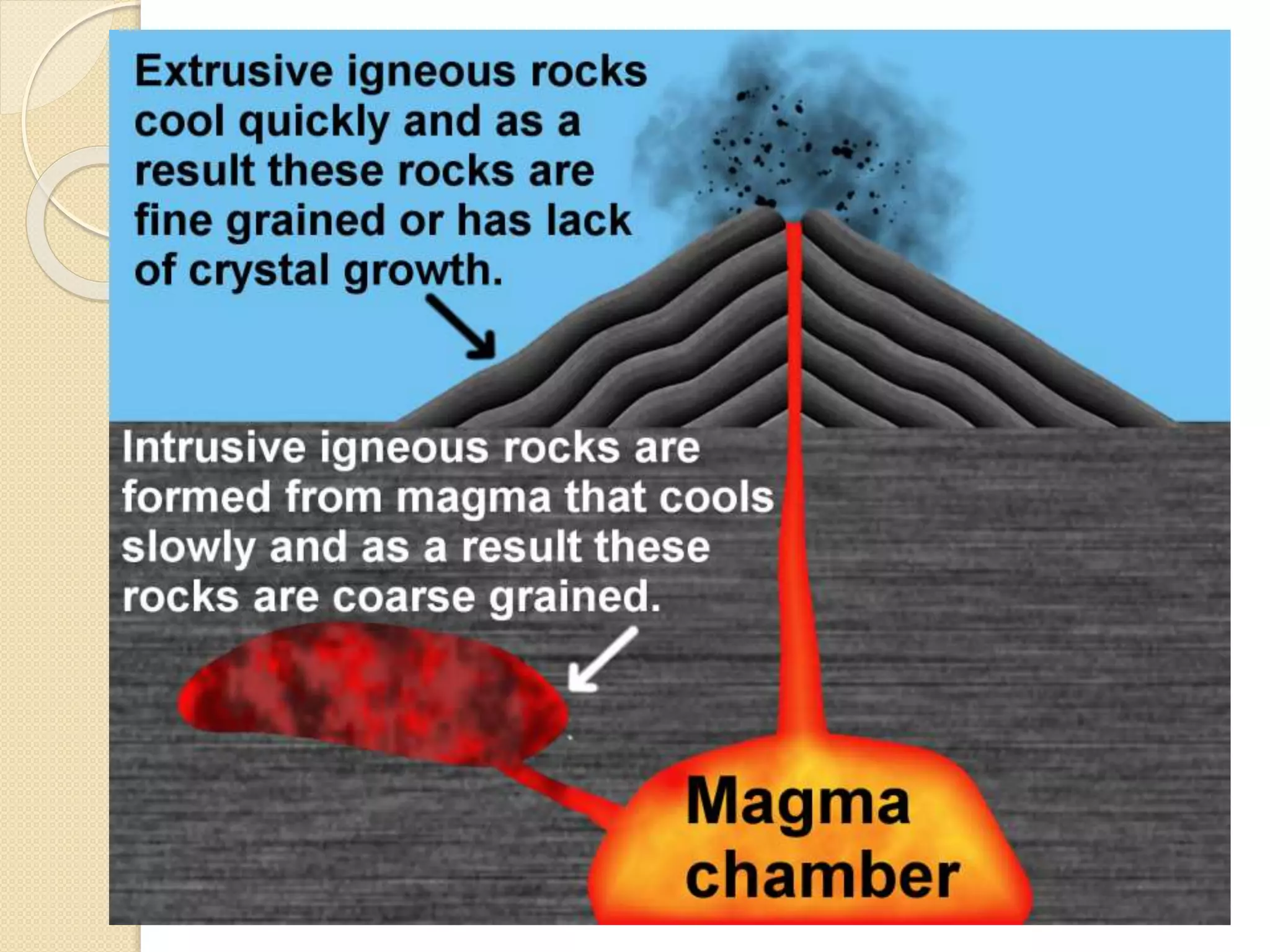
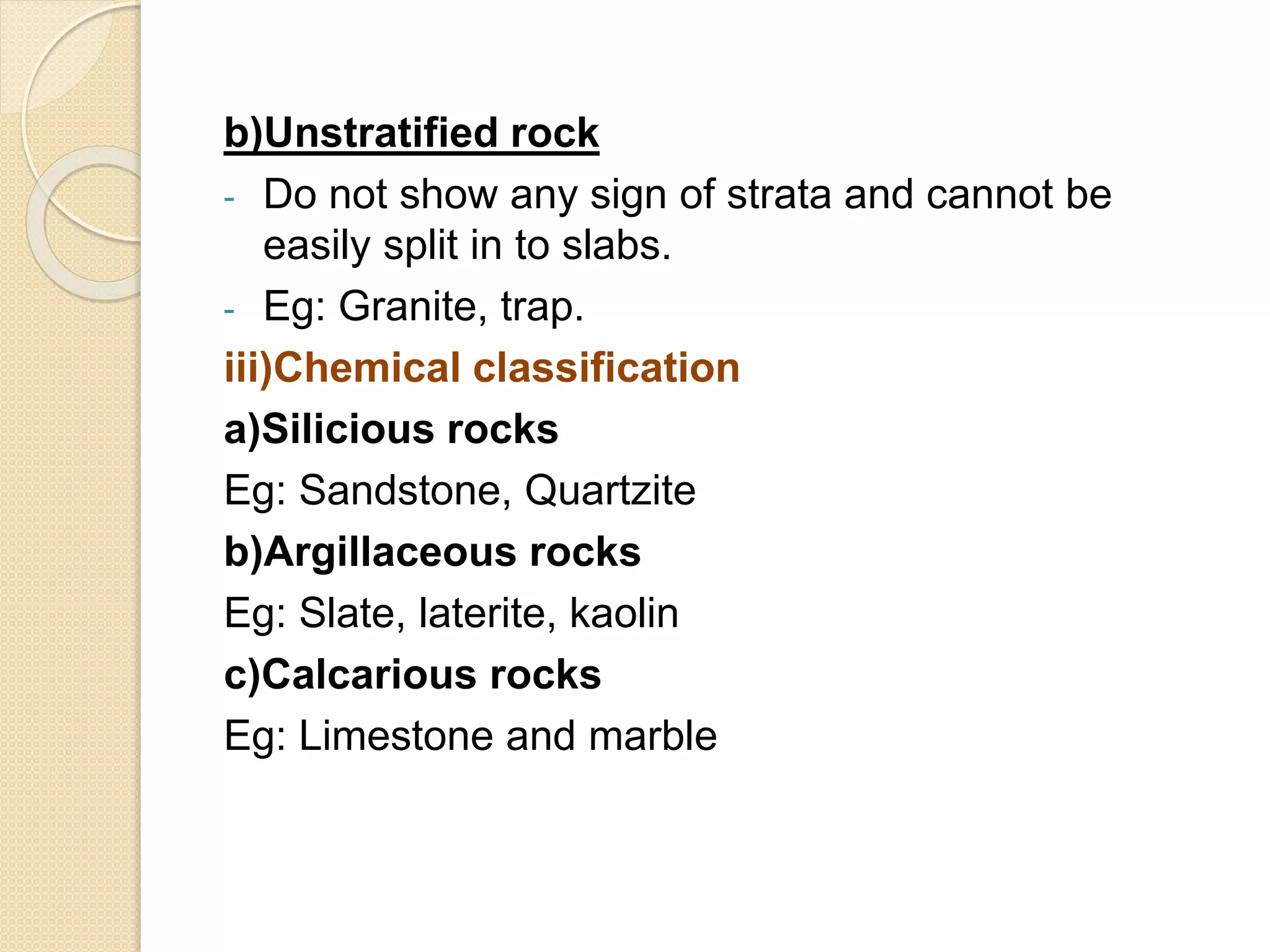
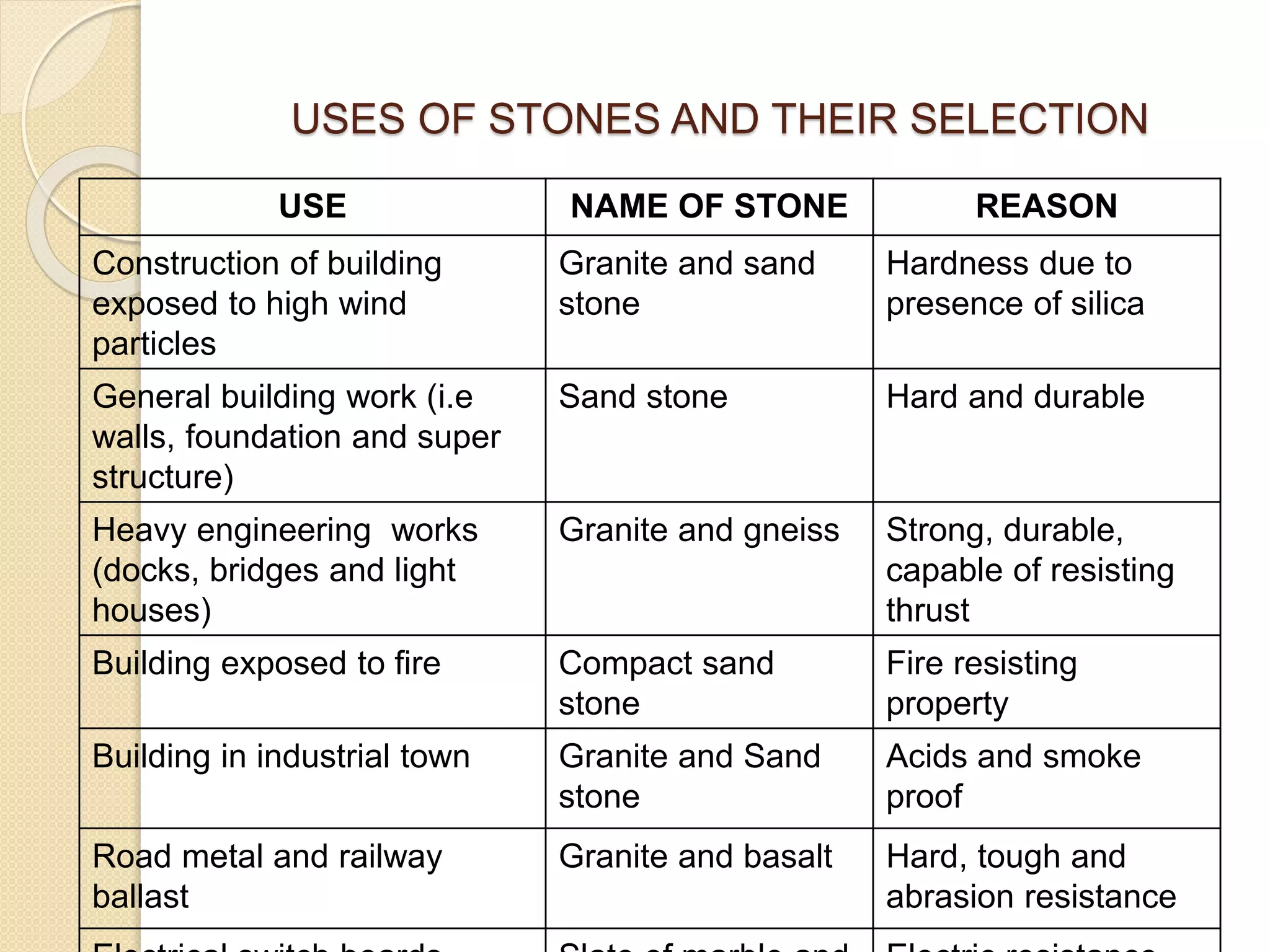
