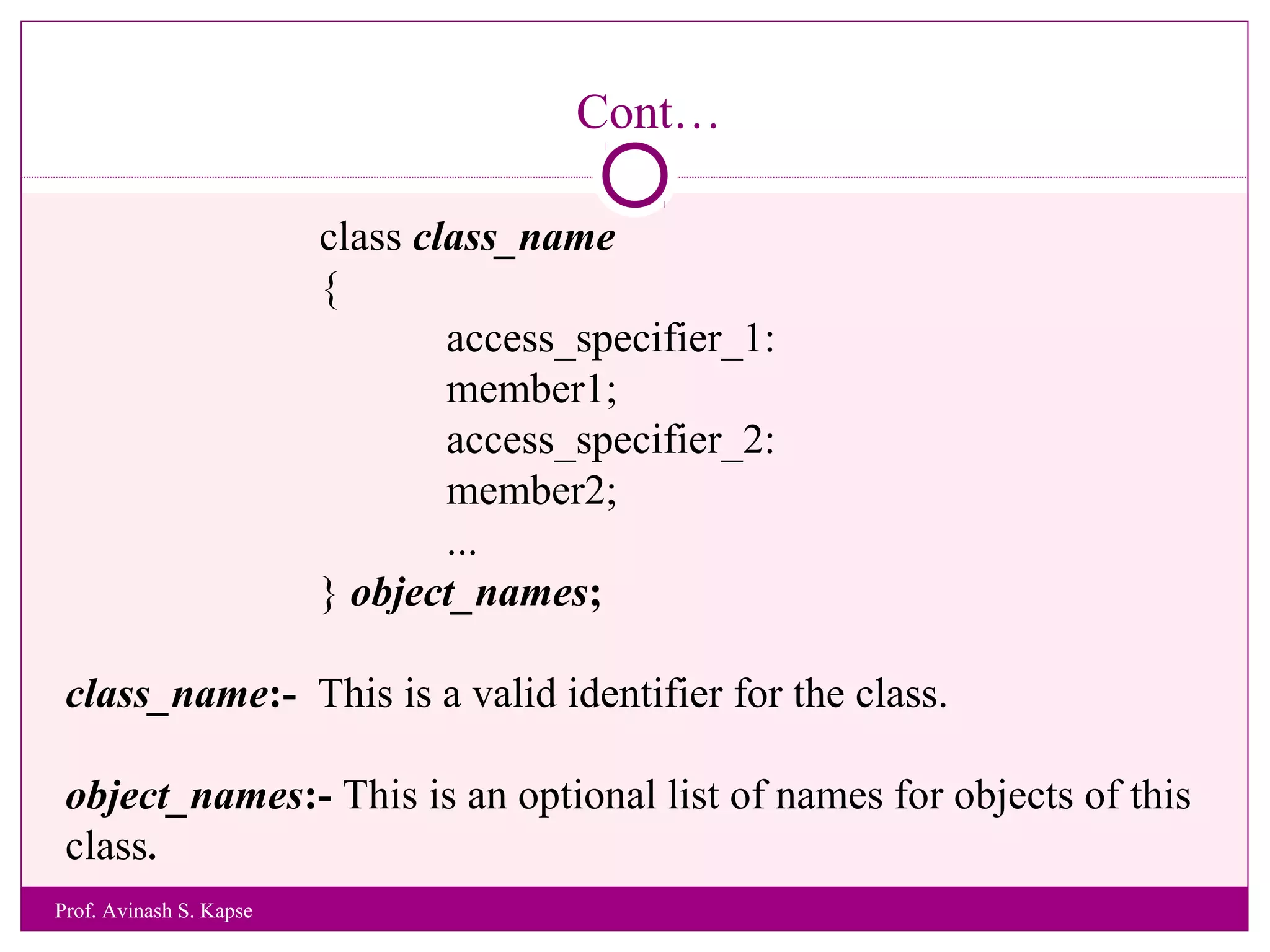
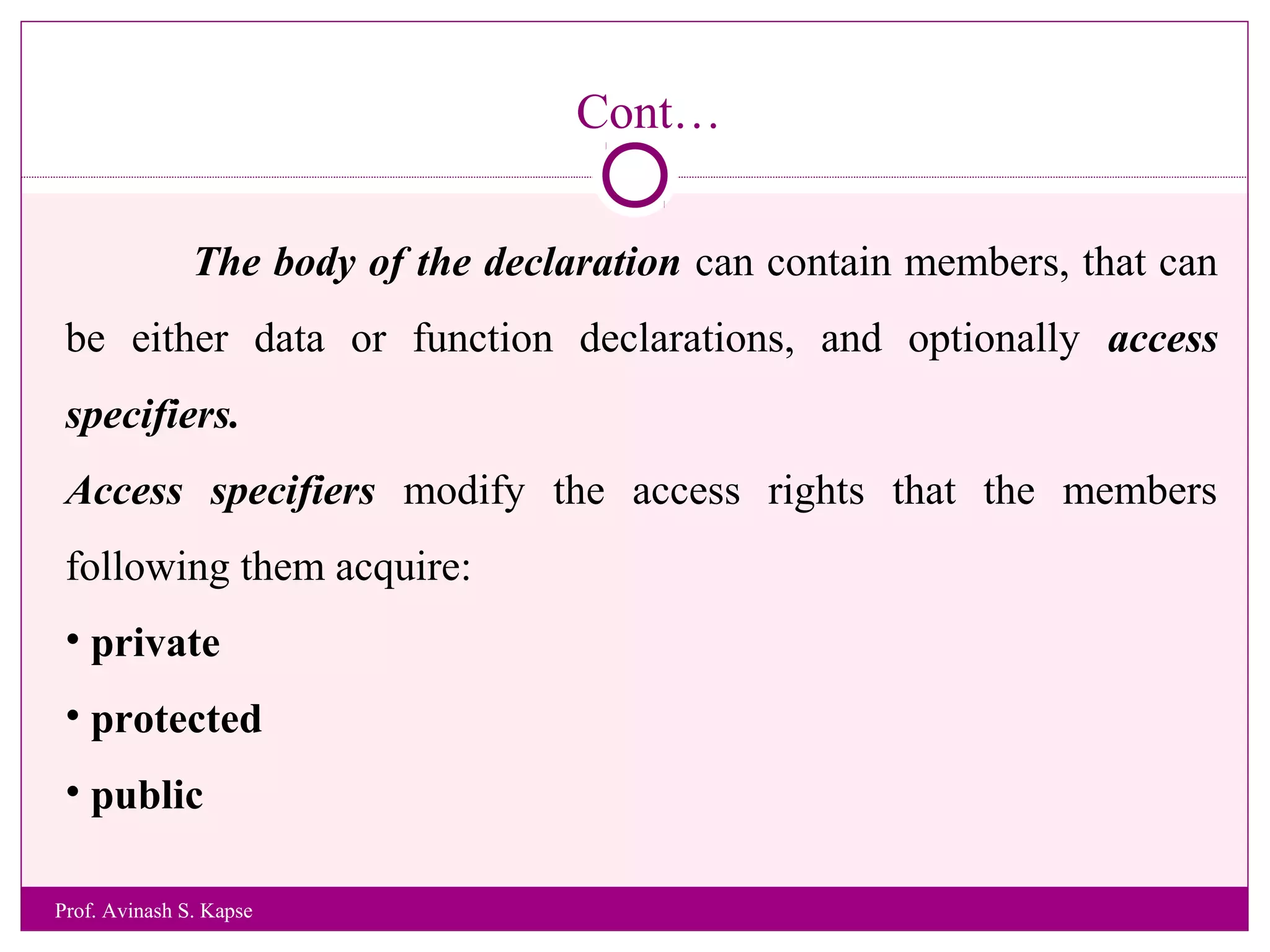
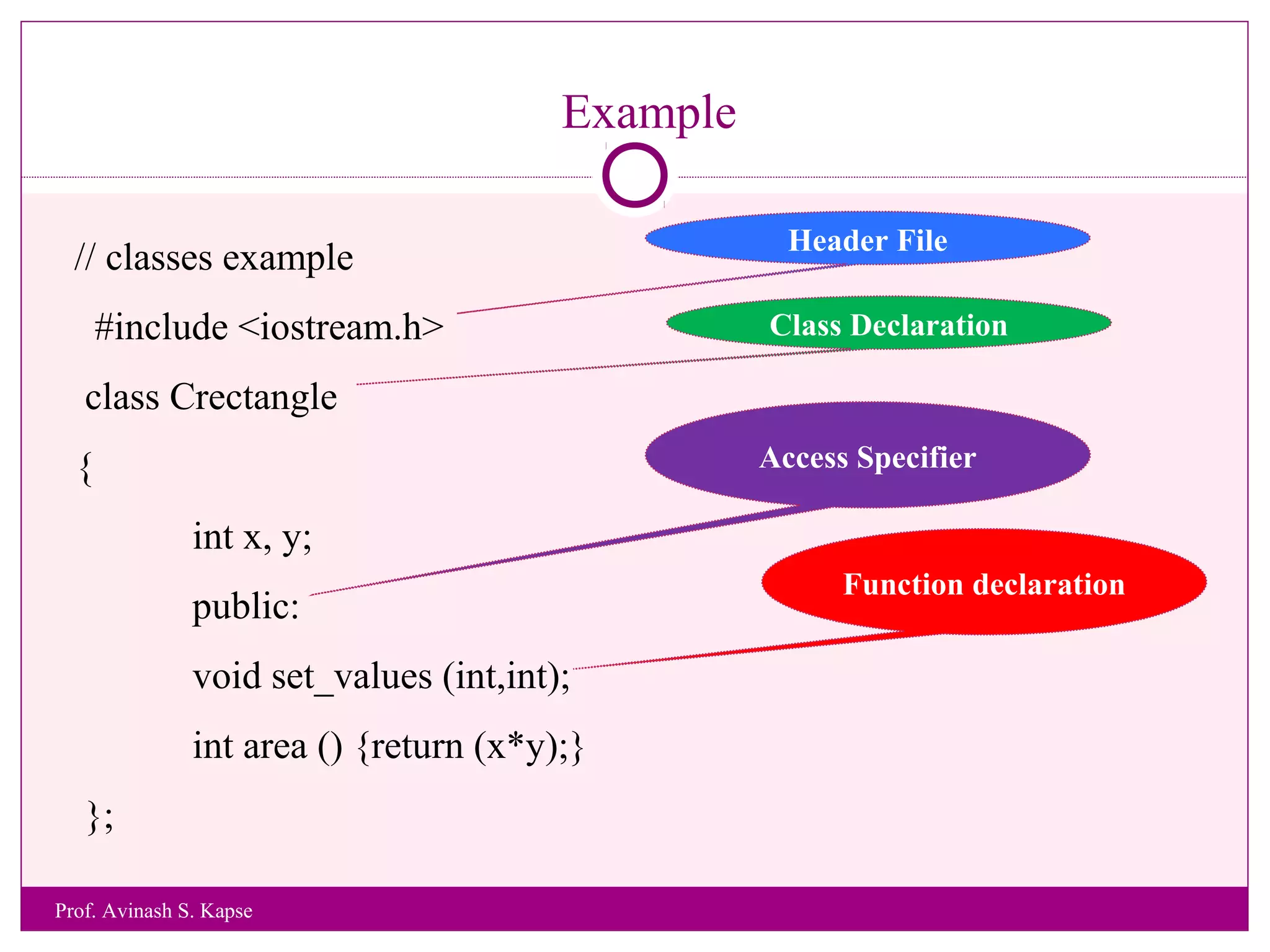
1. The document discusses a lecture on object oriented programming in C++. It introduces classes and objects, and explains how to declare a class and create objects in C++.
