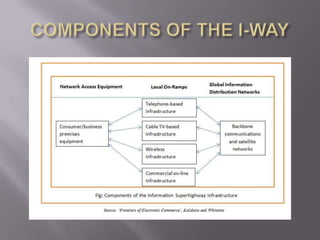
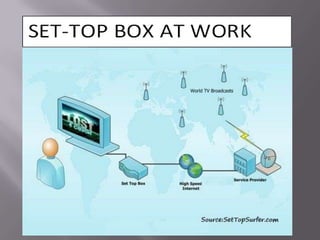
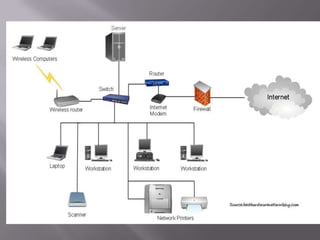
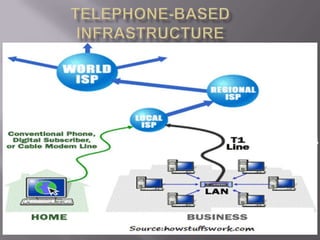
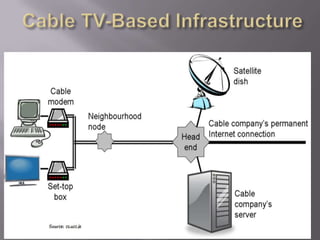
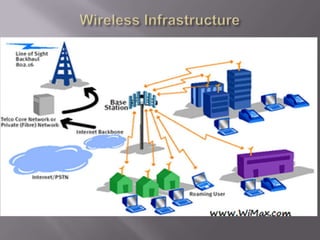
The document discusses the information superhighway (I-Way). It describes I-Way as a high-capacity, interactive electronic pipeline providing integrated services. The document outlines the key components of I-Way, including network access equipment, the last mile, and global information distribution networks. It also examines the public policy issues that shape I-Way, such as cost, subsidies, regulation, and universal access.