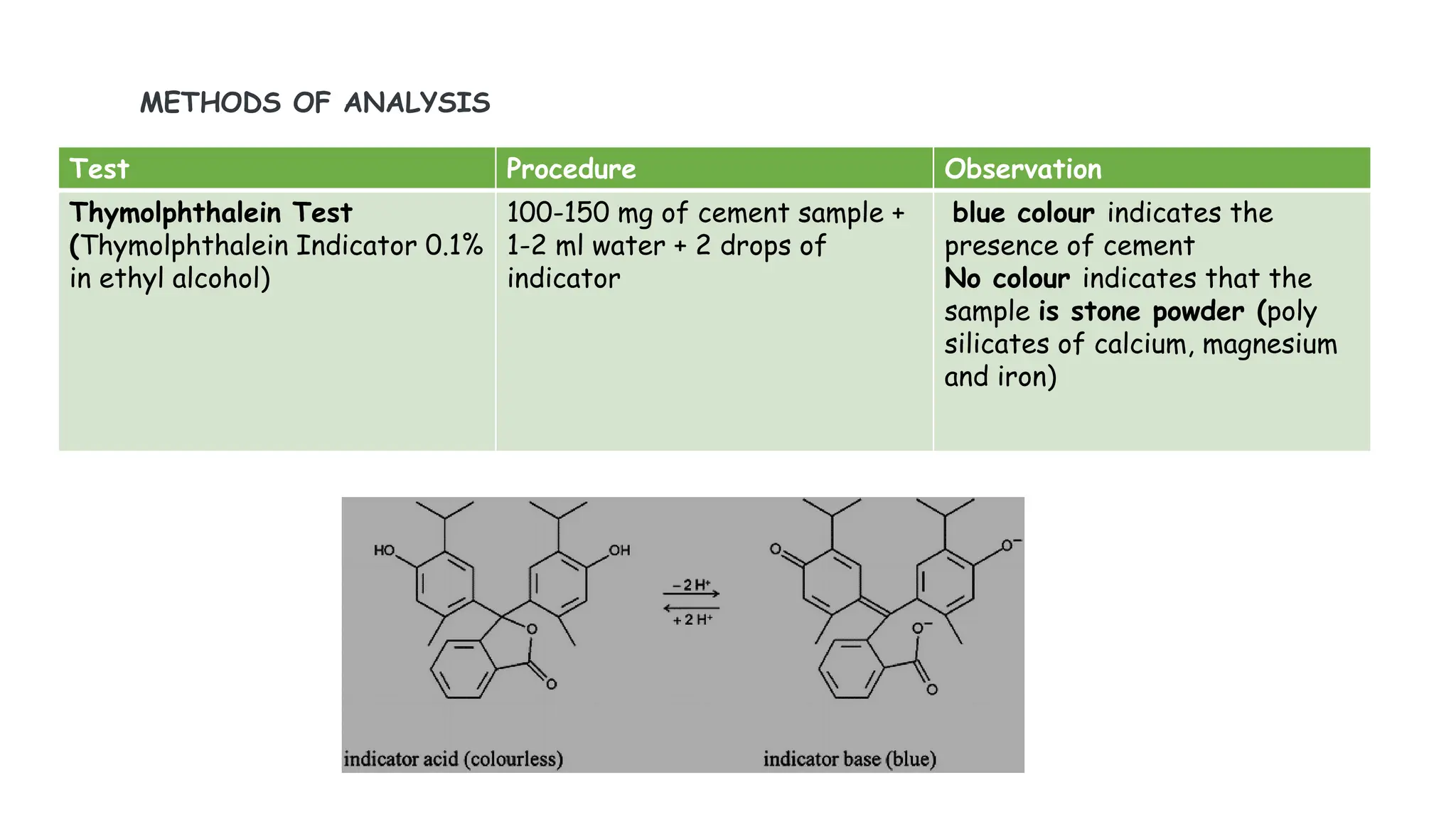
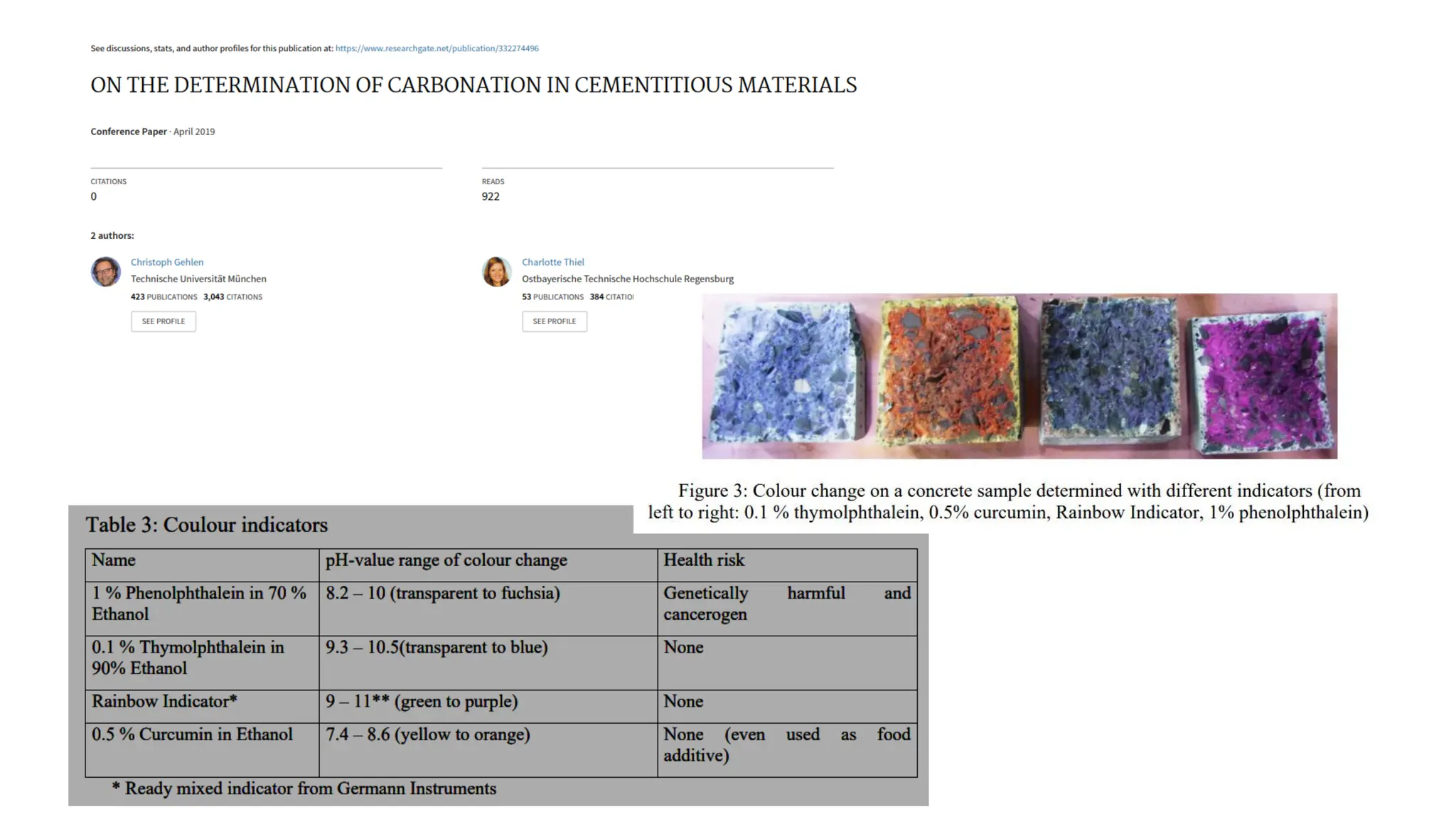
