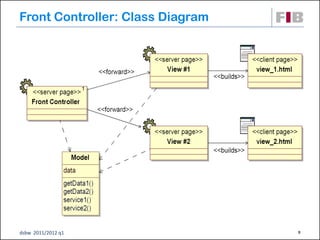
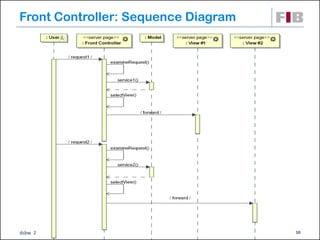
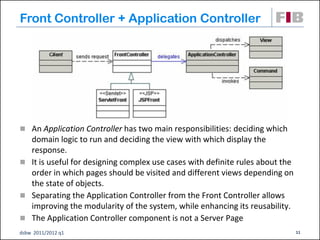
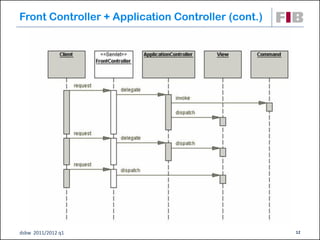
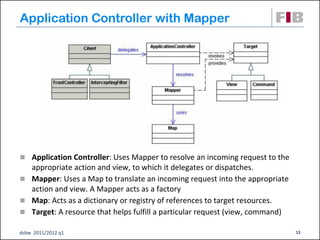
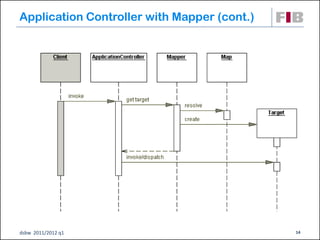
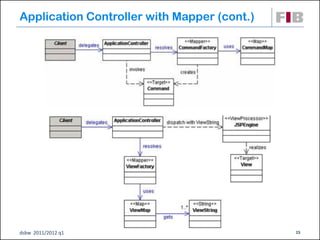
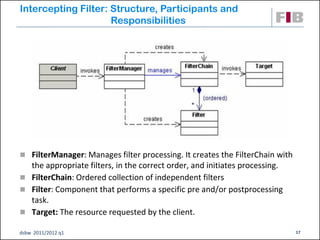
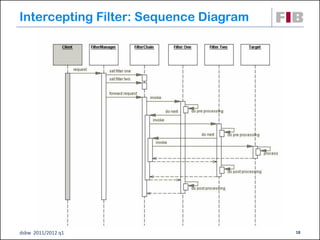
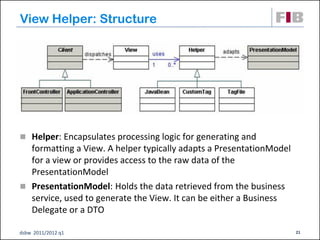
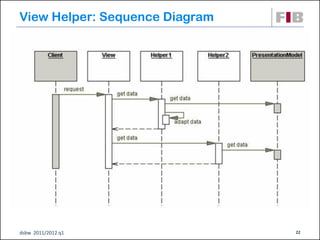
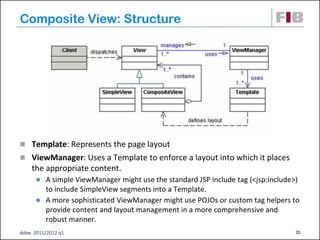
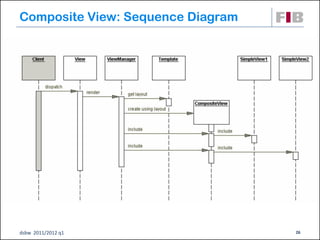
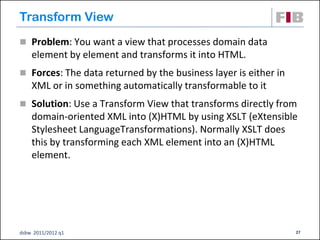
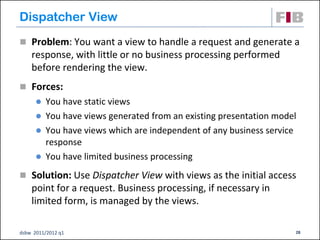
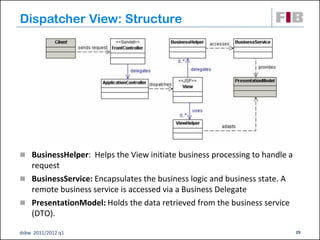
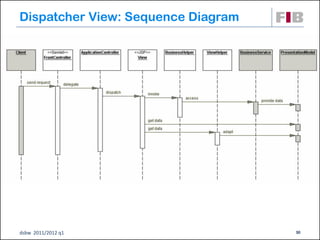
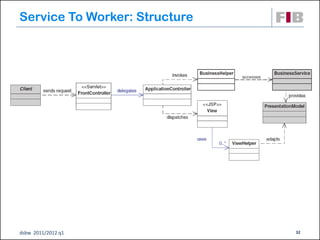
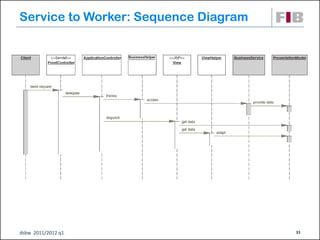
Unit 7 covers web presentation layer patterns including the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern and related patterns. It discusses the MVC pattern in detail, dividing an application into three components: the model containing core functionality, the view for displaying information, and the controller for handling user input. It then provides a catalog of MVC-based patterns including page controller, front controller, application controller, and intercepting filter patterns.