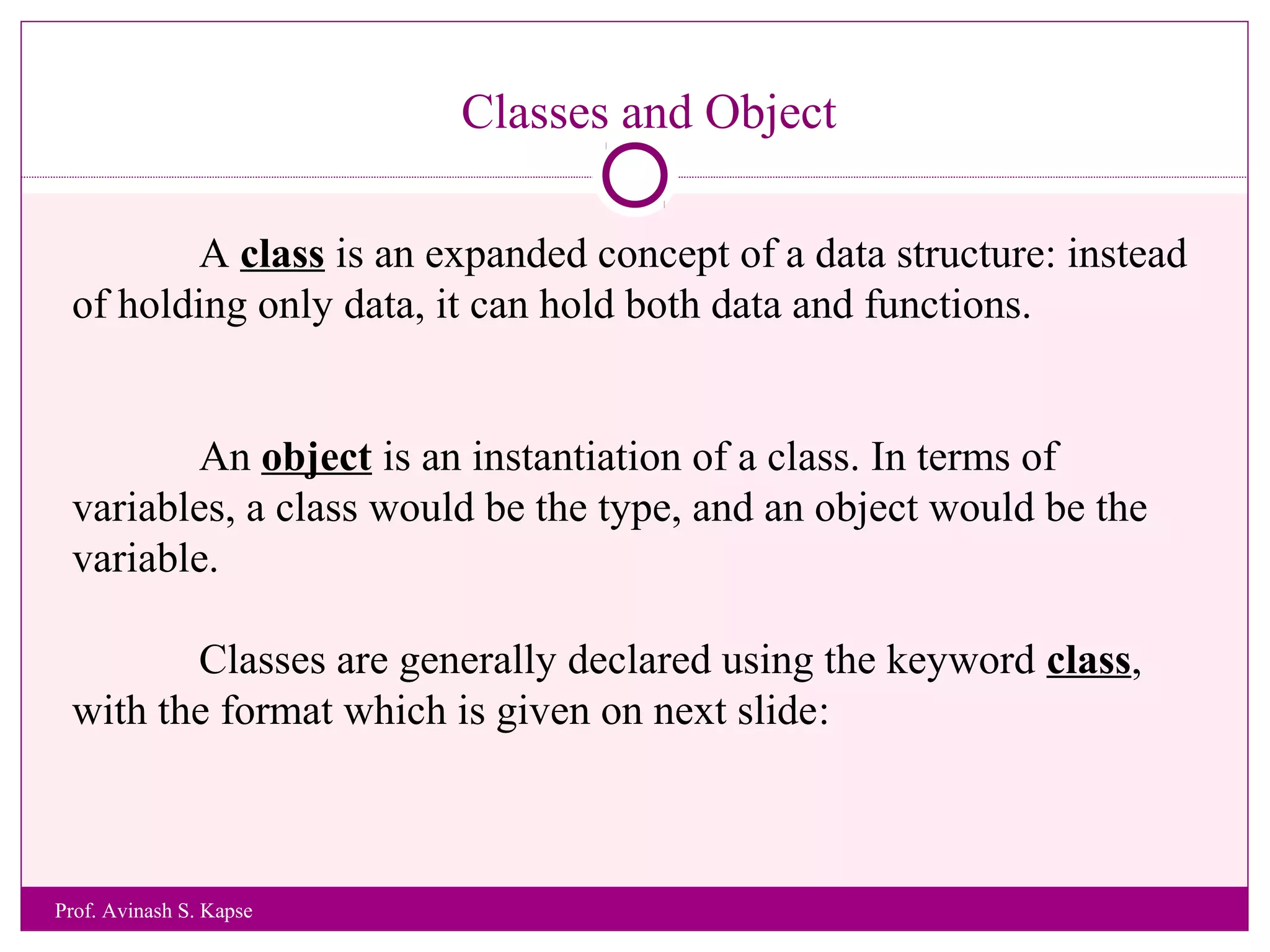
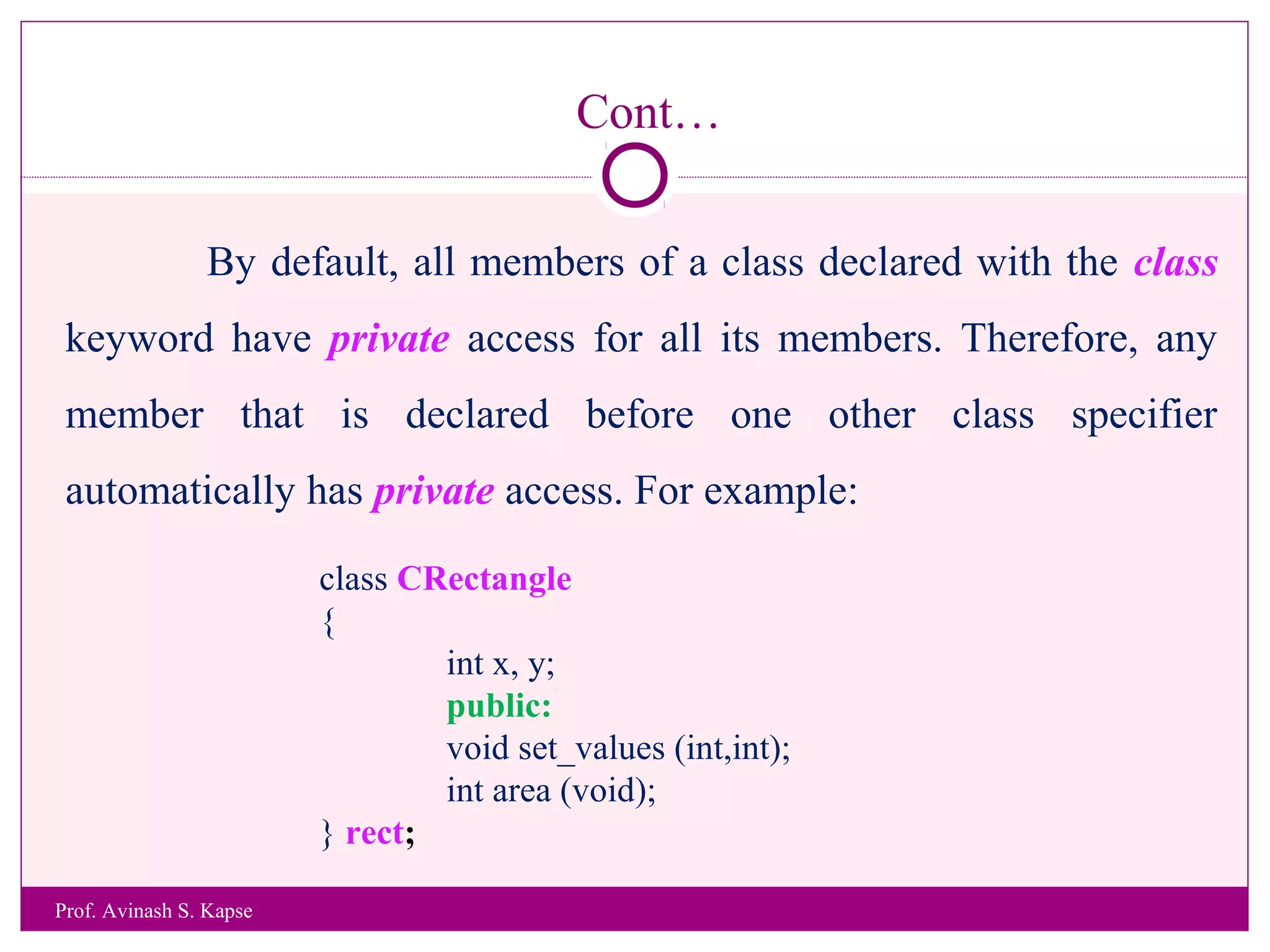
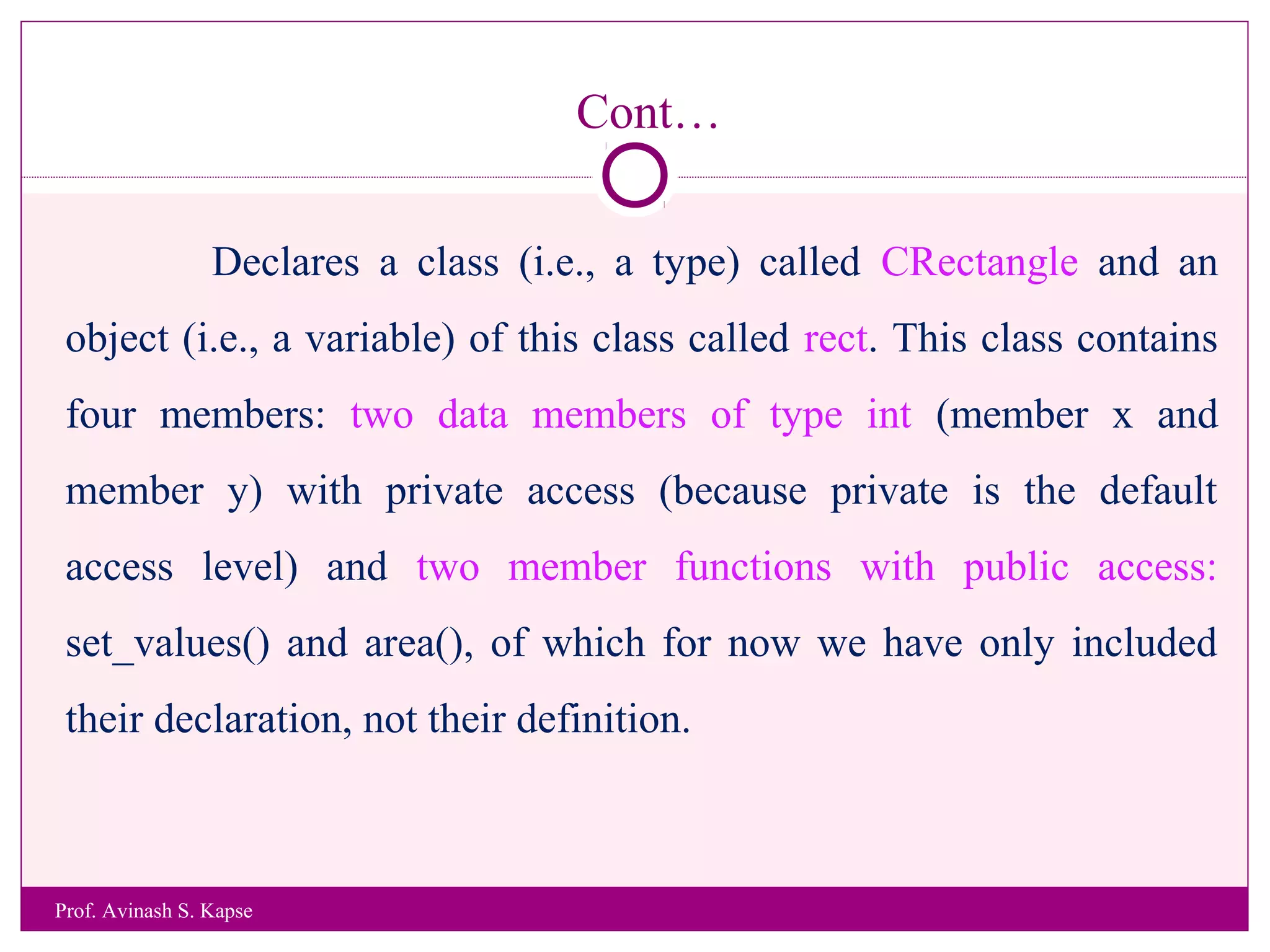
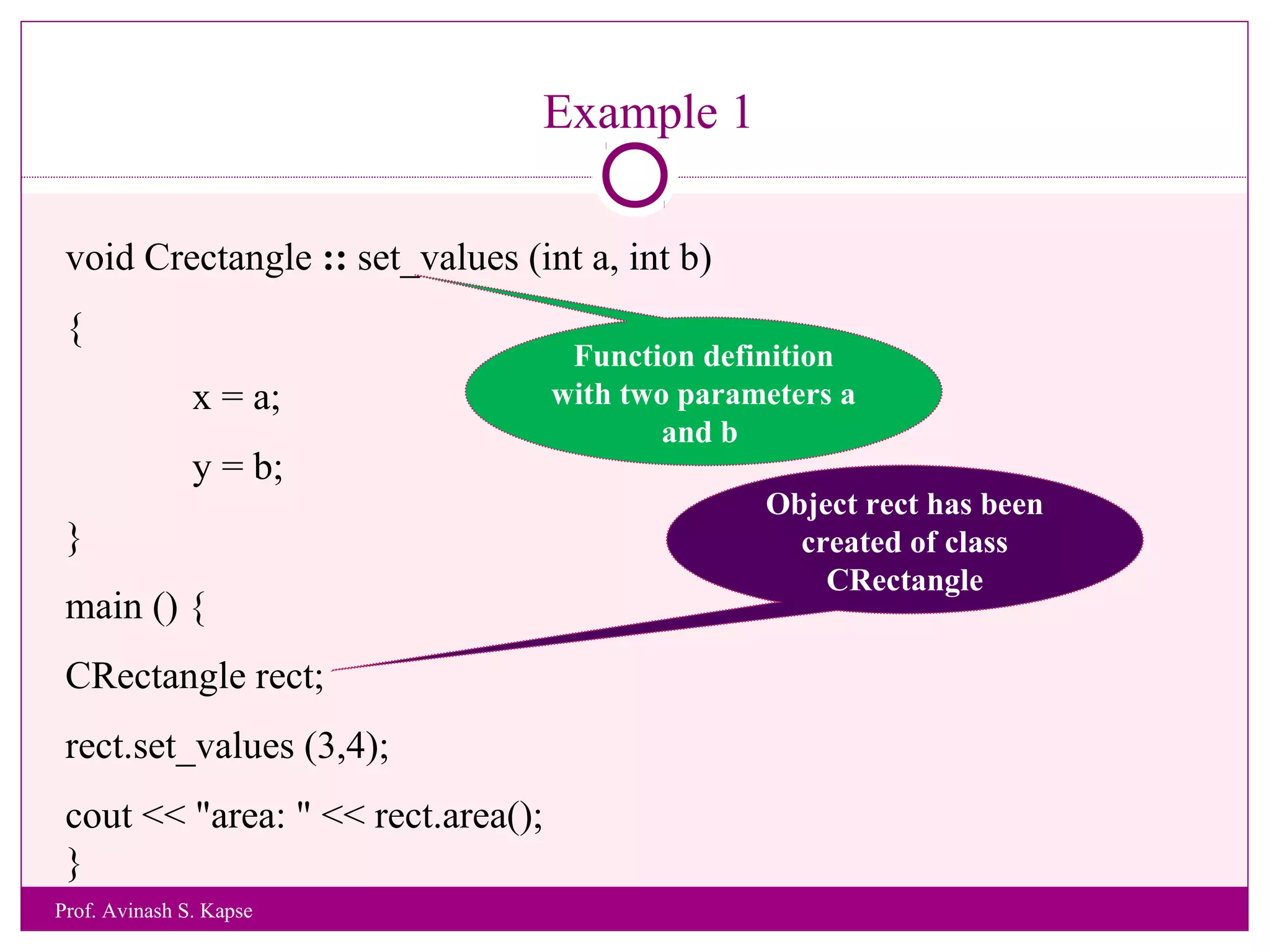