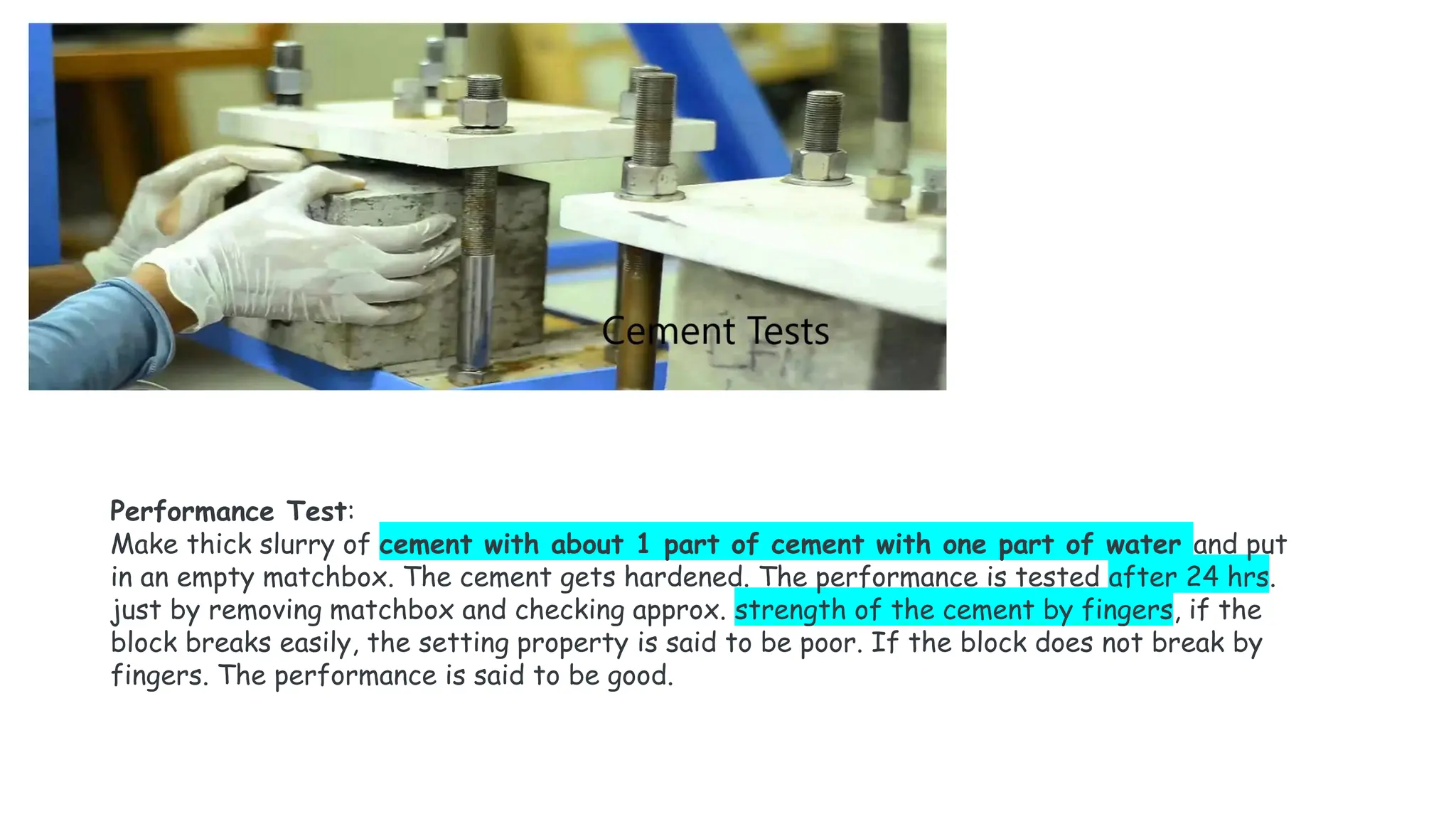
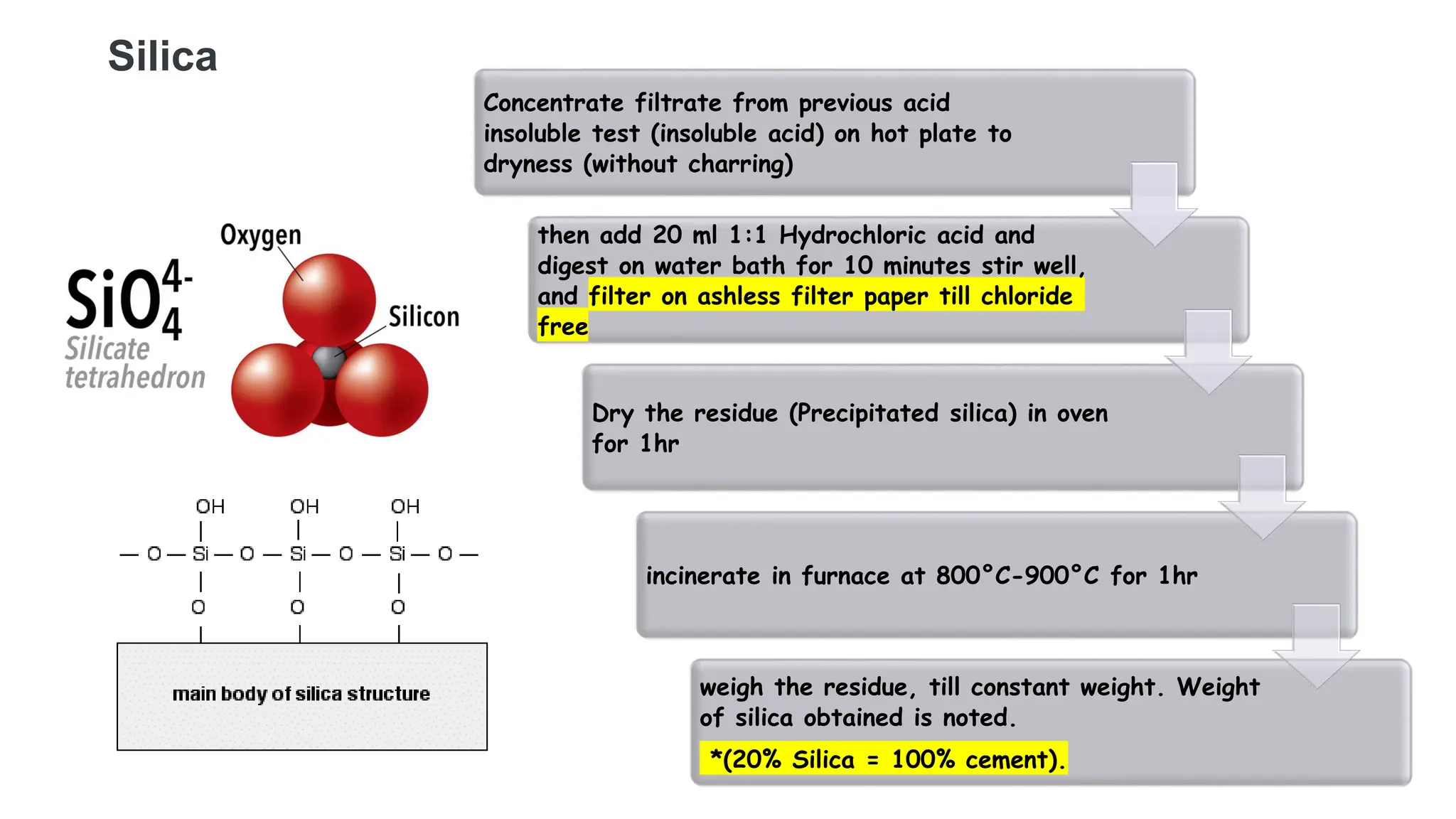
