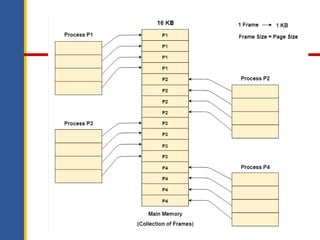
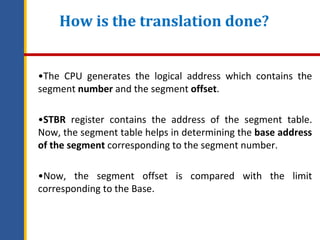
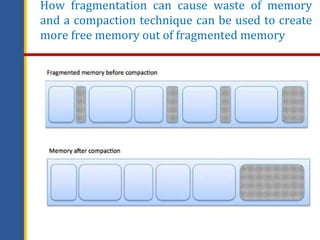
Memory management involves controlling and coordinating computer memory to optimize system performance, allocate memory to processes, and ensure applications do not interfere with each other. It includes concepts such as logical and physical addresses, memory allocation techniques like contiguous and non-contiguous allocation, and methods to mitigate fragmentation through techniques like compaction and swapping. Various memory management techniques, such as paging and segmentation, help in the effective mapping and utilization of memory resources.


















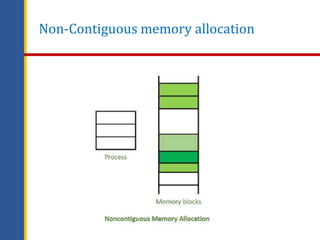




















![Non-Contiguous Memory
Allocation Technique
•In the non-contiguous memory allocation technique,
different parts of the same process are stored in
different places of the main memory.
Types:
•Paging [Fixed partitioning]
•Segmentation[Variable partitioning]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymanagment-240222143306-f406c35d/85/memory-managment-on-computer-science-ppt-42-320.jpg)