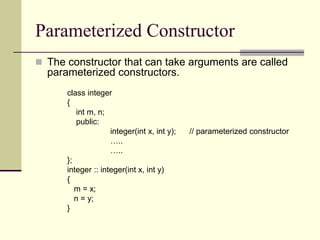
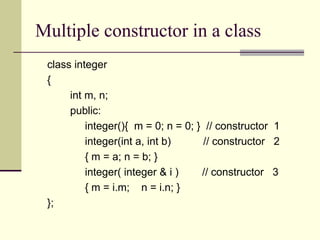
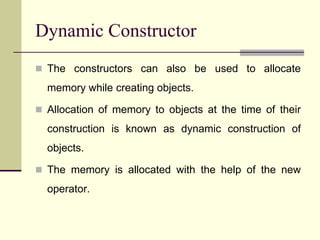
Constructors are used to initialize objects and allocate memory. A constructor has the same name as its class and is invoked when an object is created. There are different types of constructors including default, parameterized, copy, and dynamic constructors. A destructor is used to destroy objects and does not have any arguments or return values.








![Dynamic Constructor
class string
{
char *name;
int length;
public:
string()
{
length = 0;
name = new char [ length +1];
}
string (char *s)
{
length = strlen(s);
name = new char [ length + 1];
strcpy(name, s);
}
void display(void)
{ cout << name << “n” ; }
void join(string &a, string &b);
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/constructors-destructors-171229094329/85/Constructors-destructors-12-320.jpg)
![Dynamic Constructor
void string :: join(string &a, string &b)
{
length = a.length + b.length;
delete name;
name = new char [ length + 1];
strcpy(name, a.name);
strcat(name, b.name);
}
int main()
{
char *first = “Mathew”;
string name1(first), name2(“Joseph”), s1;
s1.join(name1, name2);
s1.display();
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/constructors-destructors-171229094329/85/Constructors-destructors-13-320.jpg)










