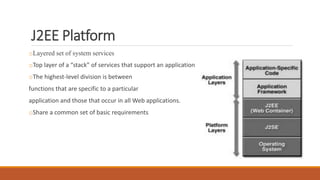
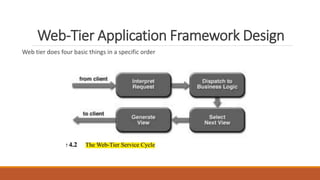
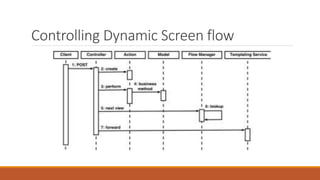
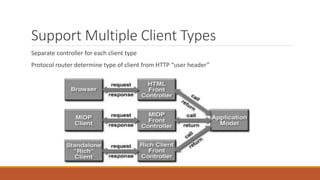
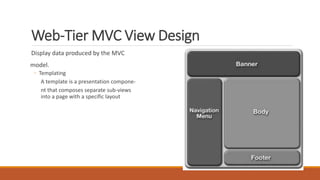
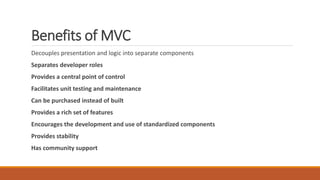
The document discusses web-tier design for enterprise applications using the J2EE platform, highlighting the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern to separate concerns and improve manageability. It describes two models of web-tier structure, with Model 2 providing a centralized controller for client communication and business logic. Additionally, it reviews various web application frameworks like J2EE Blueprints and Apache Struts, emphasizing their features and benefits in developing complex web applications.