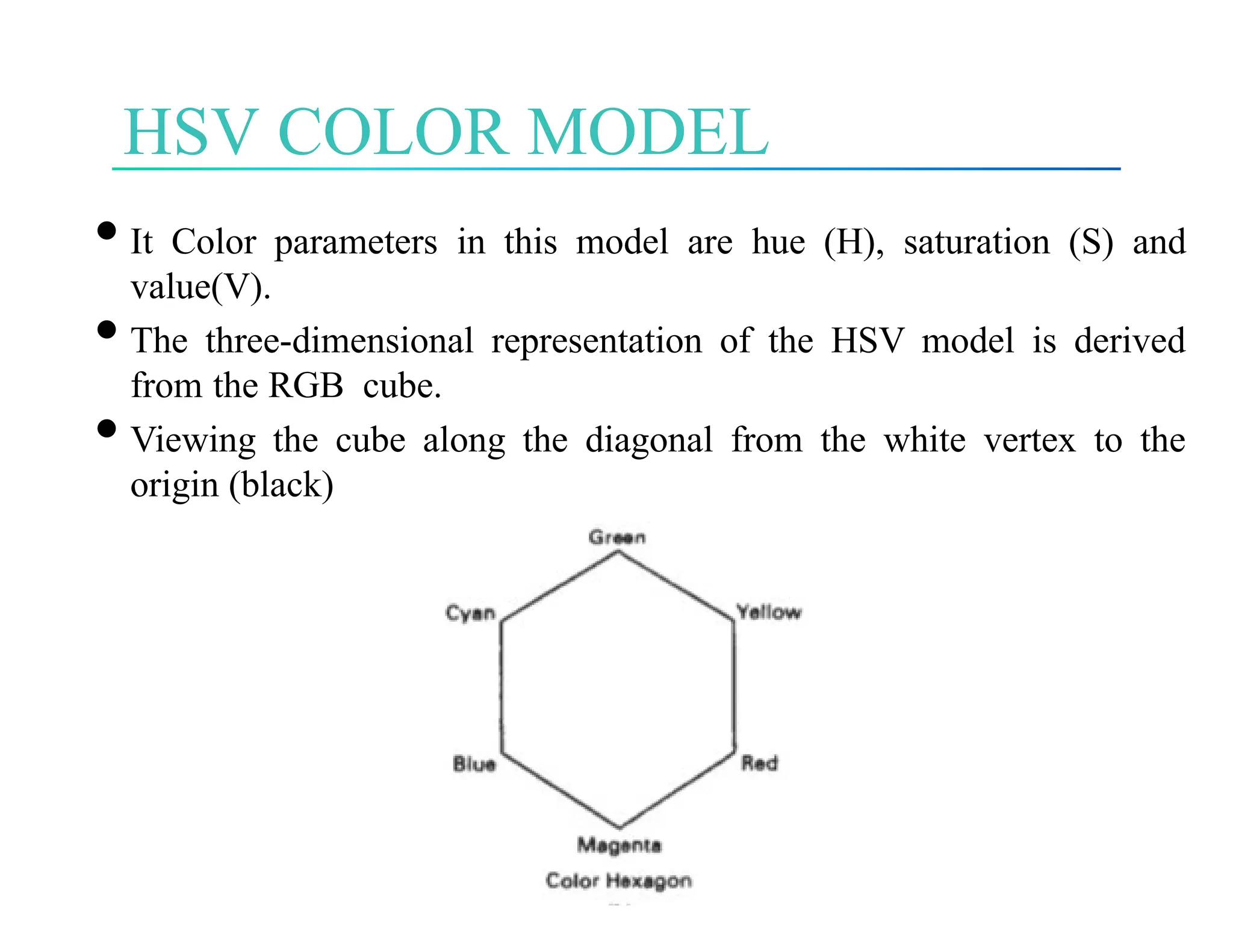
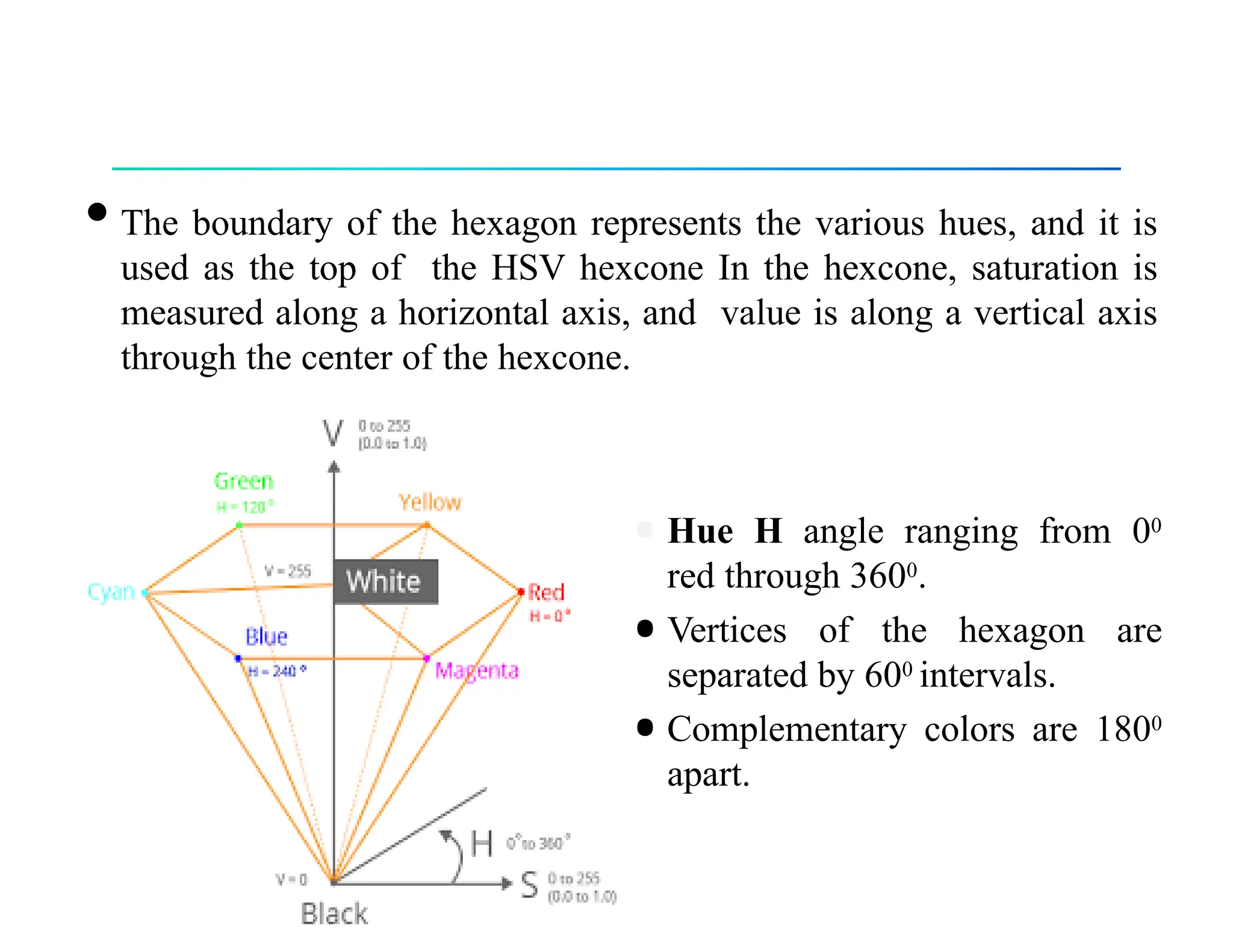
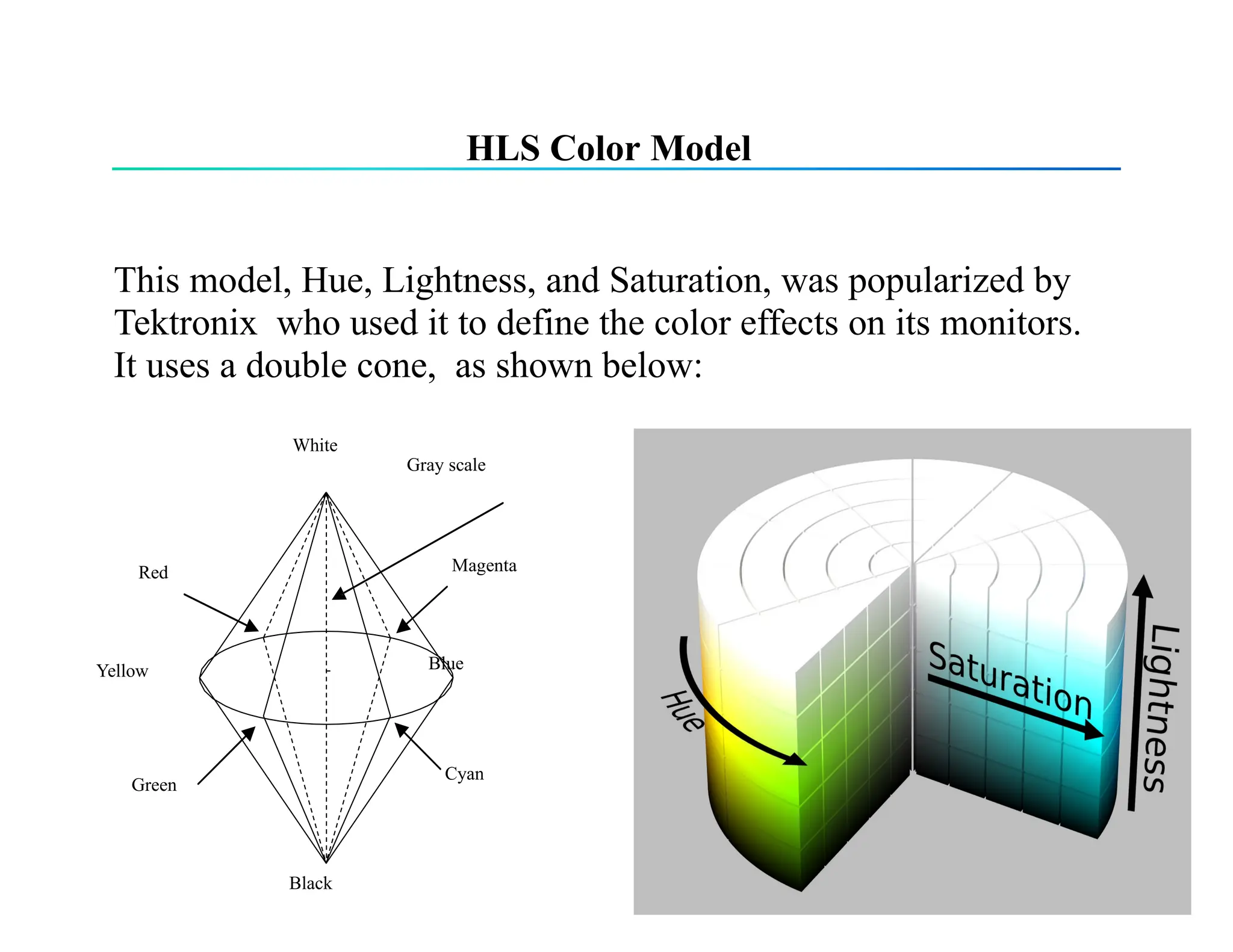
