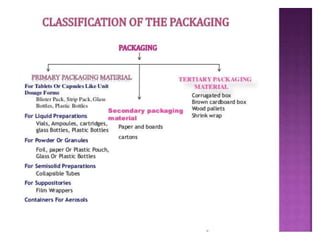
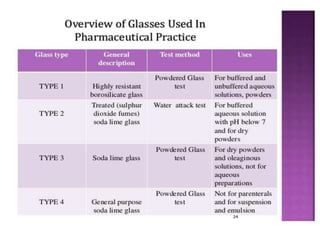
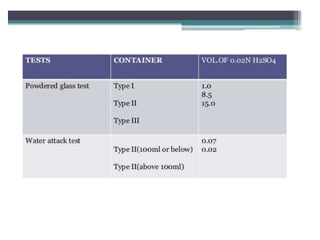
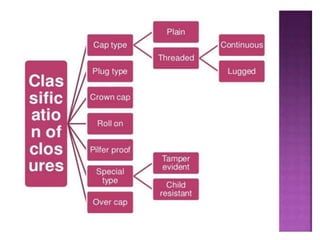
This document discusses quality control tests for pharmaceutical packaging materials. It defines primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging. Primary packaging directly contains the product, secondary provides additional protection, and tertiary is for bulk handling and shipping. Some key quality control tests mentioned for containers include permeation testing to check for transmission of gases, vapors, or liquids through packaging materials. For rubber closures, common quality control tests evaluate properties like extractable content and curing. Proper quality control testing ensures packaging and closures maintain product quality and integrity during storage and distribution.