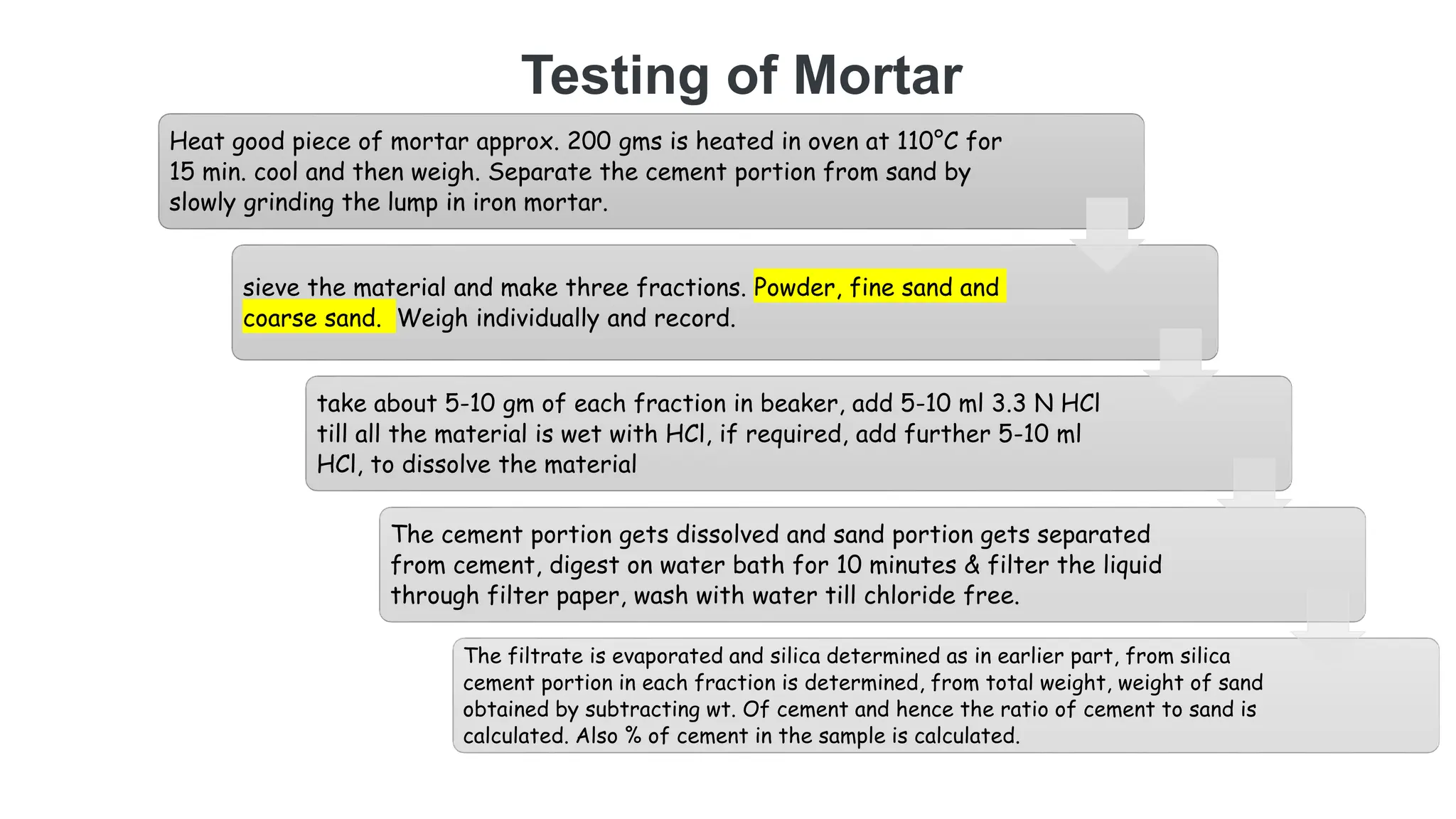
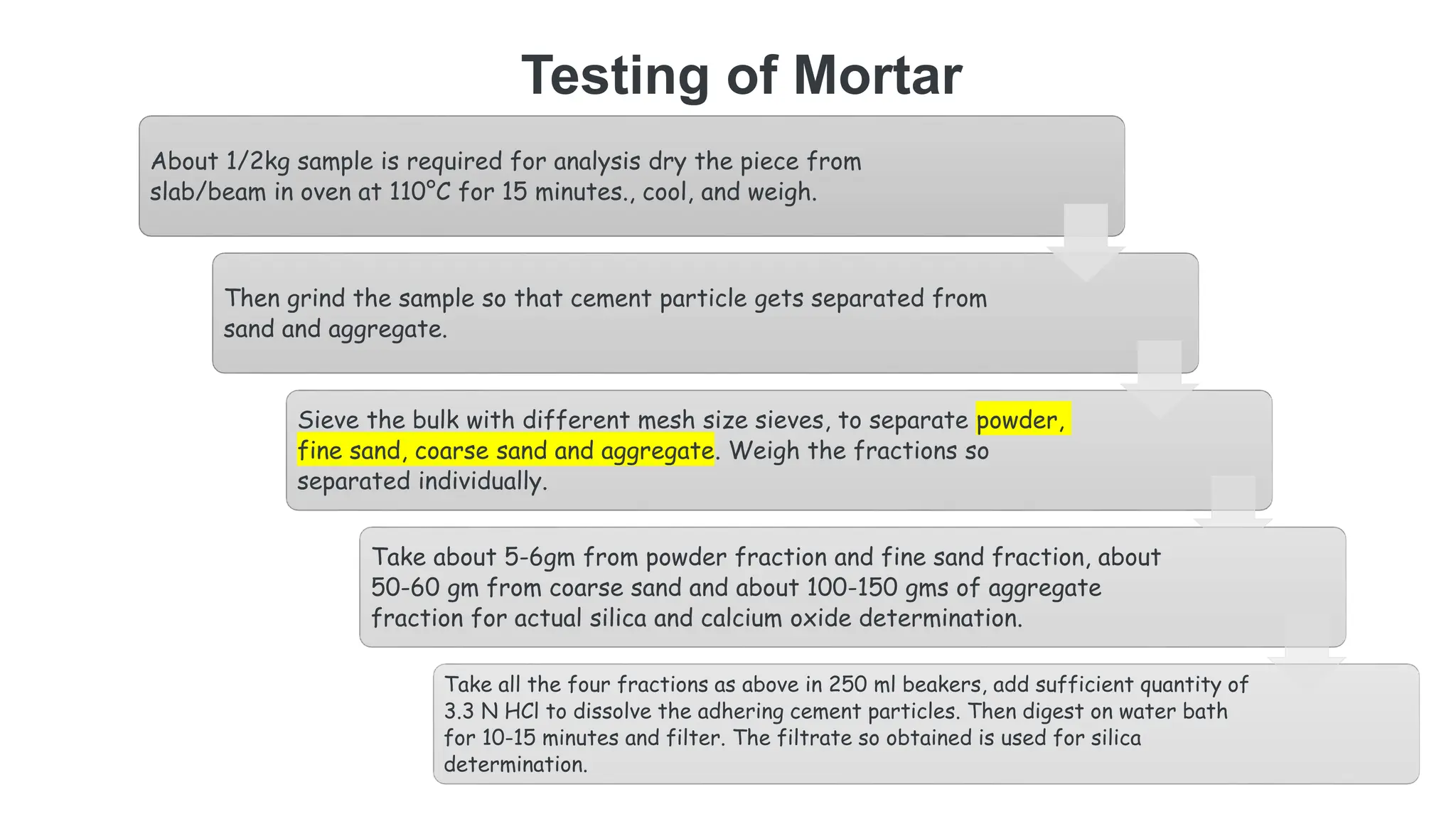
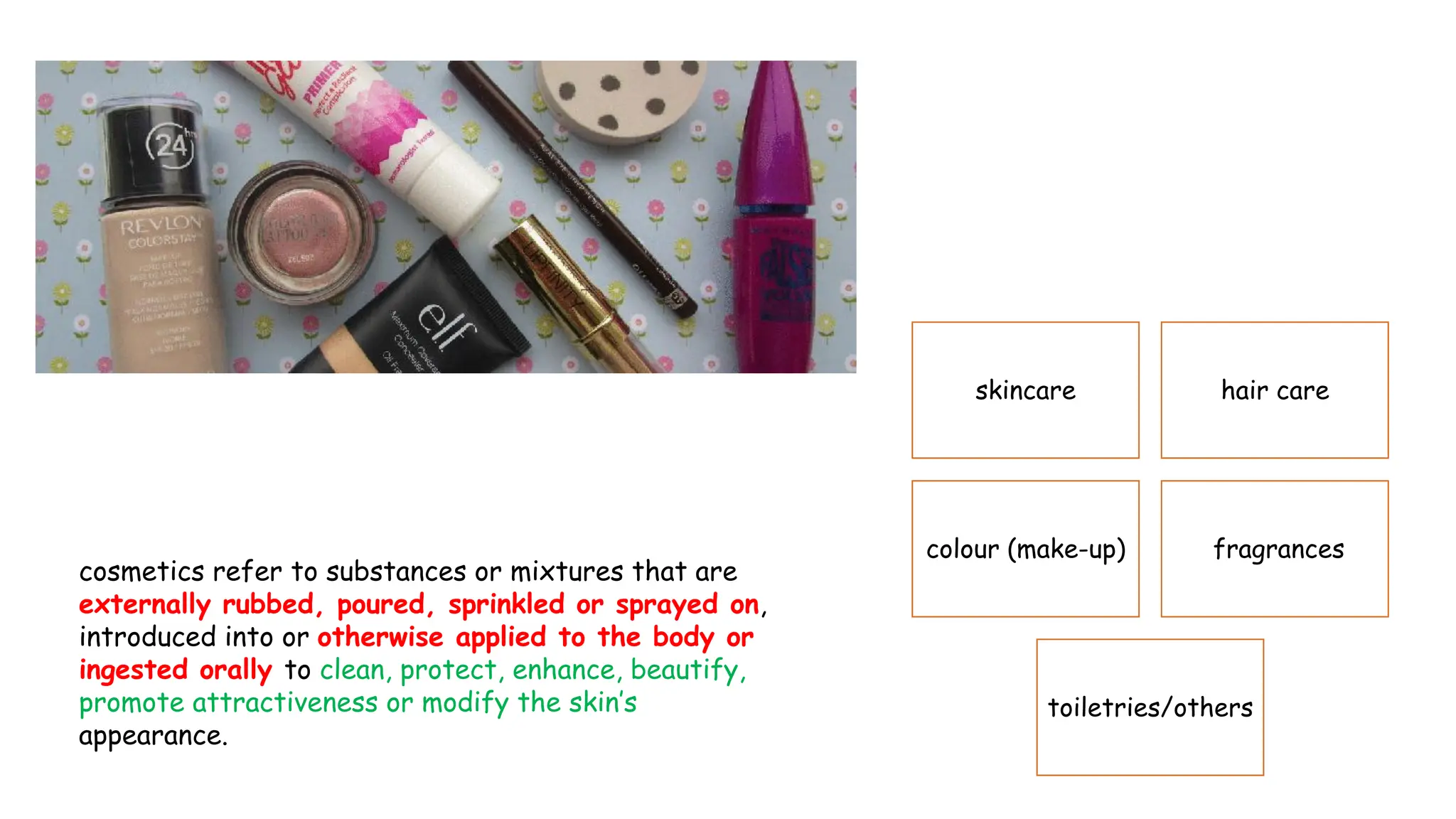