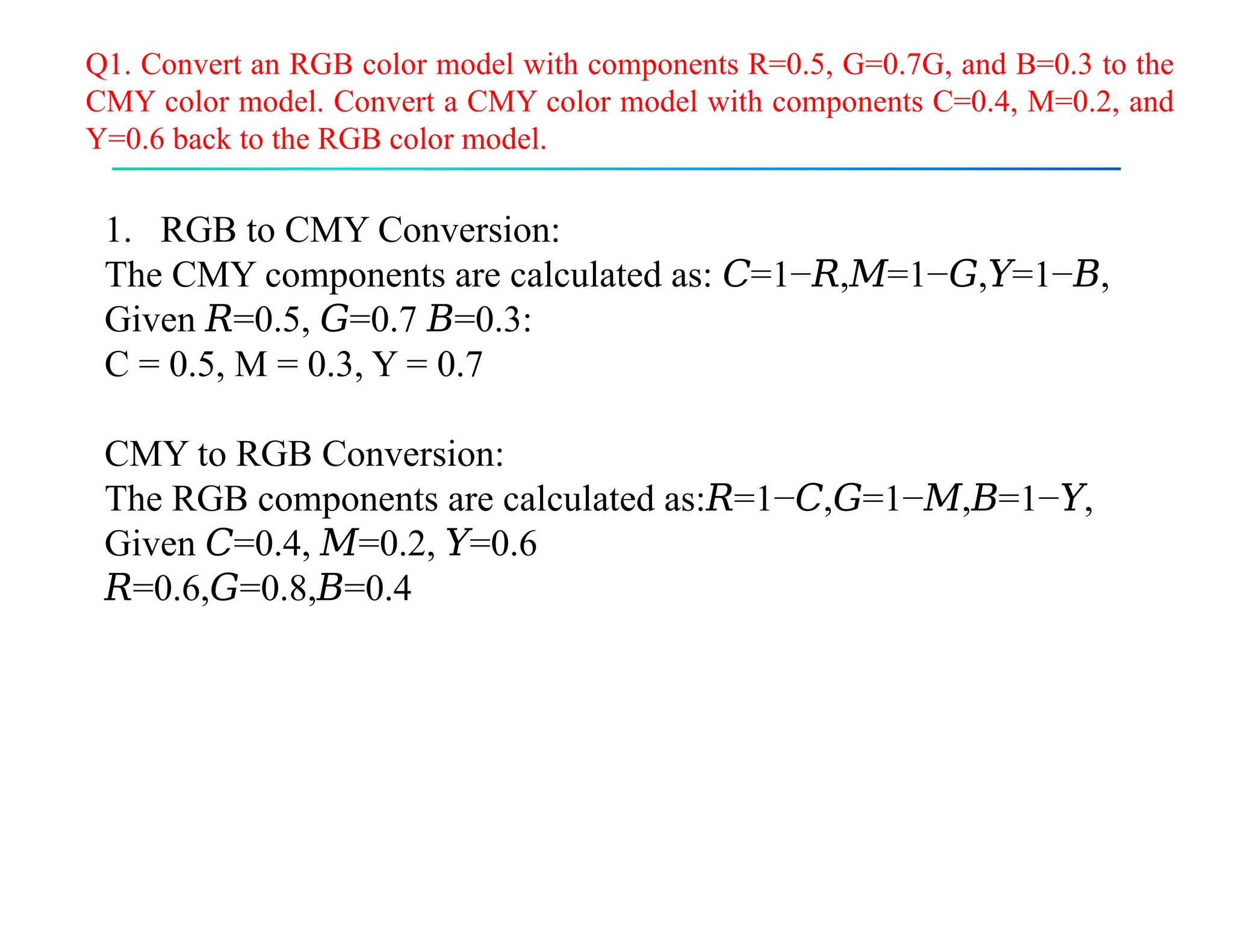
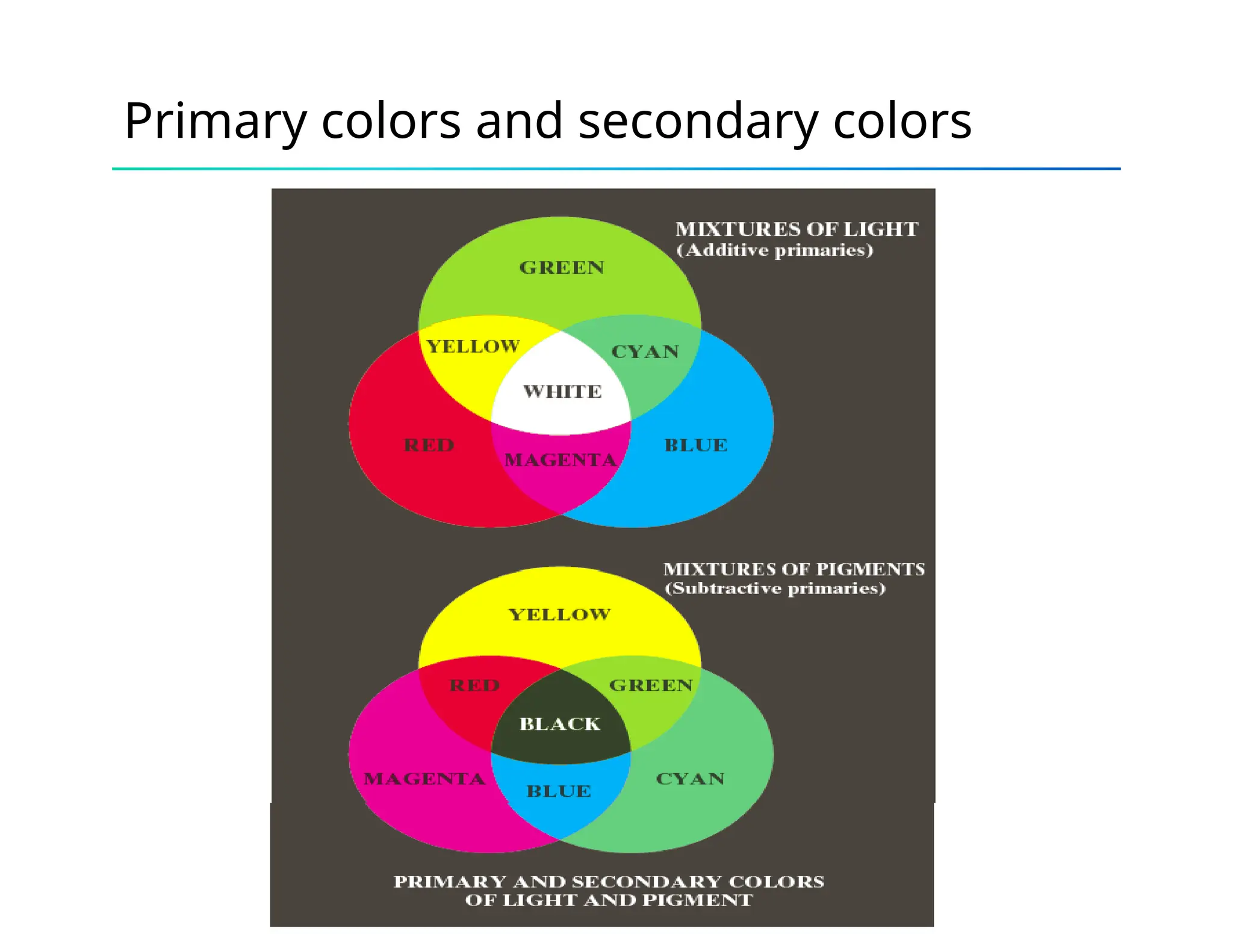
