The document discusses various concepts related to C++ classes including:
1. Structure definitions, accessing structure members using dot operator and pointers. Class definitions include data members and member functions.
2. Class objects are created using the class name followed by the object name. Class members are accessed using dot operator. Member functions can be defined inside or outside the class.
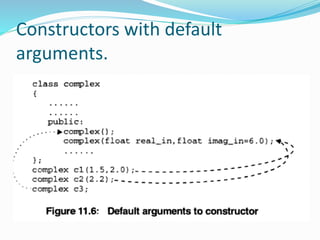
3. Access specifiers like private, public, and protected control access to class members. Constructors and destructors are special member functions for object initialization and destruction.













![Dynamic memory
Operators new and new[]
The new operator offers dynamic storage allocation similar to
the standard library function malloc.
Throws an exception when memory allocation fails.
pointer = new type
pointer = new type [number_of_elements]
int * b;
b = new int [5];
Operators delete and delete[]
delete pointer;
delete [] pointer;
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-ii-151229061048/85/Unit-ii-14-320.jpg)