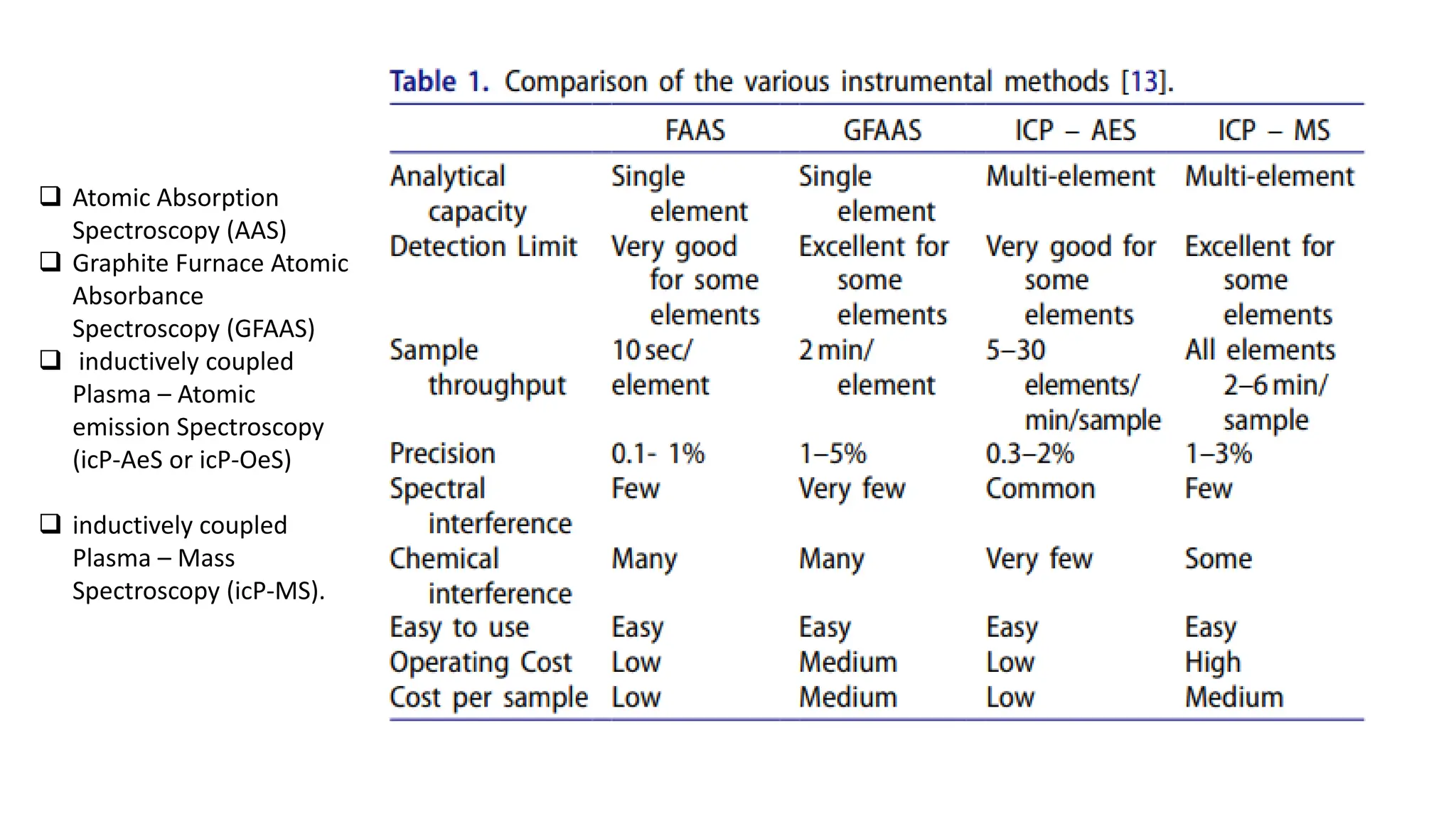
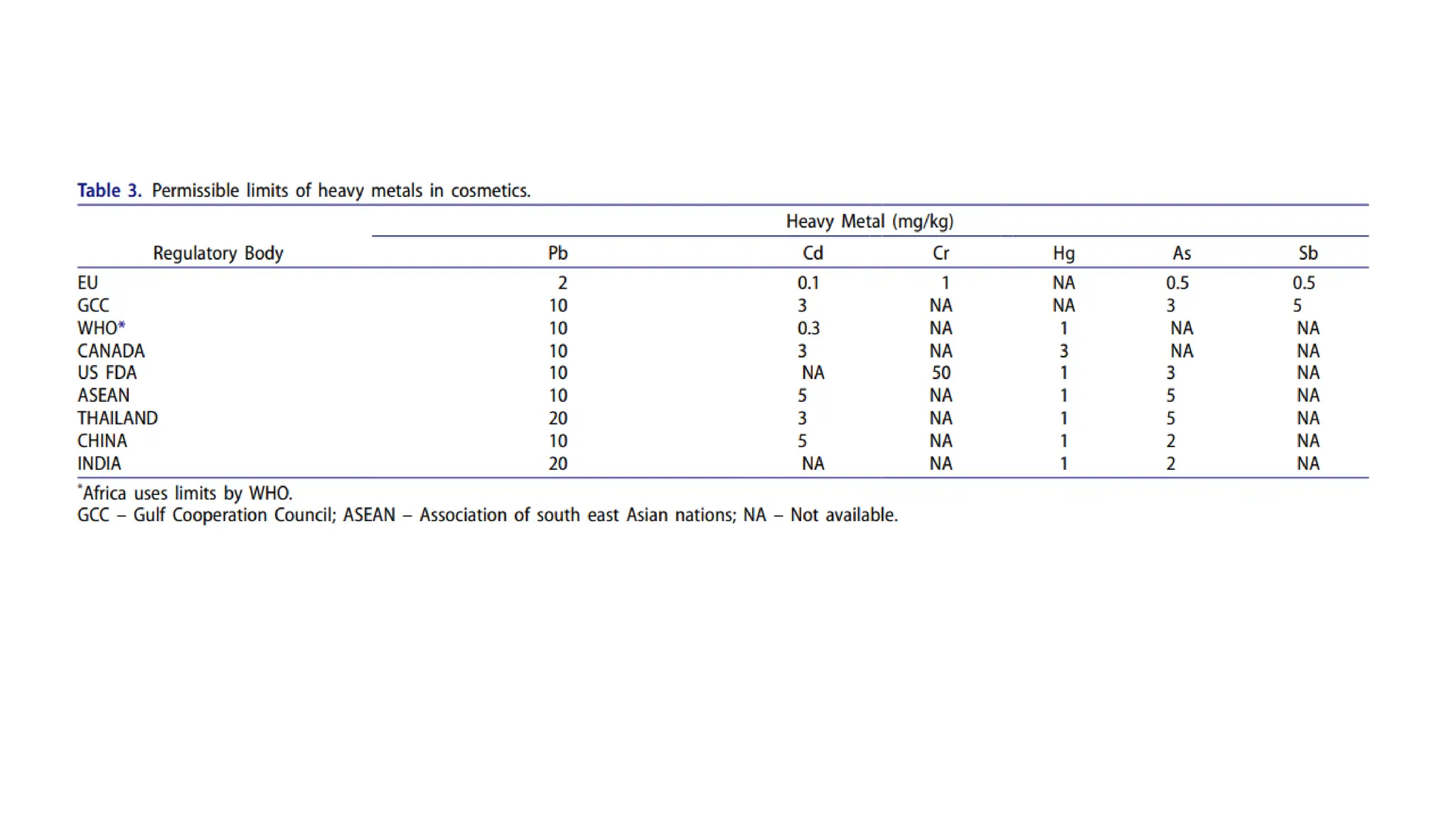