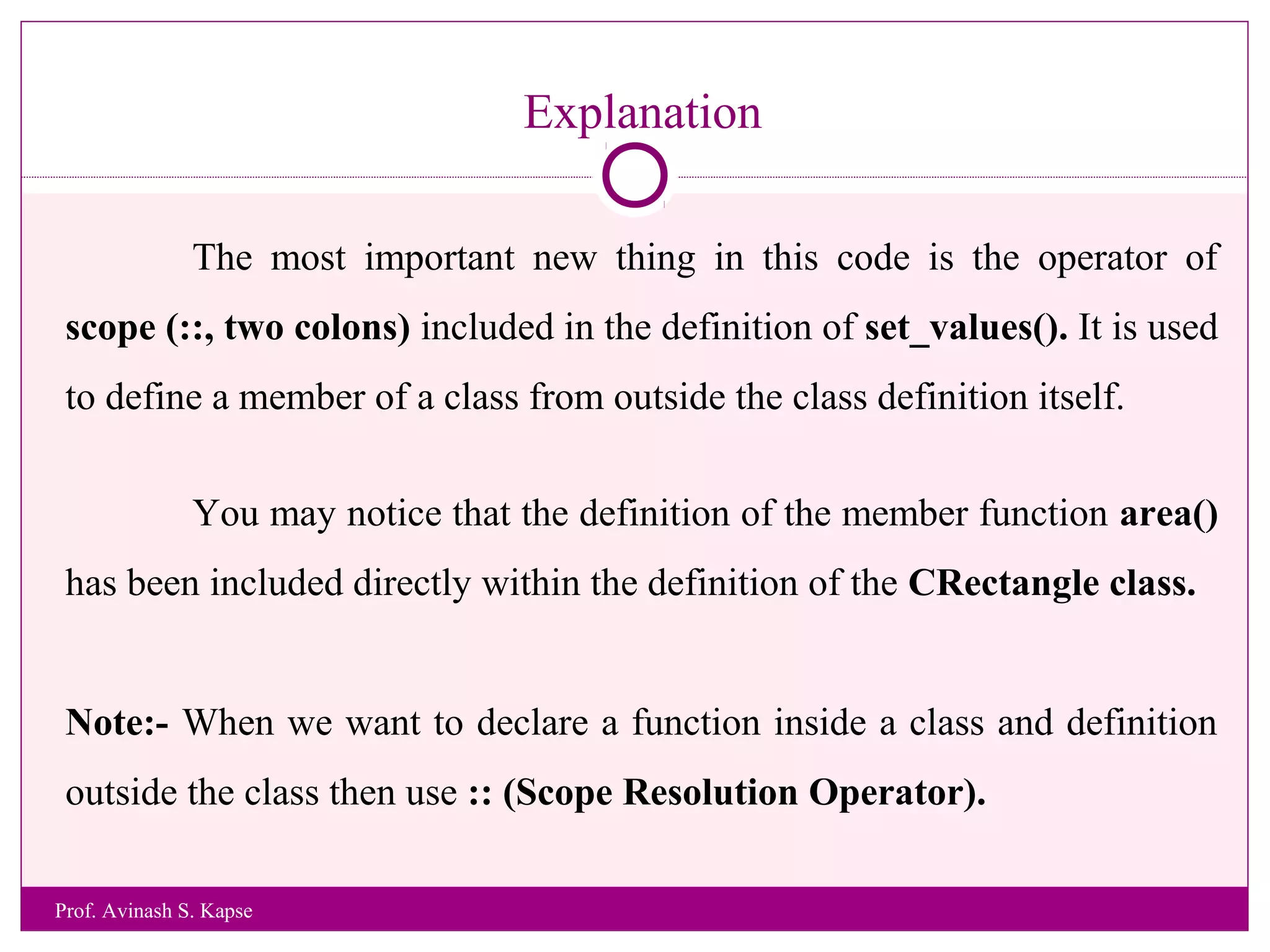
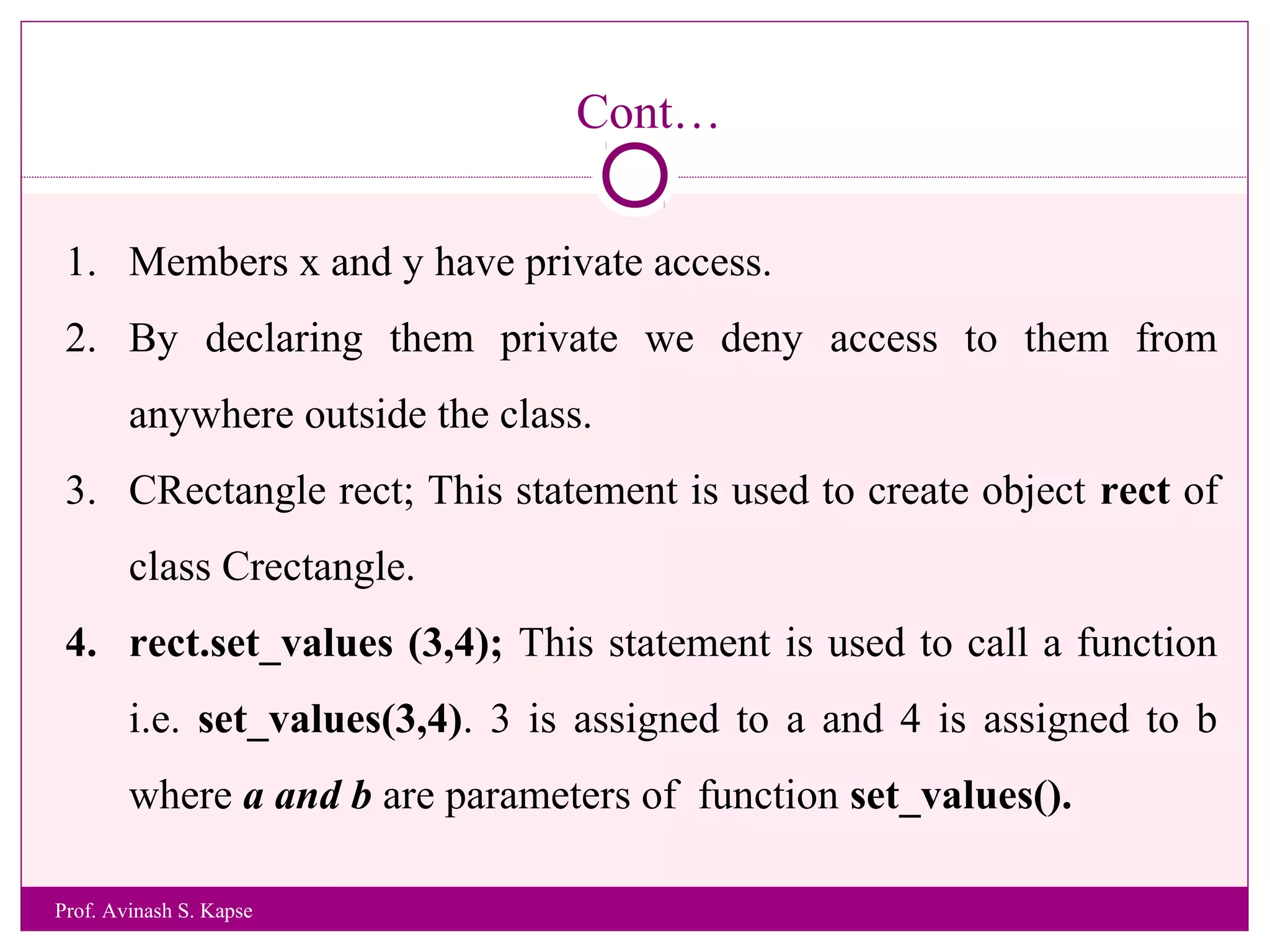
2. It provides an example class called CRectangle with data members and member functions to demonstrate class