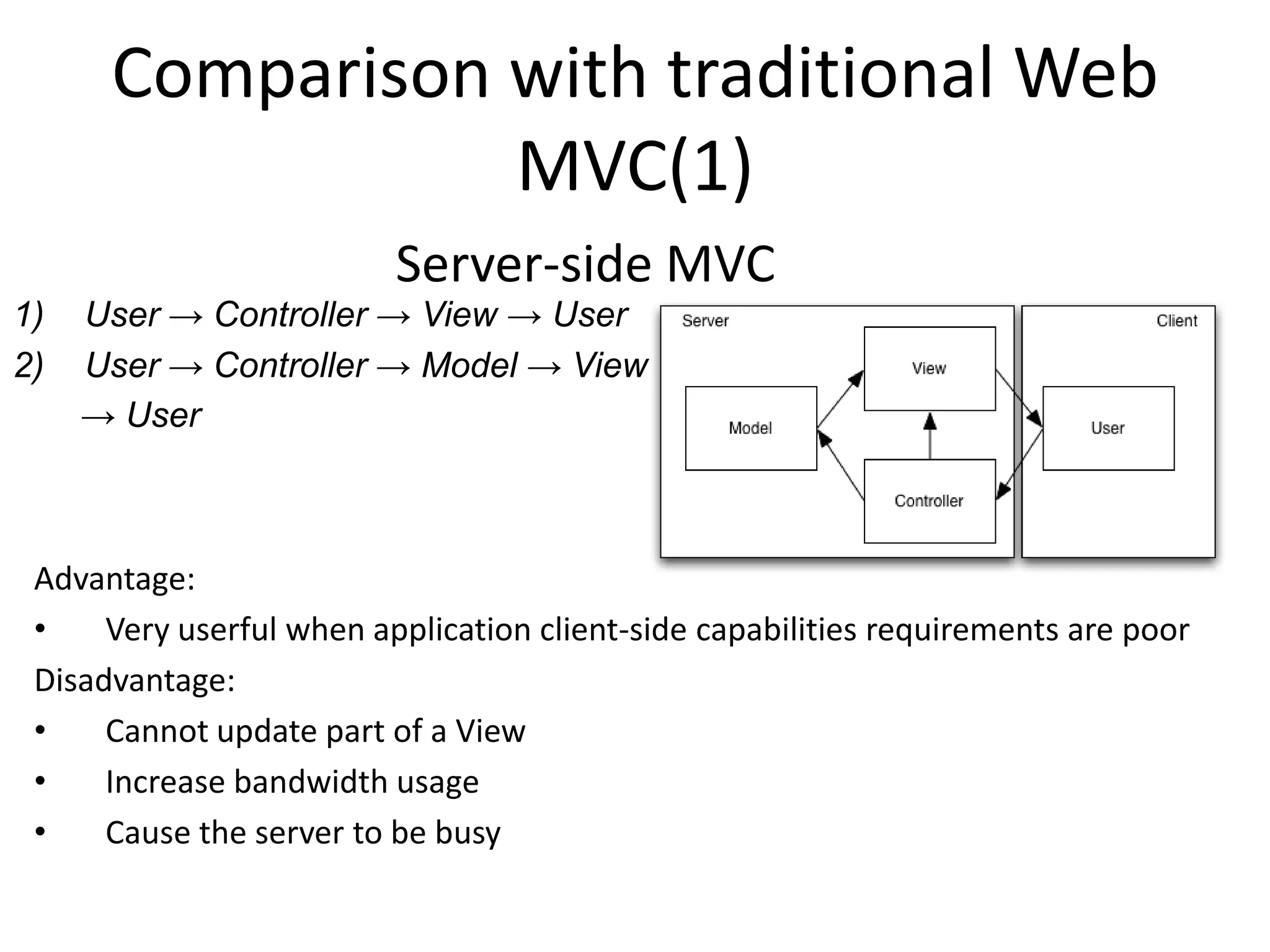
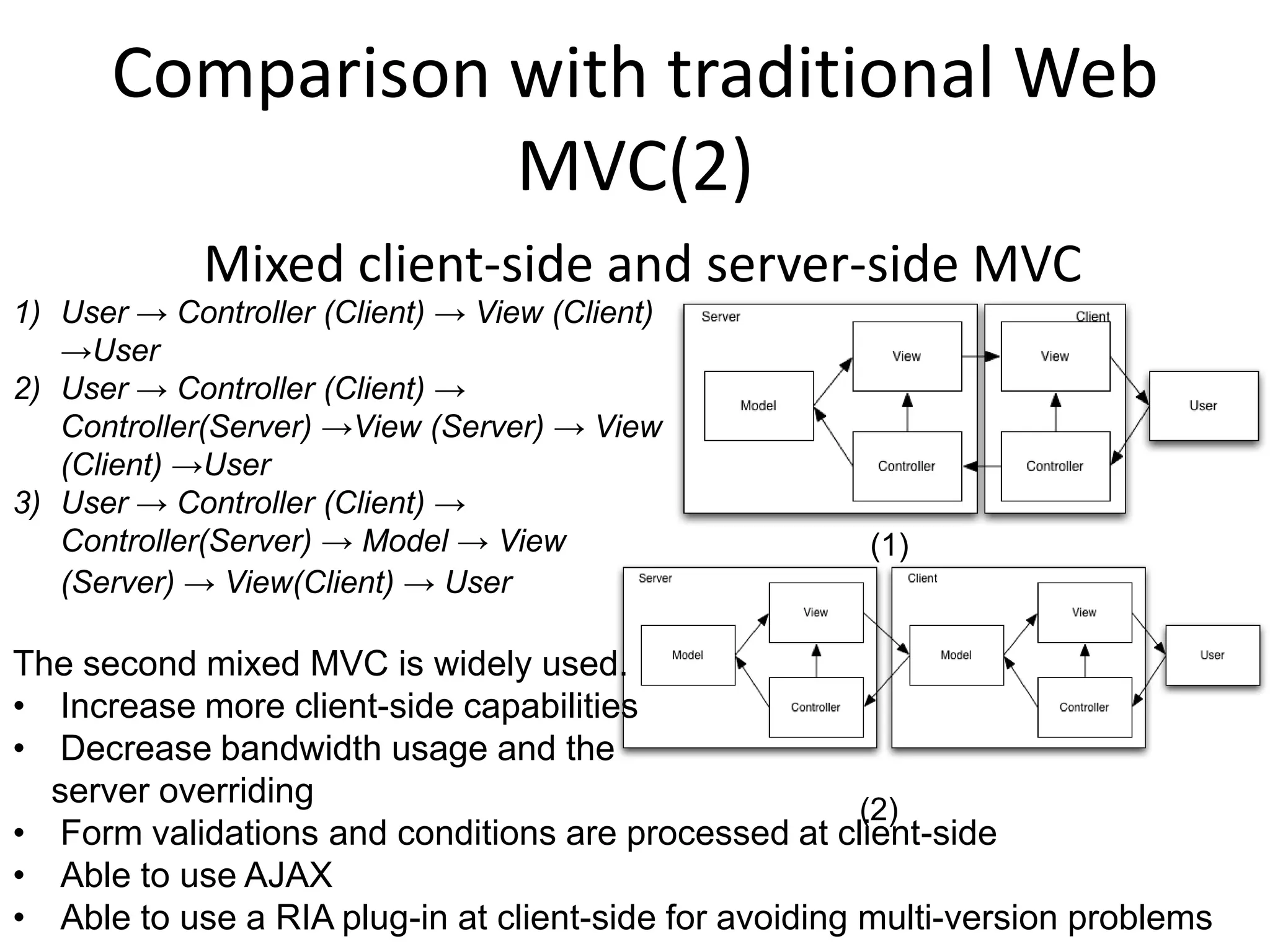
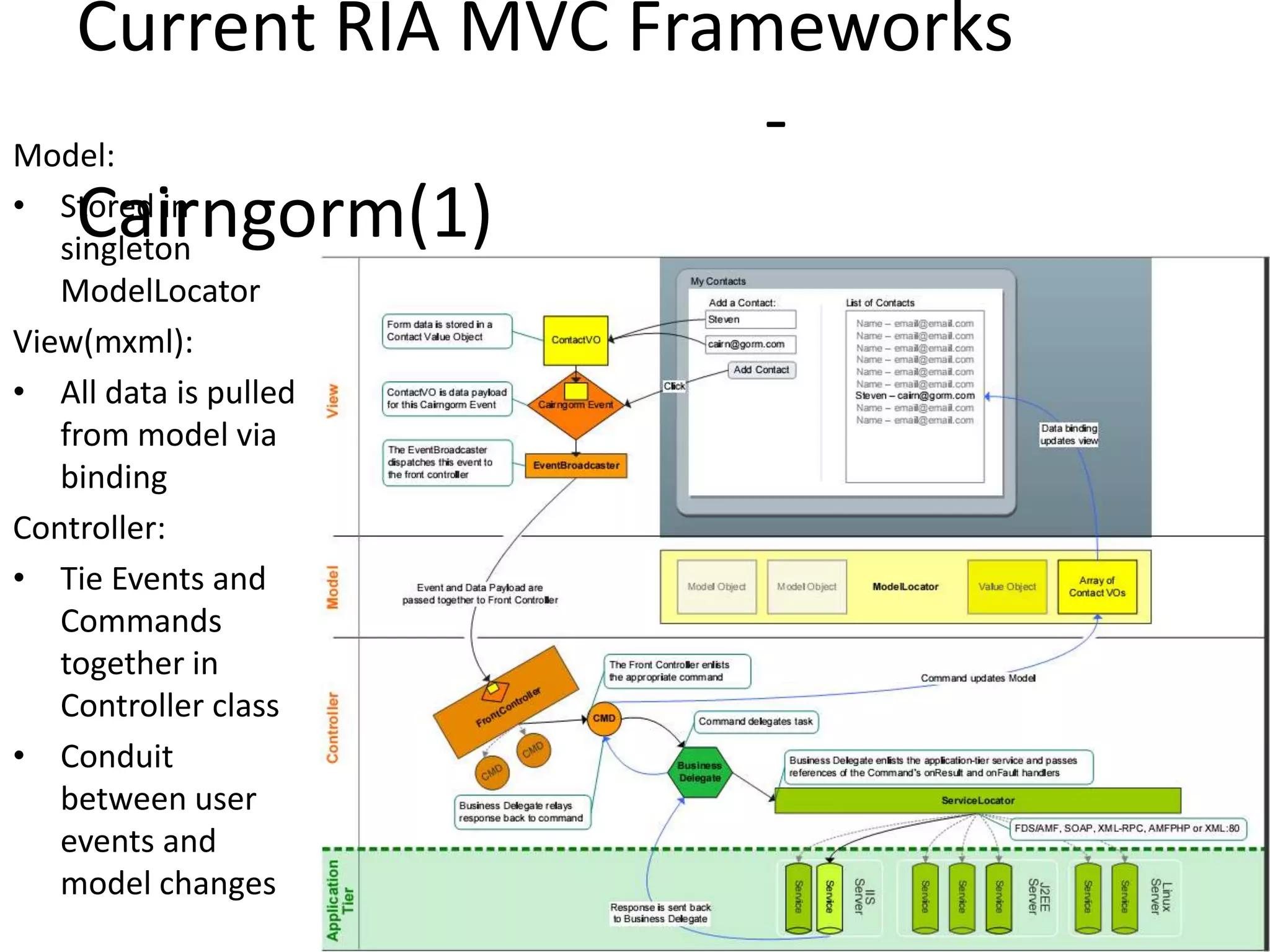
The document discusses the architecture of Rich Internet Applications (RIAs) and compares traditional web MVC to RIA MVC. It outlines the benefits of RIA MVC such as updating models at the client to minimize bandwidth. Current RIA frameworks discussed include JavaScriptMVC, PureMVC, Cairngorm and others. The document provides an overview of these frameworks and their strengths and weaknesses for developing complex RIAs.