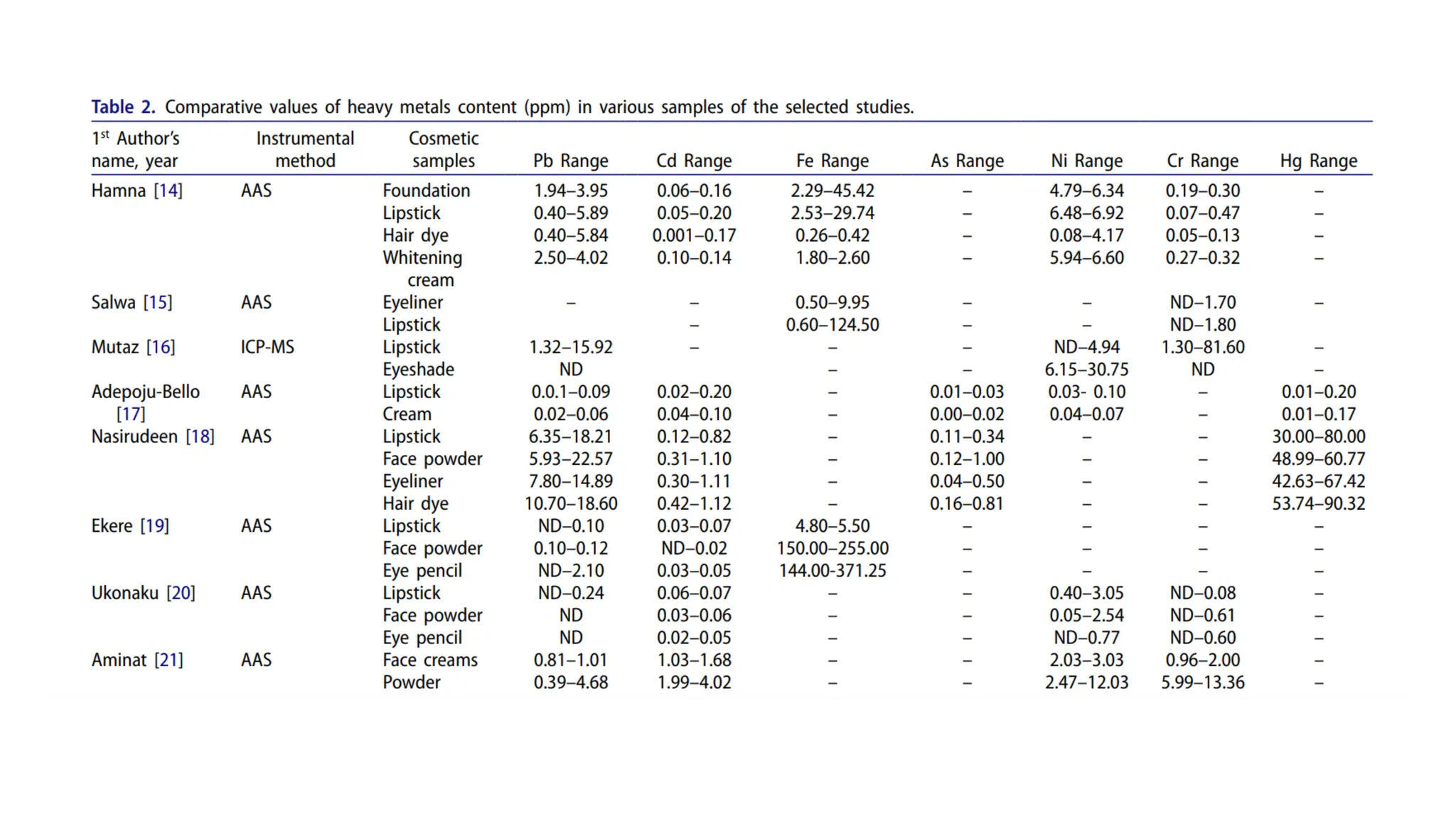
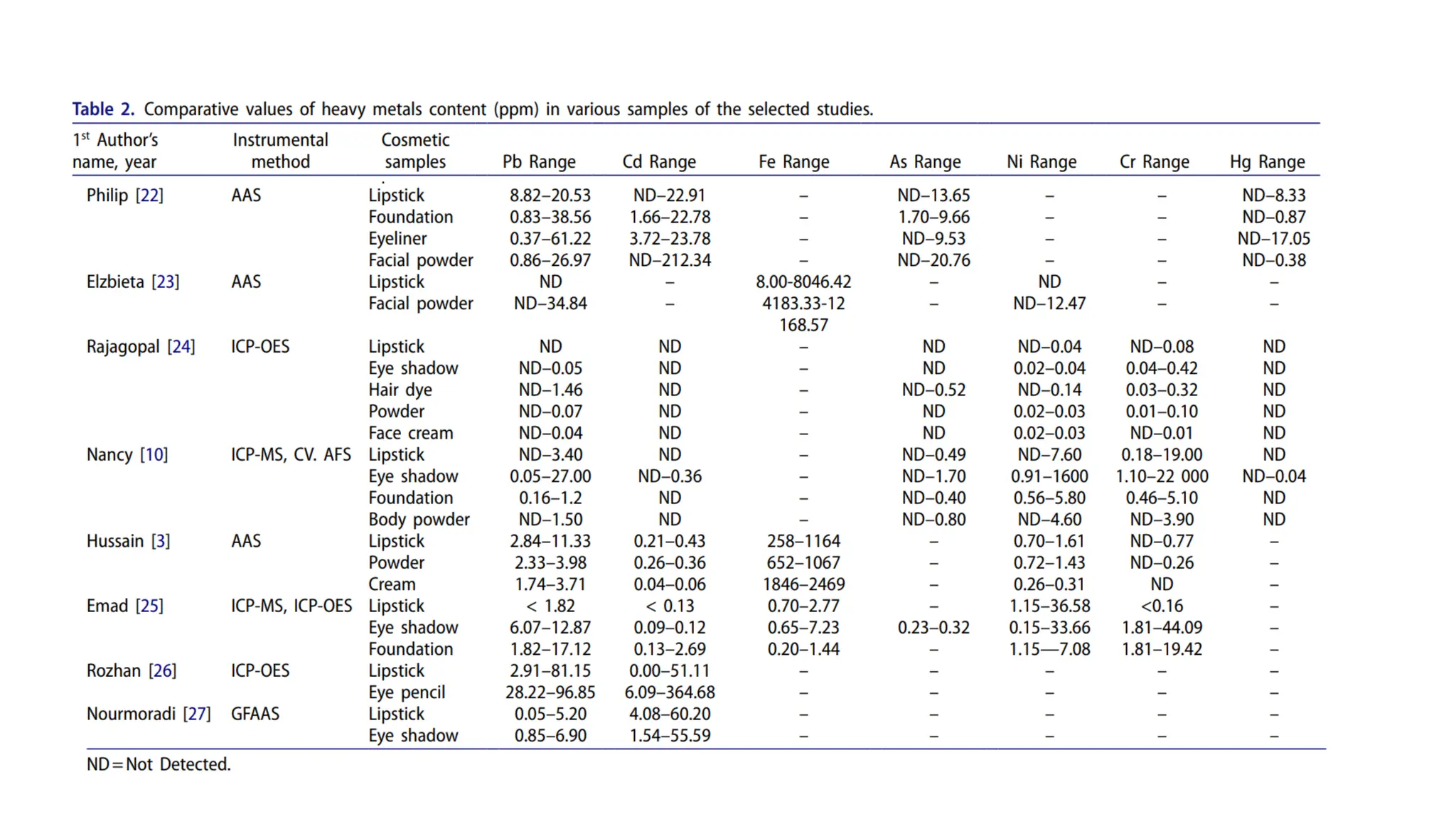
