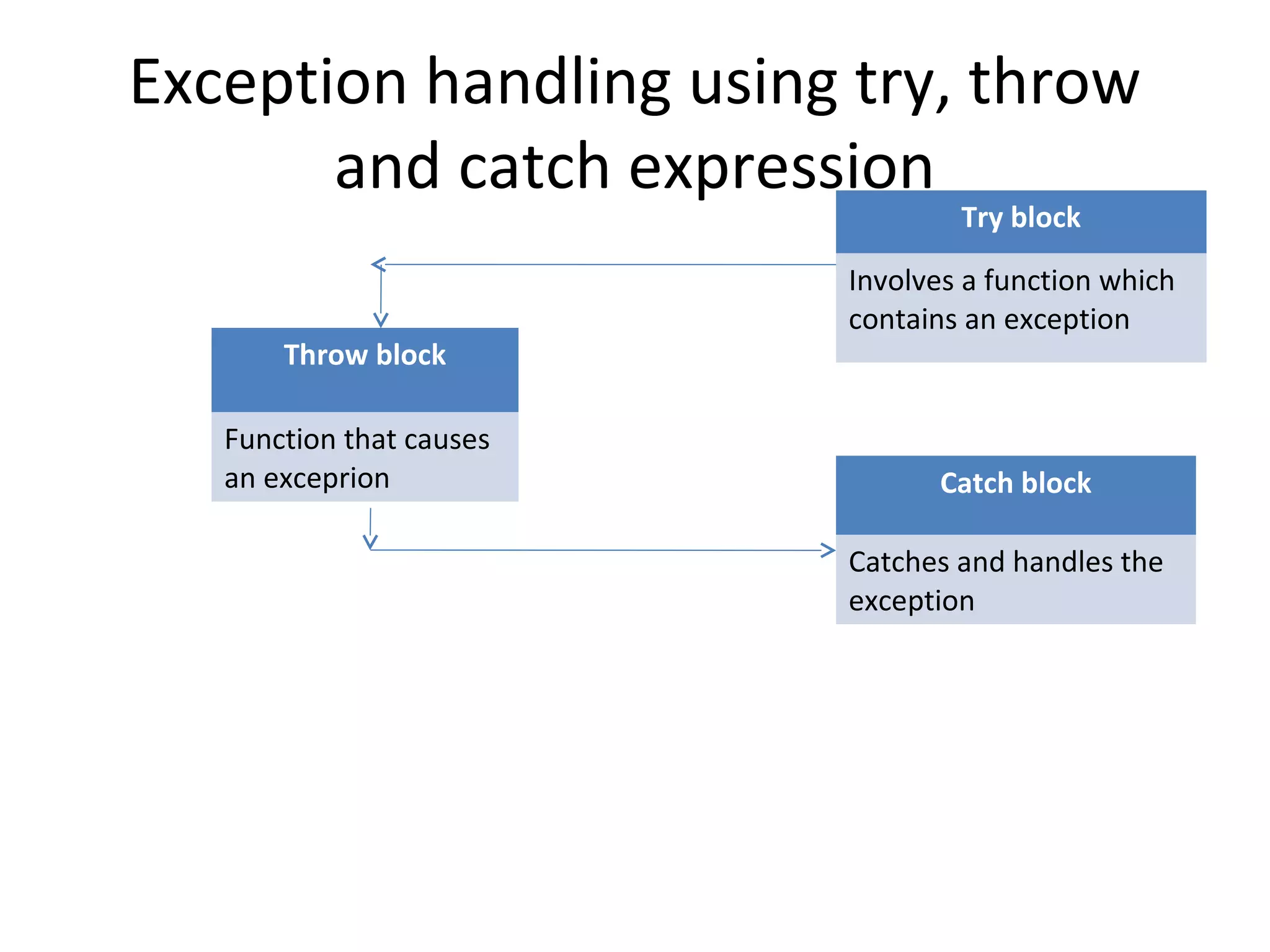
The document discusses exception handling in C++. It explains that exceptions provide a way to transfer control from one part of a program to another in response to problems. The key concepts are try, catch, and throw blocks. Try blocks identify code that can throw exceptions. Catch blocks catch and handle exceptions. Throw blocks cause exceptions to be thrown. The document provides examples of using try, catch, and throw to handle exceptions like division by zero. It also summarizes several standard C++ libraries that provide common functions and templates.