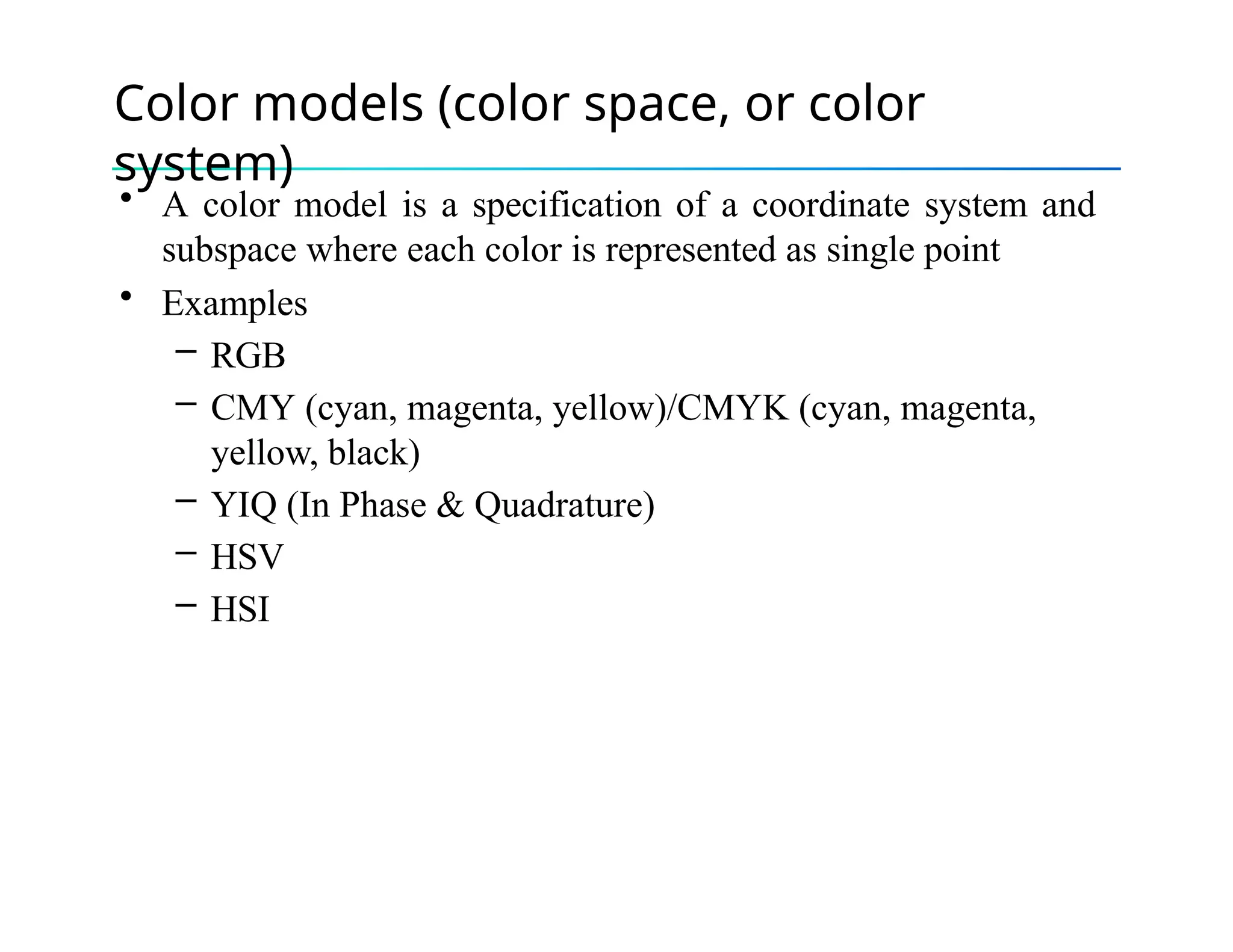
The document discusses color theory, outlining primary and secondary colors, and their characteristics such as brightness, hue, and saturation. It describes various color models including RGB, CMY, CMYK, HSI, HSV, and HLS, along with detailed conversion formulas and examples between RGB and CMY models. Additionally, it provides calculations related to image size and pixel color intensity in digital images.