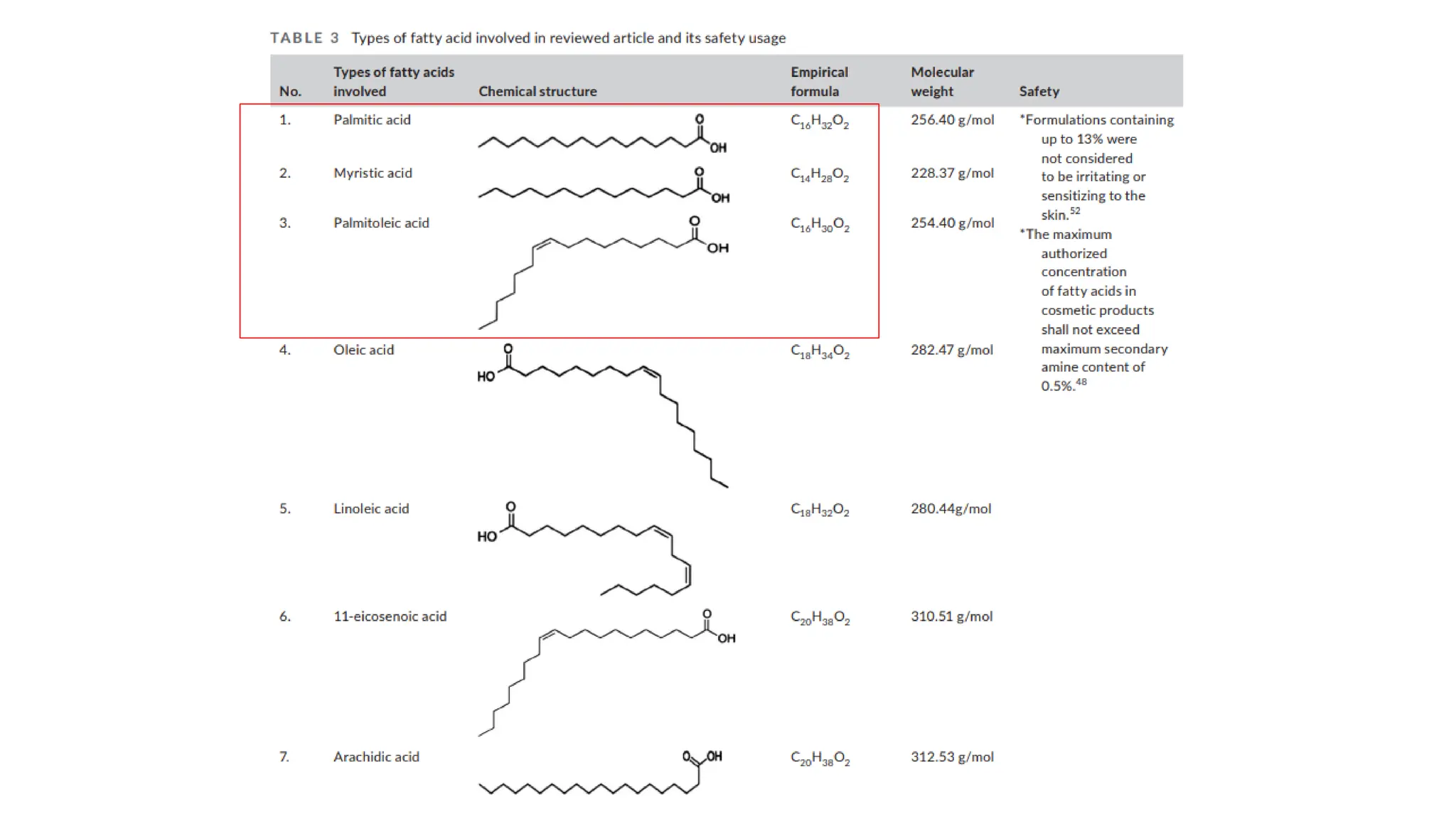
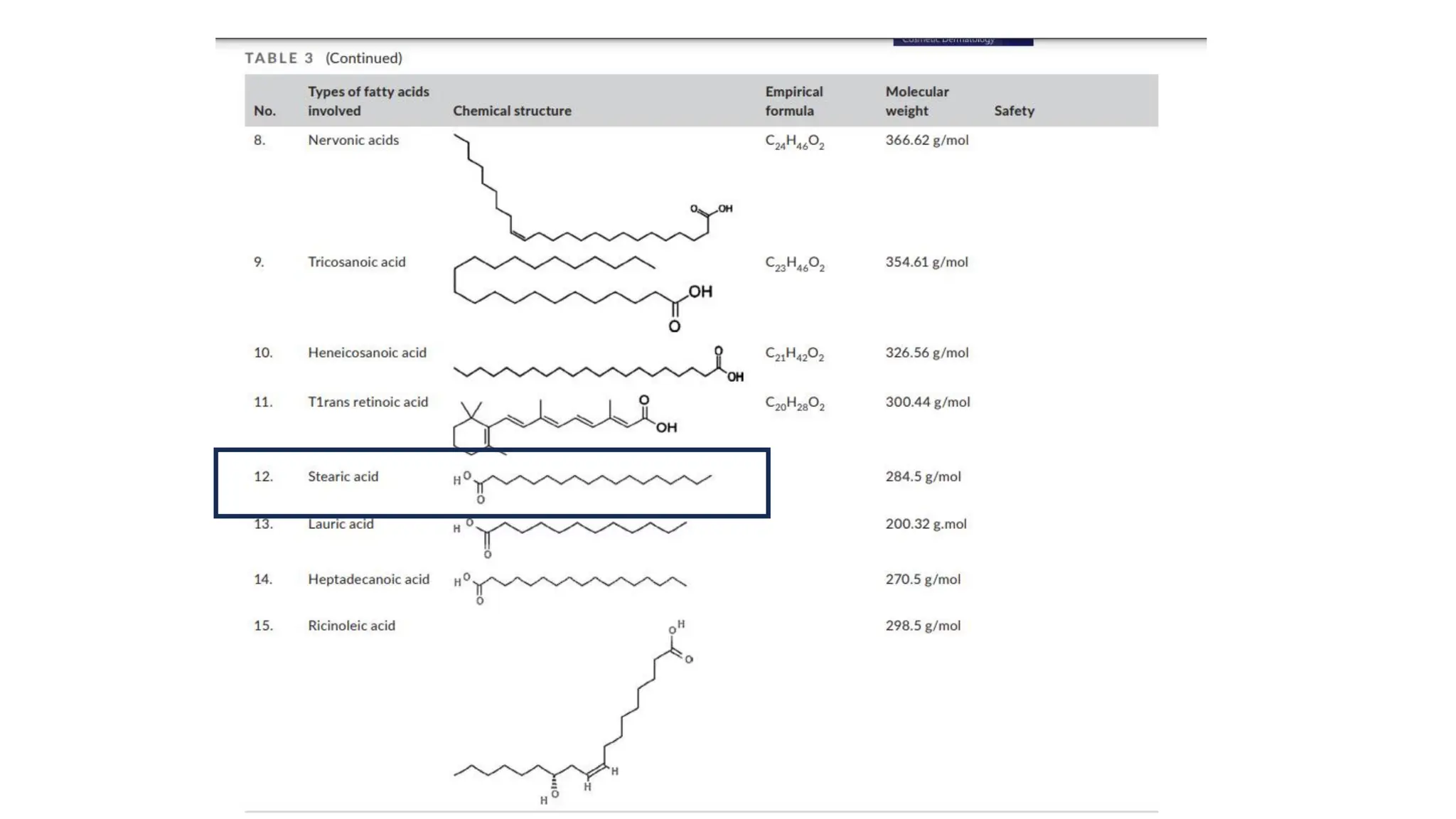
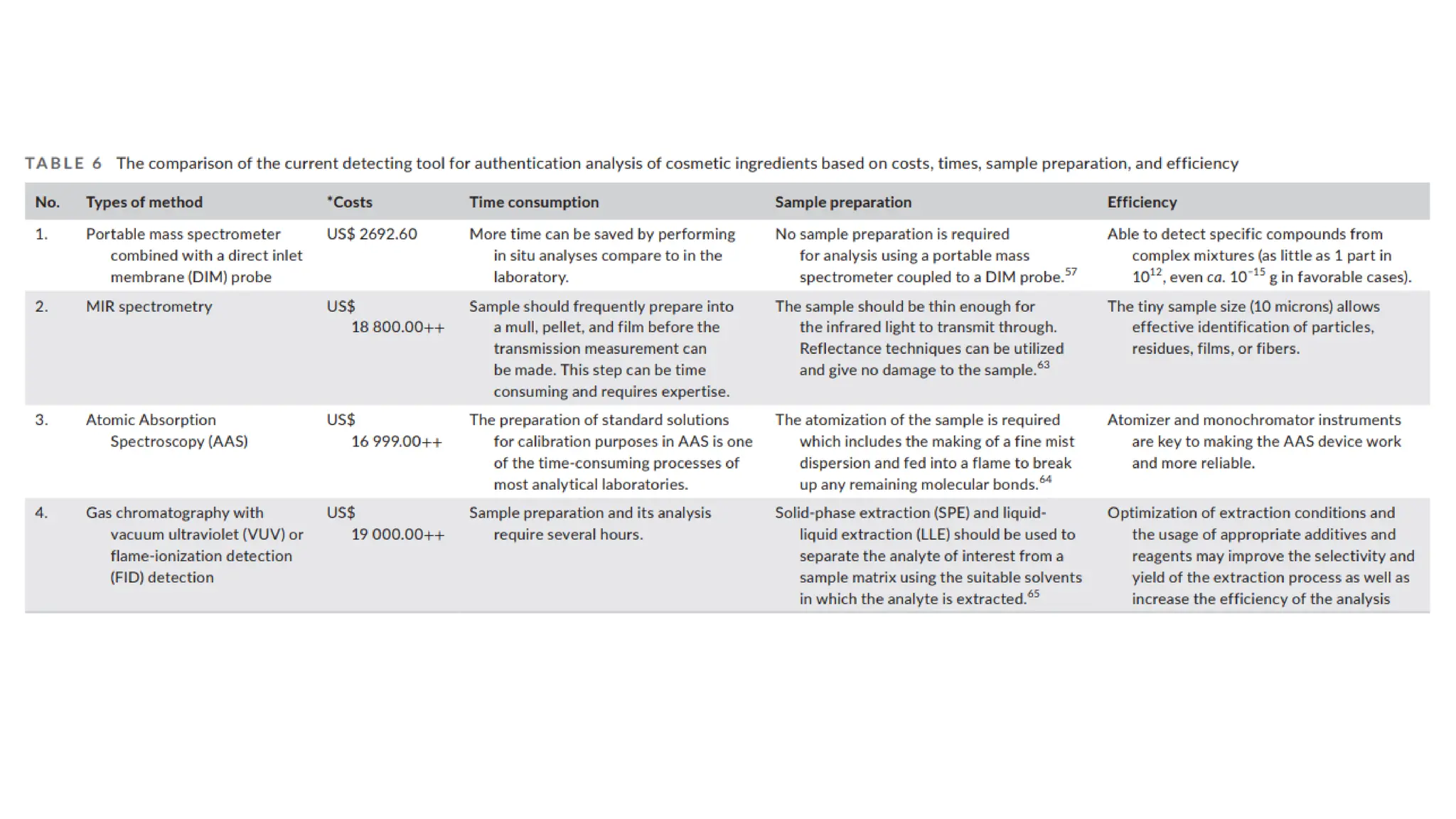
