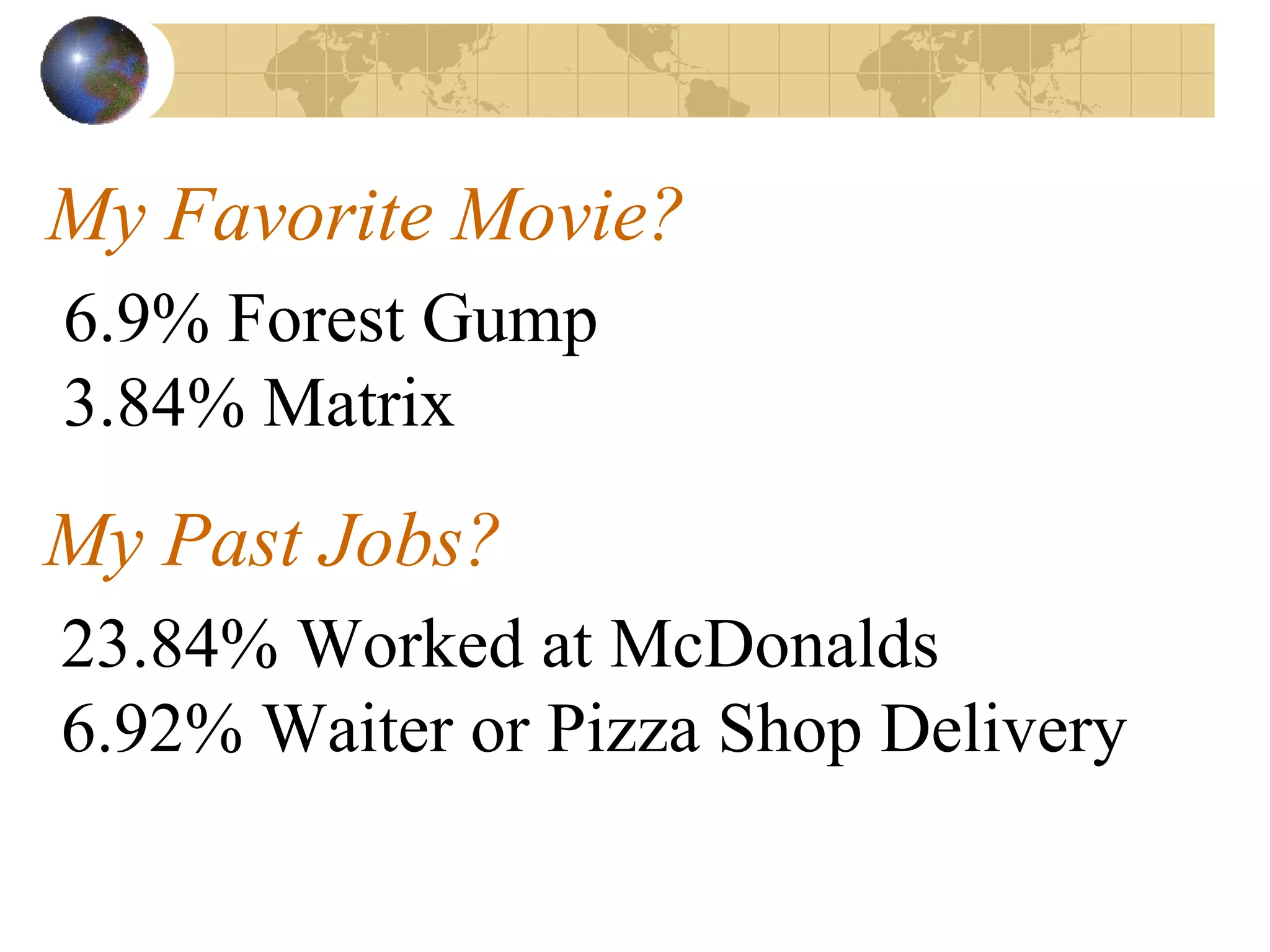1. The document discusses different types of claims that can be made in an argument, including designative, definitive, evaluative, and advocative claims.
2. It also discusses different types of support or data that can be used to back up claims, such as receiver beliefs, source credibility, evidence from others, and reasoning.
3. The document provides an example of conducting an audience analysis and includes sample data about the demographics, preferences, and affiliations of the target audience.