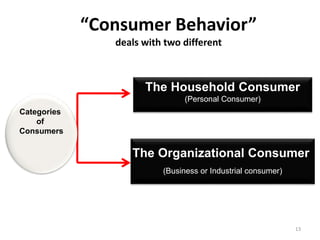
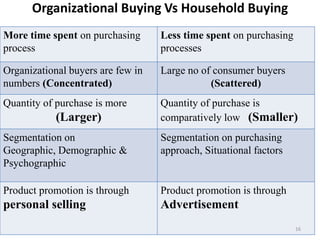
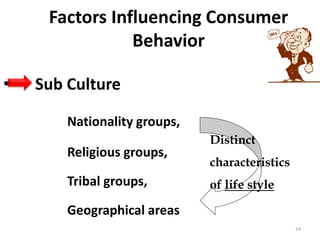
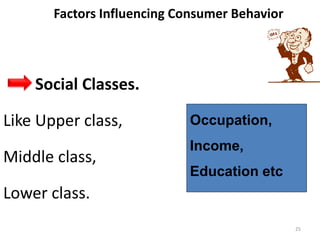
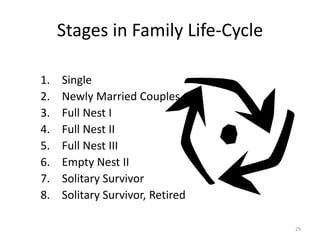
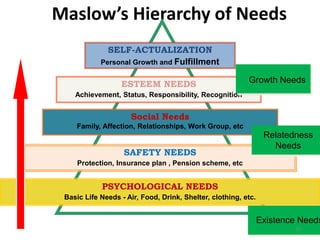
This document outlines a marketing management course that covers 6 units: marketing concepts, product decision, price decision, physical distribution decision, promotion decision, and consumer behavior. It provides an overview of the topics that will be discussed in each unit, including marketing mix, branding, pricing policies, distribution channels, the promotion mix, and factors that influence consumer purchasing behavior. The document also explains the AIDAS formula used in marketing to attract attention, build interest, create desire, and lead to action among consumers.