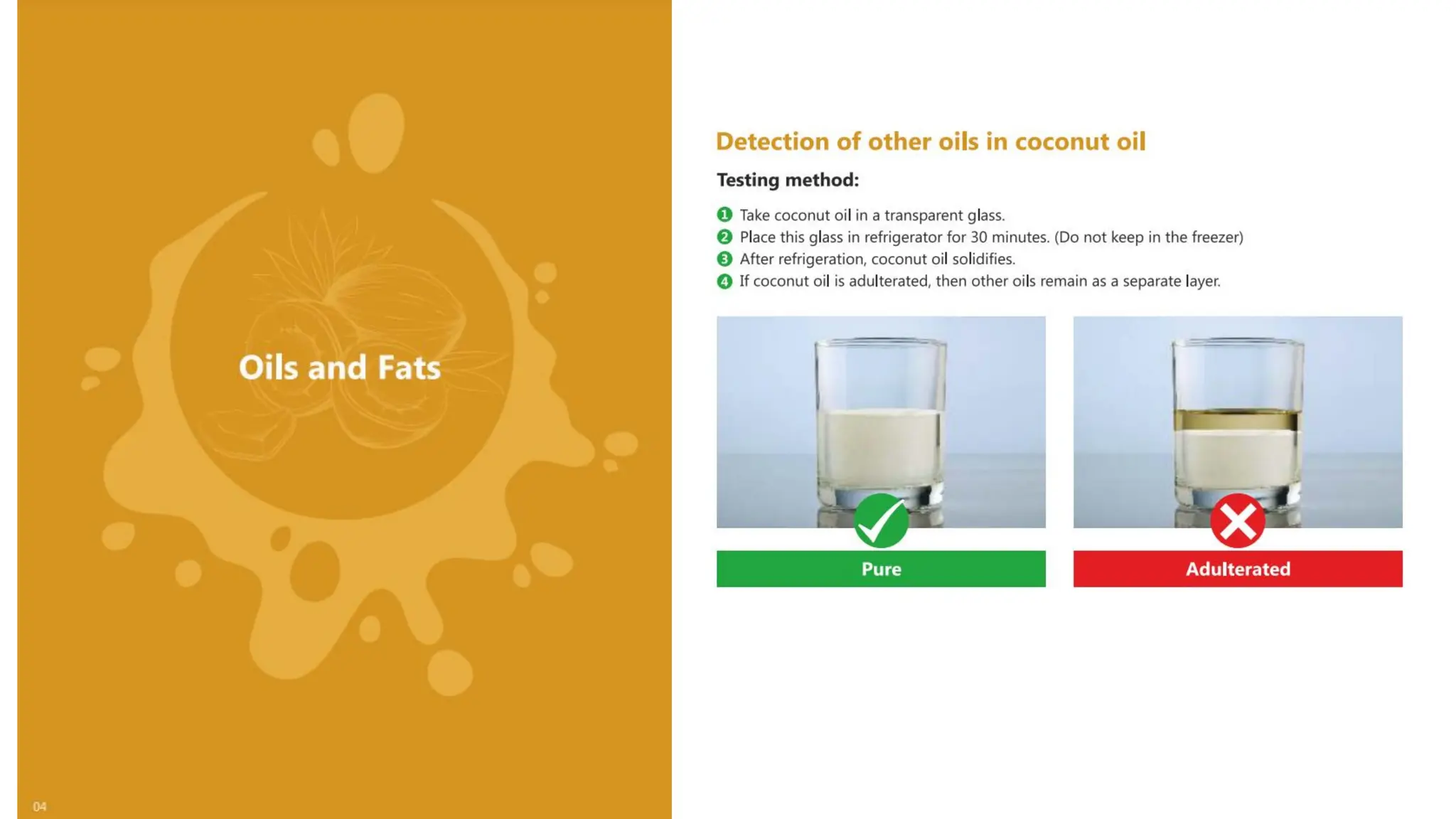
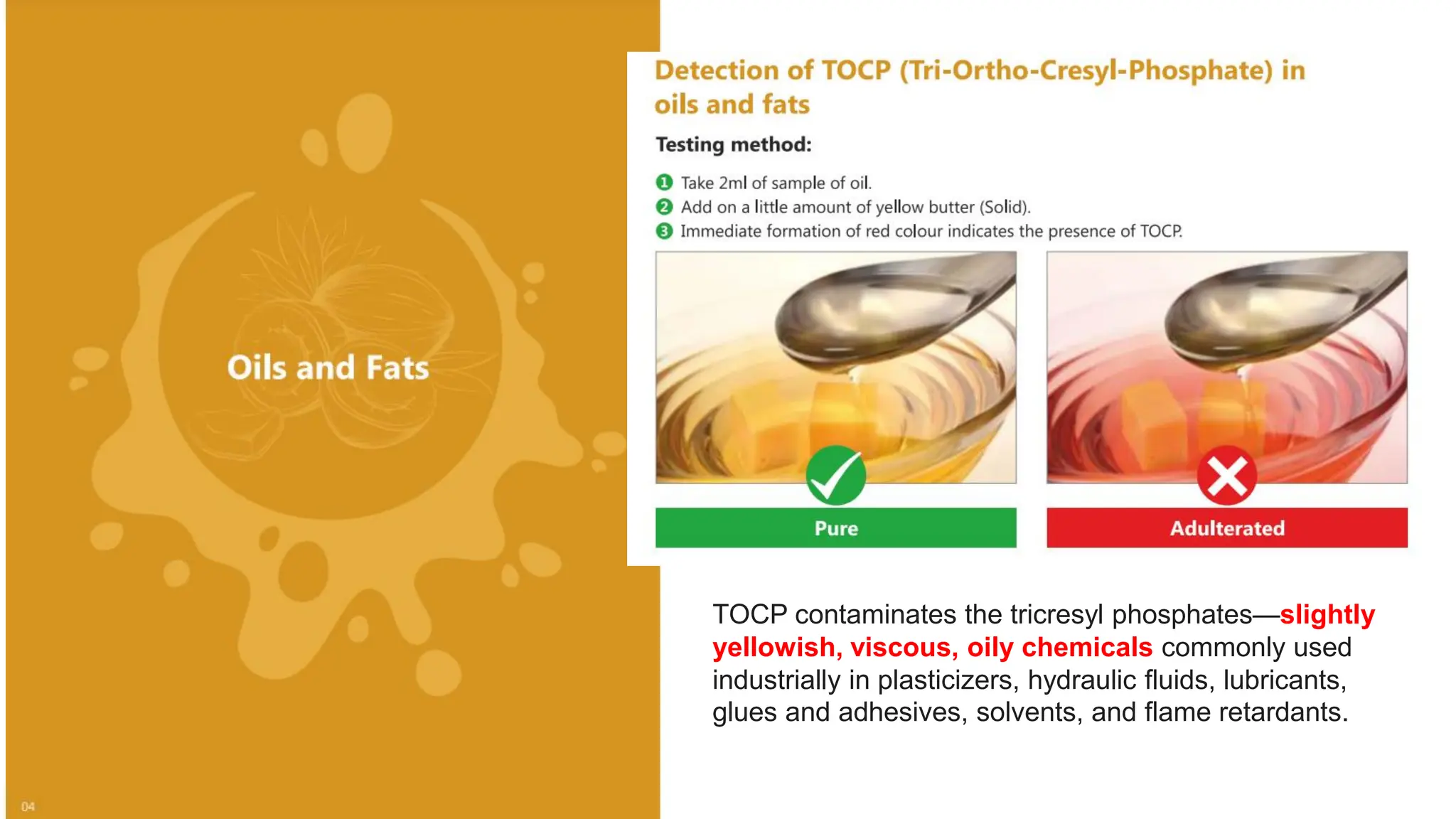