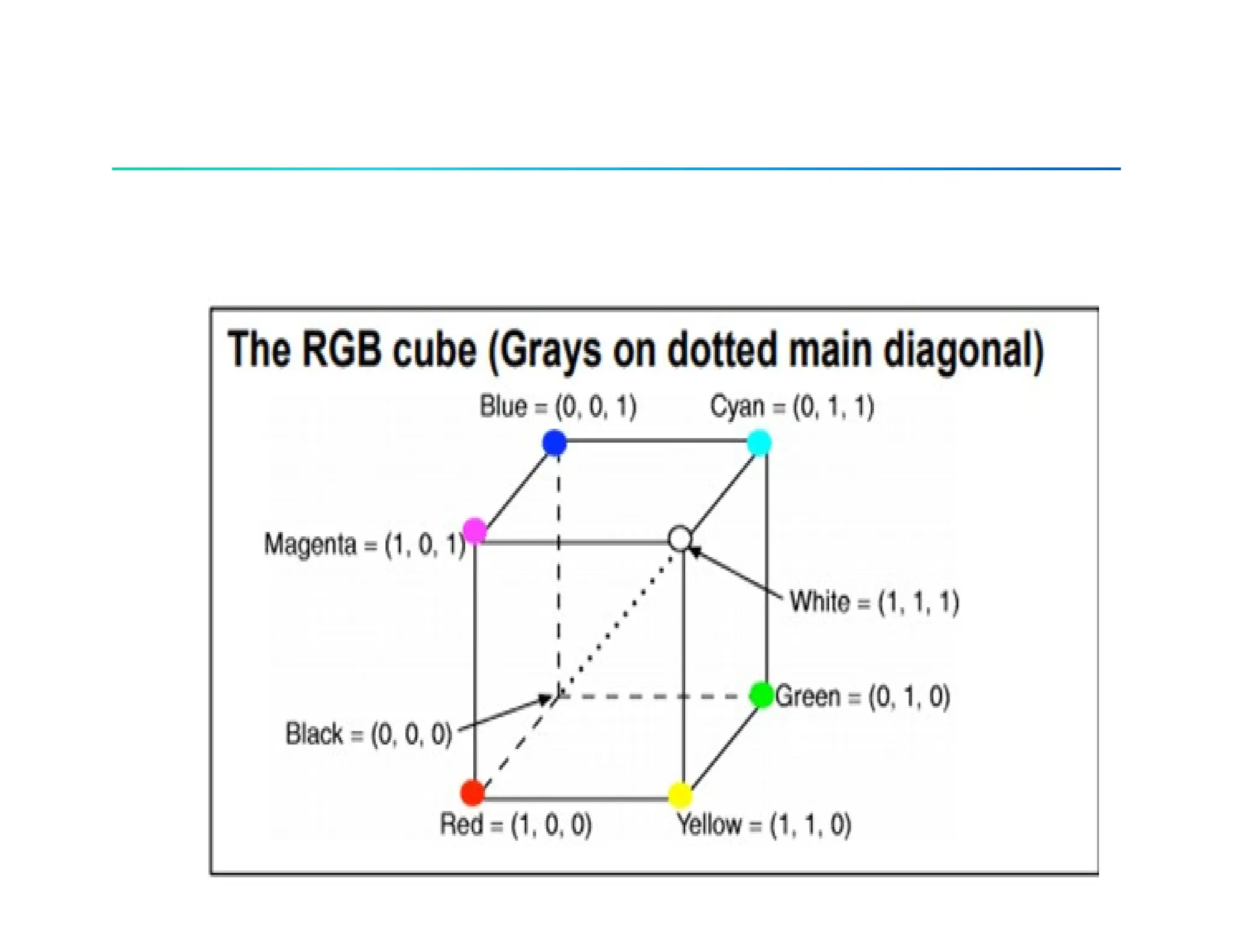
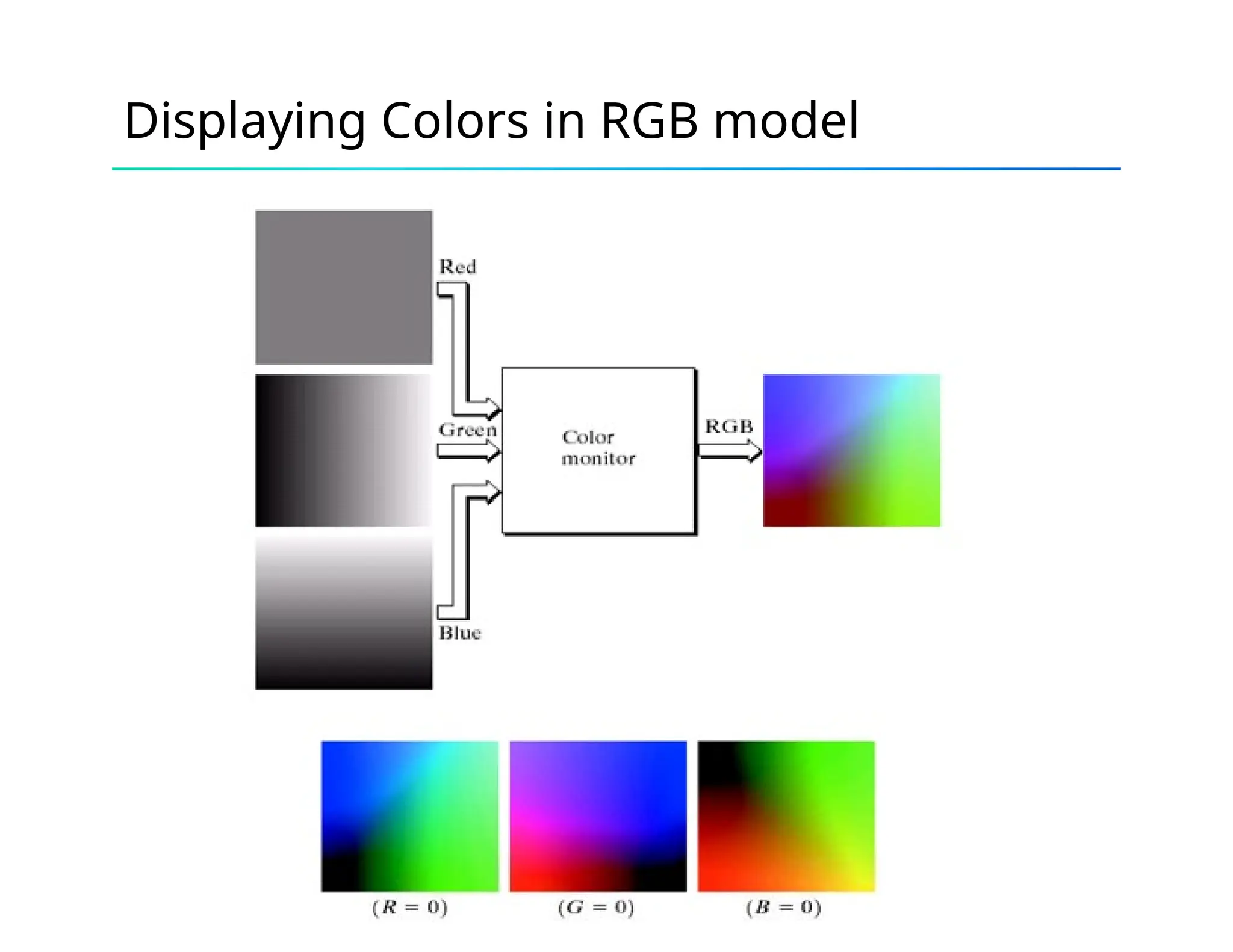
![RGB Color models
• (R, G, B): all values of R, G, B are between 0 and 1.
• With digital representation, for a fixed length of bits each color
element. The total number of bits is called color depth, or pixel
depth. For example, 24-bit RGB color (r, g, b), 8-bits for each
color. The 8-bit binary number r represents the value of r/256 in
[0,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5-colormodel-241203043809-7145087d/75/Unit-5-Color-Model-COMPUTER-GRAPHICS-pptx-5-2048.jpg)
![CMY and CMYK model
• (C, M, Y)
[
𝐶
𝑀
𝑌 ]=
[
1
1
1]−
[
𝑅
𝐺
𝐵]
• CMYK: (C, M, Y, B), where B is a fixed black color. This
basically for printing purpose, where black is usually the
dominating color. When printing black, using B rather than using
(C, M, B) = (1, 1, 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5-colormodel-241203043809-7145087d/75/Unit-5-Color-Model-COMPUTER-GRAPHICS-pptx-7-2048.jpg)
![HSI
• HSI color space: H – hue, S-saturation, I-intensity
, B G
H
360 B G
1
[(R G) (R B)]
cos1
{ 2 }
[(R G)2
(R B)(G B)]1/ 2
3
S
1
[min(R, G,
B)]
(R G B)
I
1
(R G B) 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5-colormodel-241203043809-7145087d/75/Unit-5-Color-Model-COMPUTER-GRAPHICS-pptx-8-2048.jpg)