structure and how to define functions inside and outside the class.
3. The lecture concludes with providing some examples programs to demonstrate class concepts and exercises for students to practice.




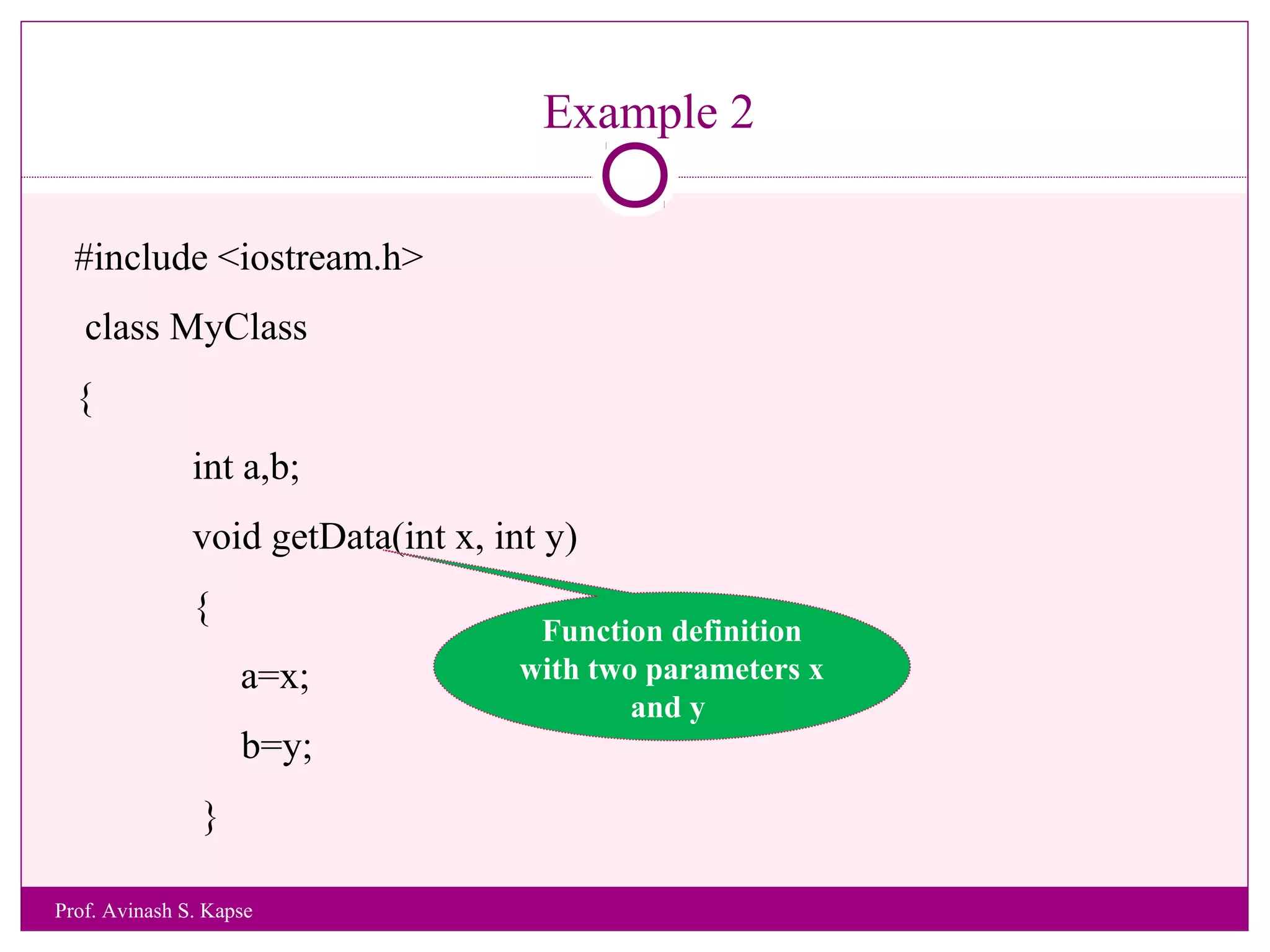
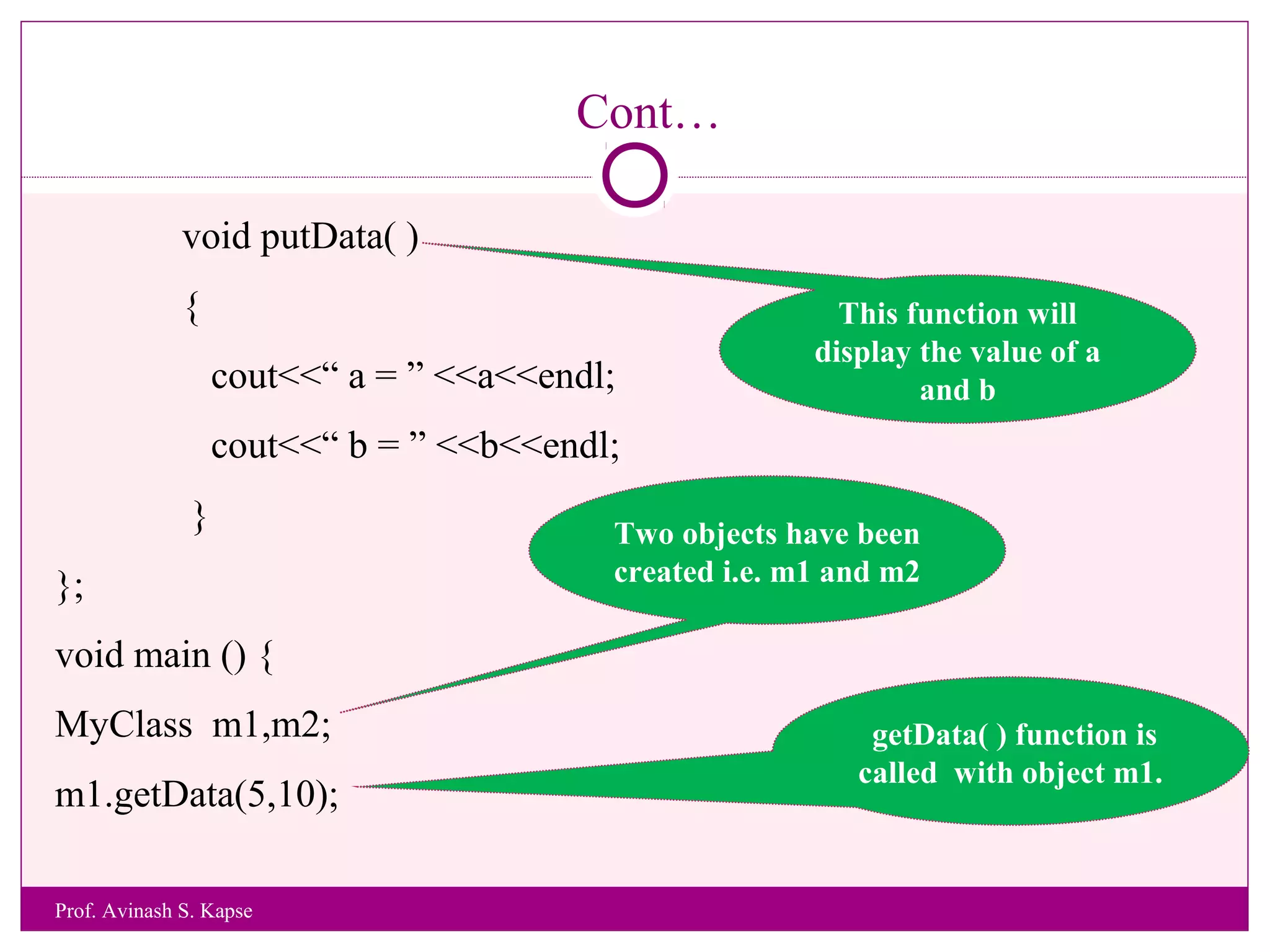
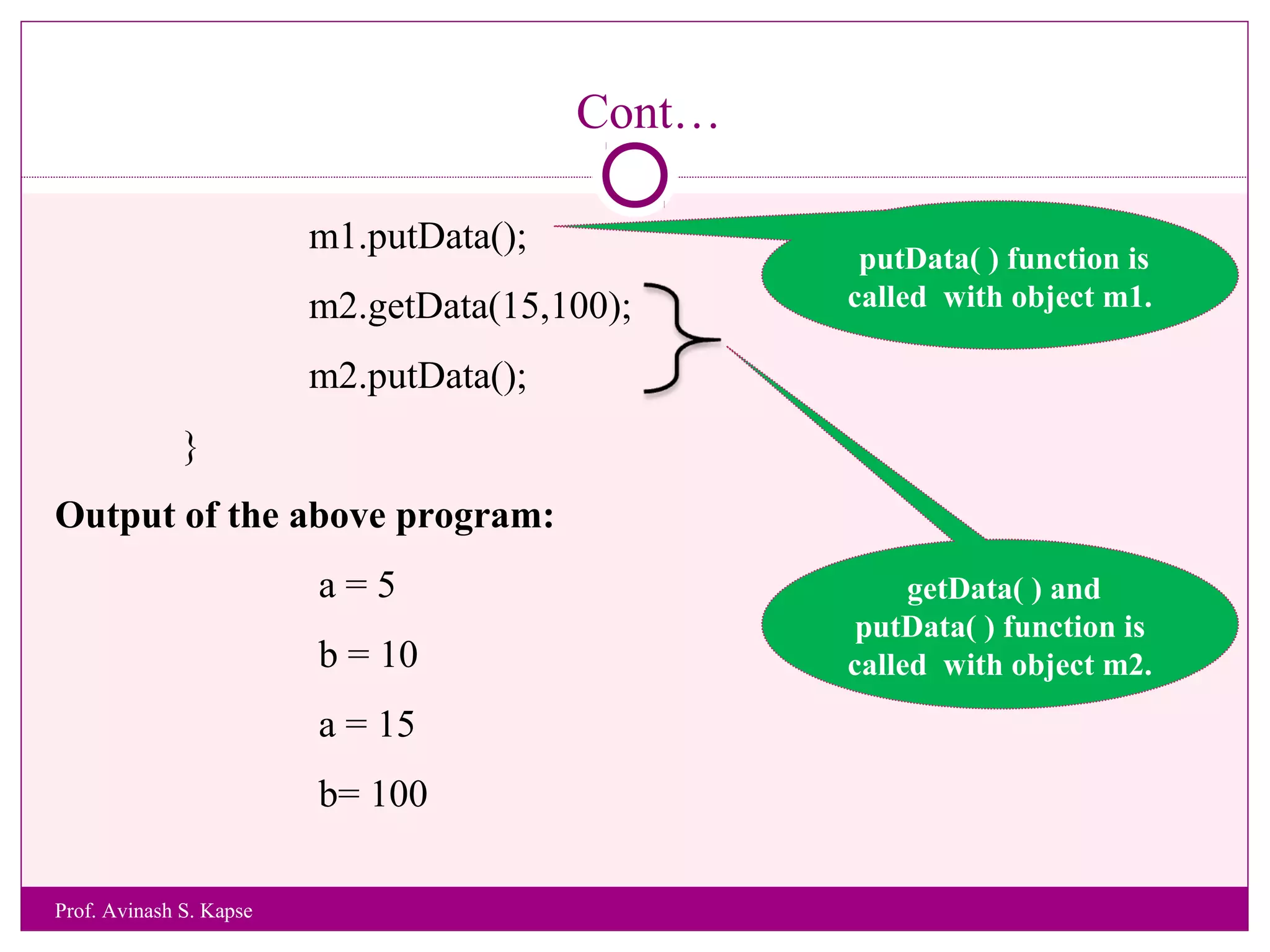
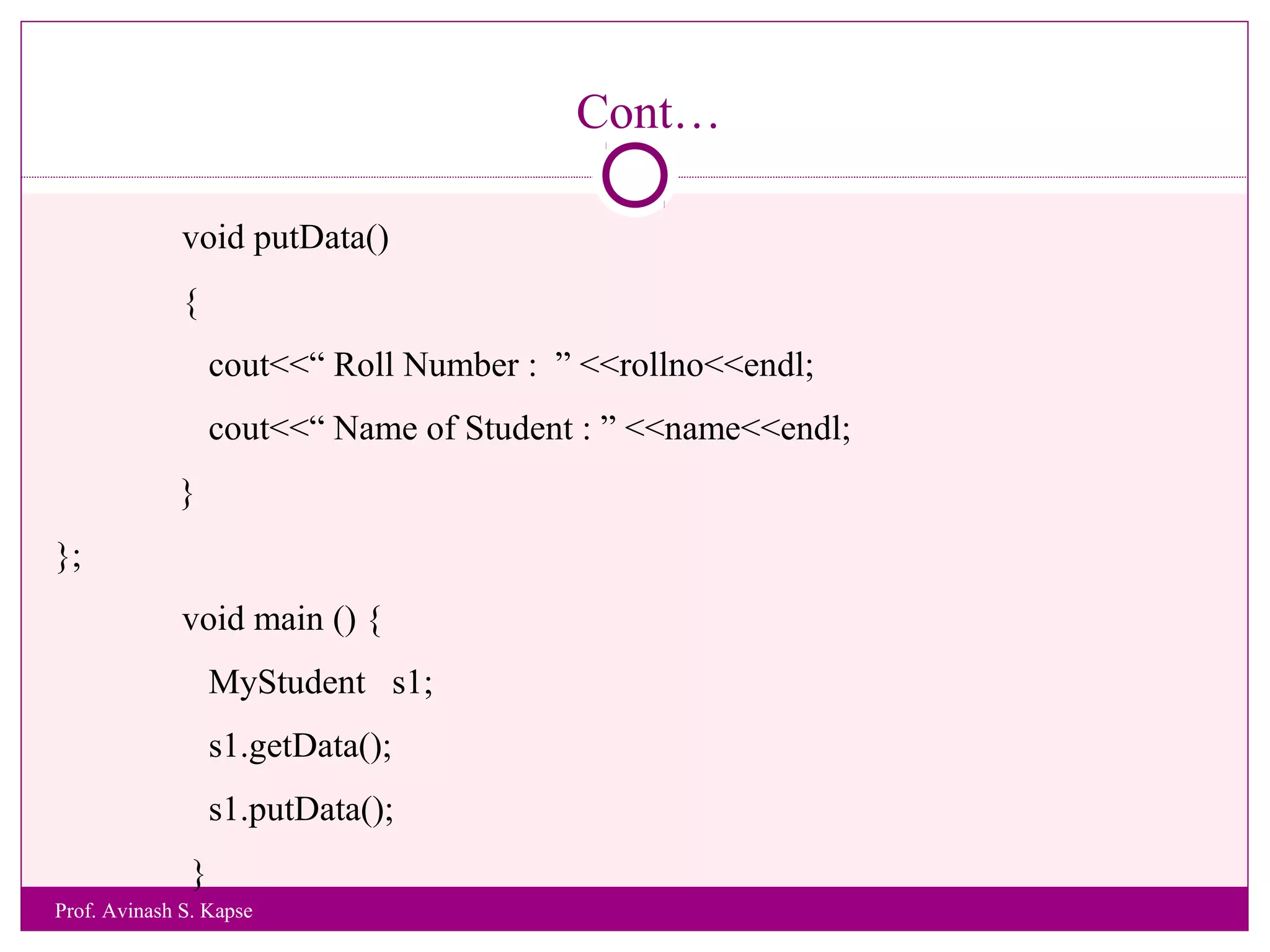
![Example 3
WAP to accept and print student Roll Number and Name of a Student.
#include <iostream.h>
class MyStudent
{
int rollno;
char name[25];
void getData()
{
cout<<“Enter Roll Number and Name of a Student”<<endl;
cin>>rollno>>name;
}
Prof. Avinash S. Kapse](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-180320090048/75/Lecture-2-19-2048.jpg)