This document describes functions for embedding Ring code in Ring programs without sharing state. It provides functions like ring_state_init() to initialize a Ring state, ring_state_runcode() to execute Ring code in a state, and ring_state_findvar() to find variables. Executing applications serially is also described using ring_state_main(). The document also covers extending the RingVM with C/C++ modules by writing functions and registering them using the Ring API. Modules are organized with initialization functions that register functions to make them available in Ring.


![Ring Documentation, Release 1.3
sysargv
3
B:ringbin/ring
B:/ring/tests/scripts/memorylist.ring
0
0
x
2
10
0
0
y
2
20
0
0
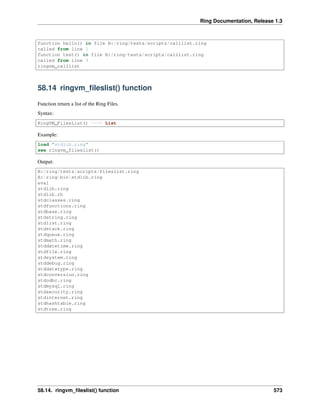
58.13 ringvm_calllist() function
The Function return a list of the functions call list.
Each List Member is a list contains the next items
• Function Type
• Function Name
• Program Counter (PC)
• Stack Pointer (SP)
• Temp. Memory List
• Method or Function Flag
• Caller PC
• FuncExec Flag
• ListStart Flag
• Nested Lists Pointer
• State List
Syntax:
RingVM_CallList() ---> List
Example:
hello()
func hello
test()
func test
mylist = ringvm_calllist()
for t in mylist see t[2] + nl next
Output:
58.13. ringvm_calllist() function 572](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/591ringring-170614010114/85/The-Ring-programming-language-version-1-3-book-Part-60-of-88-5-320.jpg)
![CHAPTER
FIFTYNINE
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter we will learn about embedding Ring in Ring programs and applications.
59.1 Embedding Ring in Ring without sharing the State
From Ring 1.0 we already have functions for embedding Ring in the C language. Also we can execute Ring code
inside Ring programs using the eval() function. In this release we provide functions for embedding Ring in Ring
programs without sharing the state.
Advantages:
1. Quick integration for Ring programs and applications together without conflicts.
2. Execute and run Ring code in safe environments that we can trace.
Example:
pState = ring_state_init()
ring_state_runcode(pState,"See 'Hello, World!'+nl")
ring_state_runcode(pState,"x = 10")
pState2 = ring_state_init()
ring_state_runcode(pState2,"See 'Hello, World!'+nl")
ring_state_runcode(pState2,"x = 20")
ring_state_runcode(pState,"see x +nl")
ring_state_runcode(pState2,"see x +nl")
v1 = ring_state_findvar(pState,"x")
v2 = ring_state_findvar(pState2,"x")
see v1[3] + nl
see V2[3] + nl
ring_state_delete(pState)
ring_state_delete(pState2)
Output:
Hello, World!
Hello, World!
10
20
10
20
574](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/591ringring-170614010114/85/The-Ring-programming-language-version-1-3-book-Part-60-of-88-7-320.jpg)