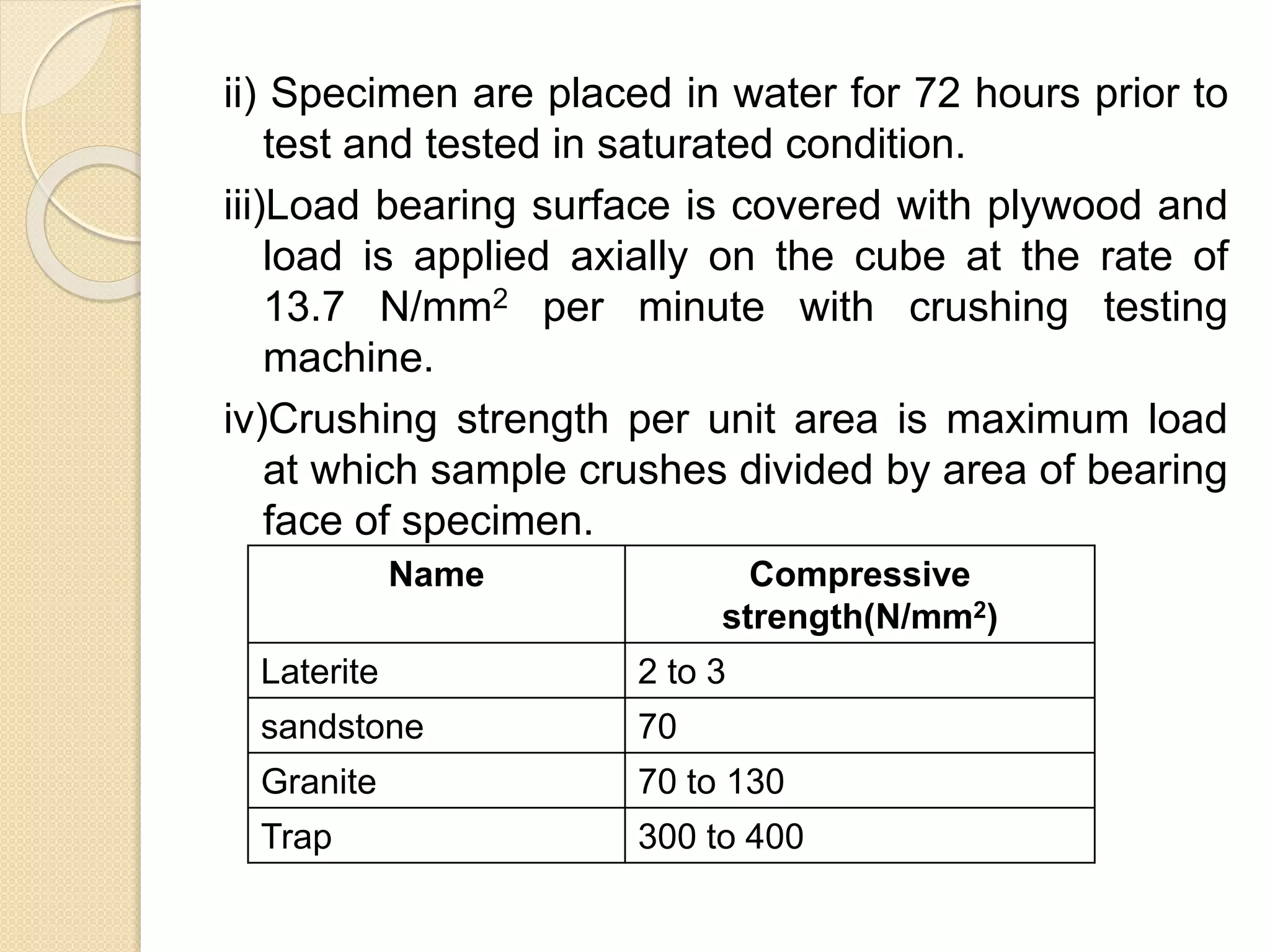
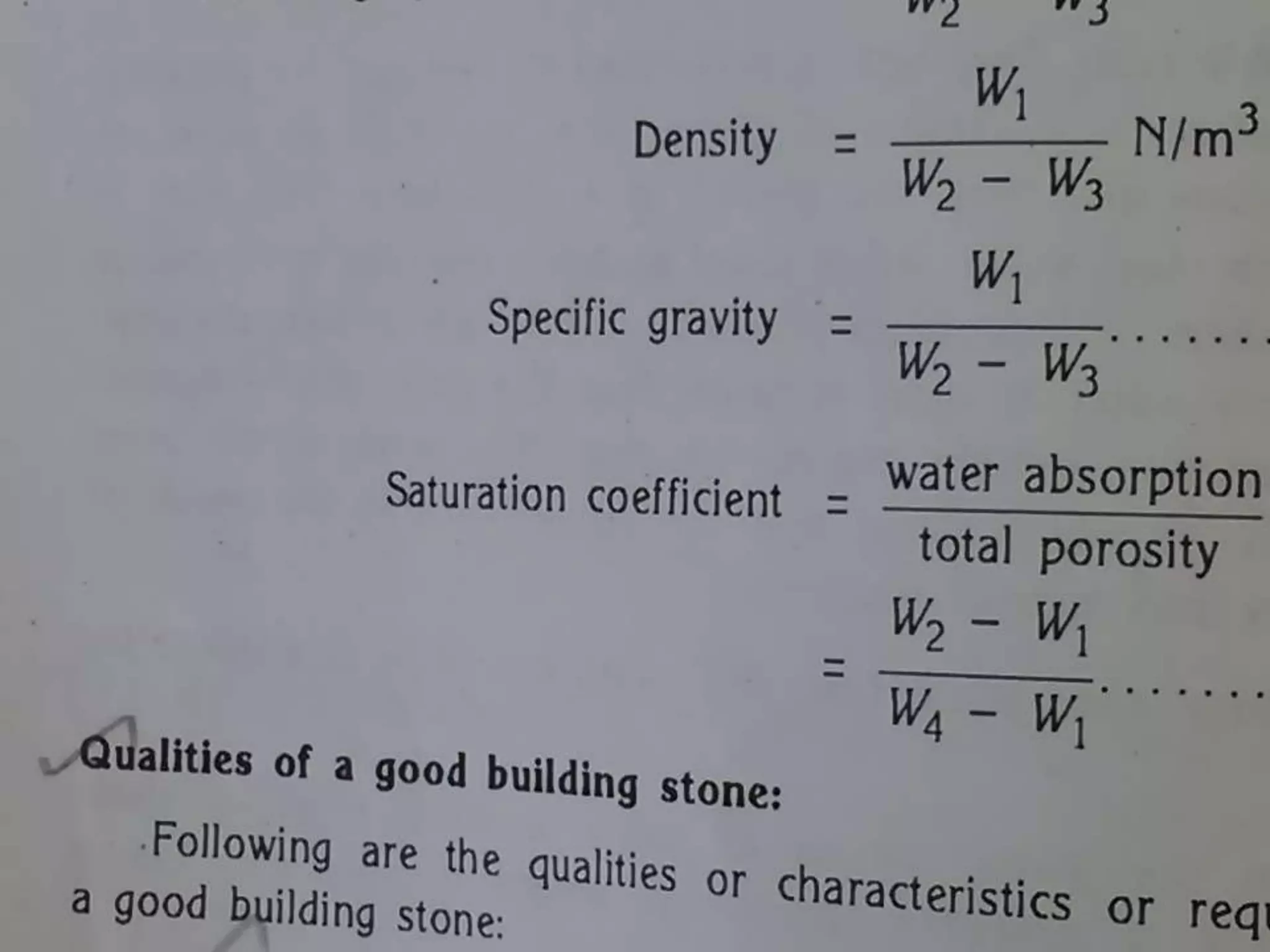
Stone is one of the oldest building materials, used since 3200 BC in ancient India. Stones are classified geologically based on their formation as igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rocks. They are also classified physically based on stratification, chemically based on composition, and practically based on their use. Various tests determine properties like hardness, strength, durability, and resistance to help select appropriate stones for building construction.