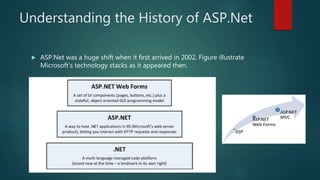
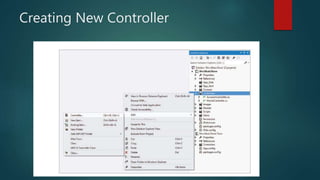
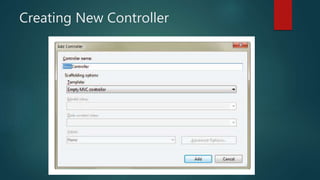
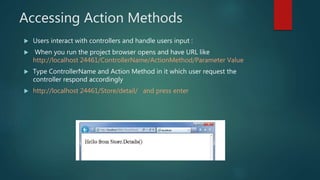
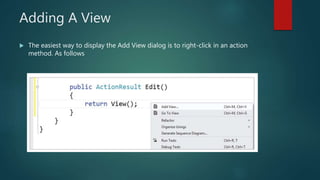
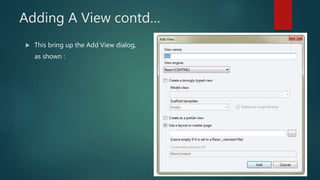
This document provides an overview of the Model-View-Controller (MVC) framework in ASP.Net. It discusses the history and components of MVC, including the model, view, and controller. The model manages the application's data logic. The view displays the user interface. The controller handles input and communication between the model and view. It provides steps for creating an ASP.Net MVC application and describes the typical file structure, including models, views, and controllers folders. It also explains how to add classes, write action methods, and create views to display and return data.