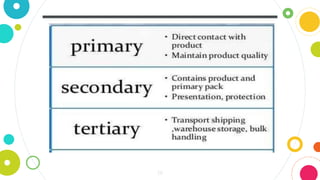
The document discusses pharmaceutical quality assurance and packaging. It states that packaging plays an important role in product quality by providing protection, presentation, identification, information, compatibility and convenience. It also lists the requirements of good packaging, including that the packaging must not react with or impart tastes/odors to the product, and must be nontoxic, FDA approved, and tamper resistant. Finally, it describes the different types of containers used for pharmaceutical products based on their purpose, such as single dose containers for injectables and light-resistant containers for photosensitive medications.