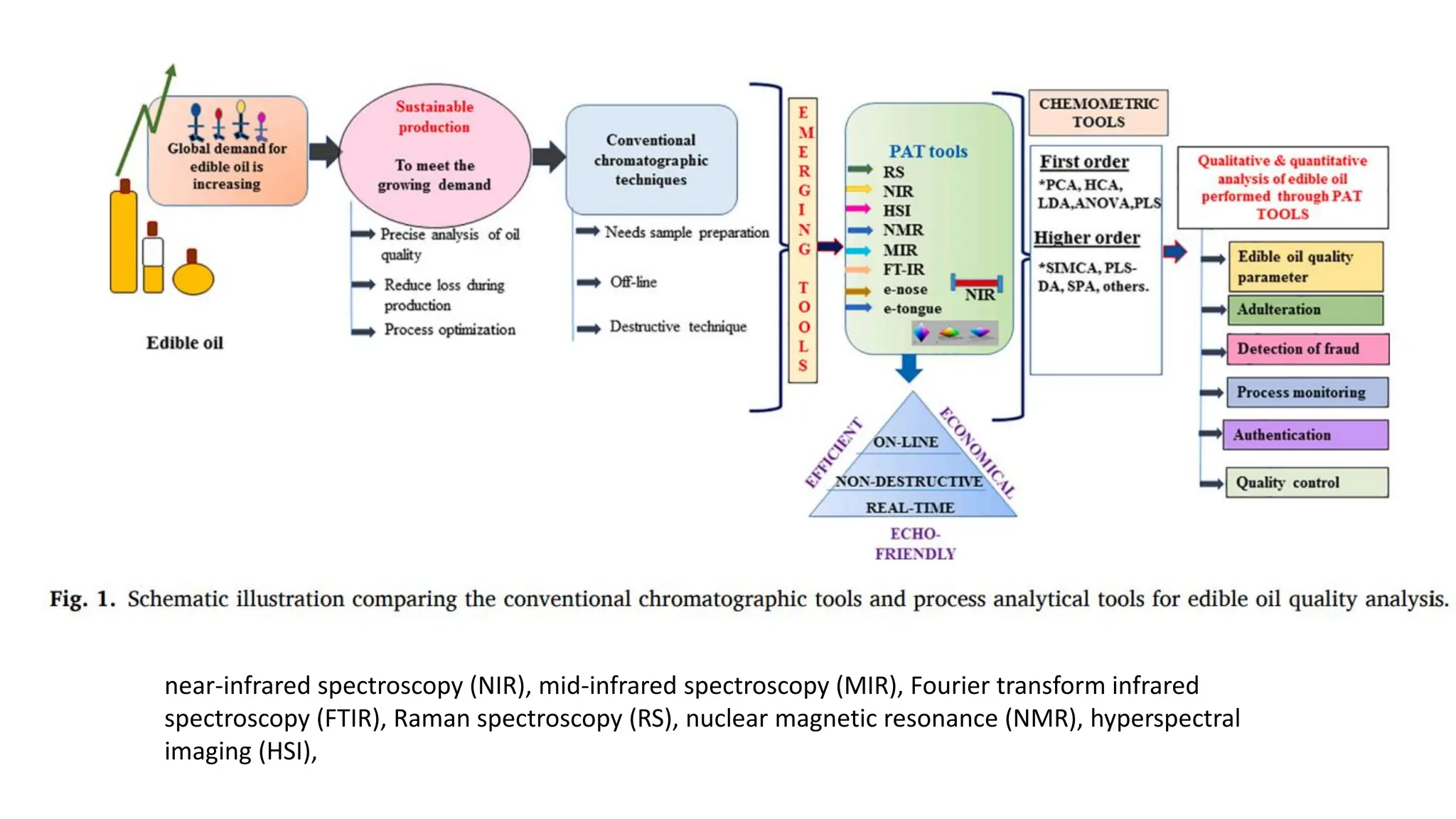
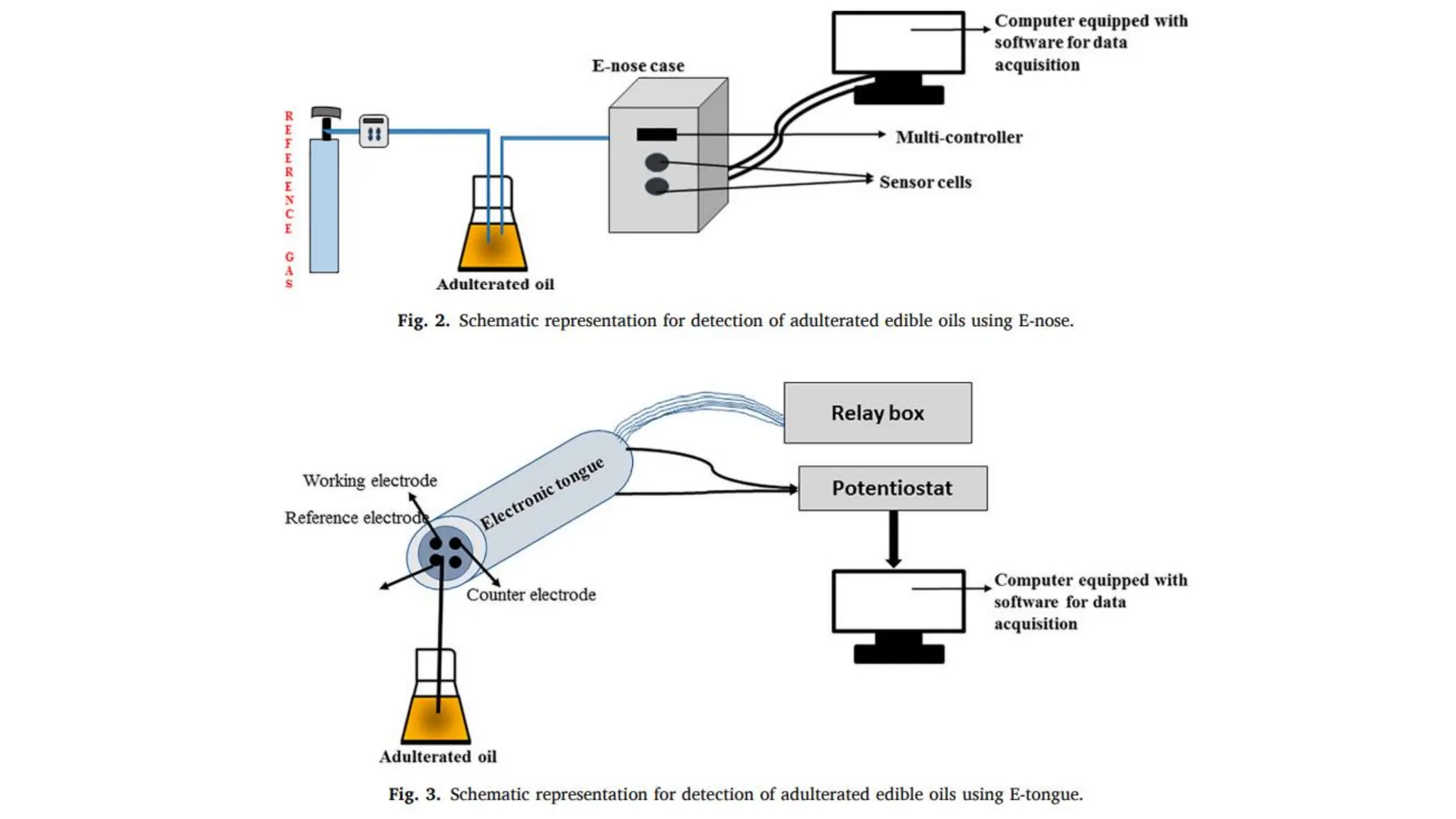
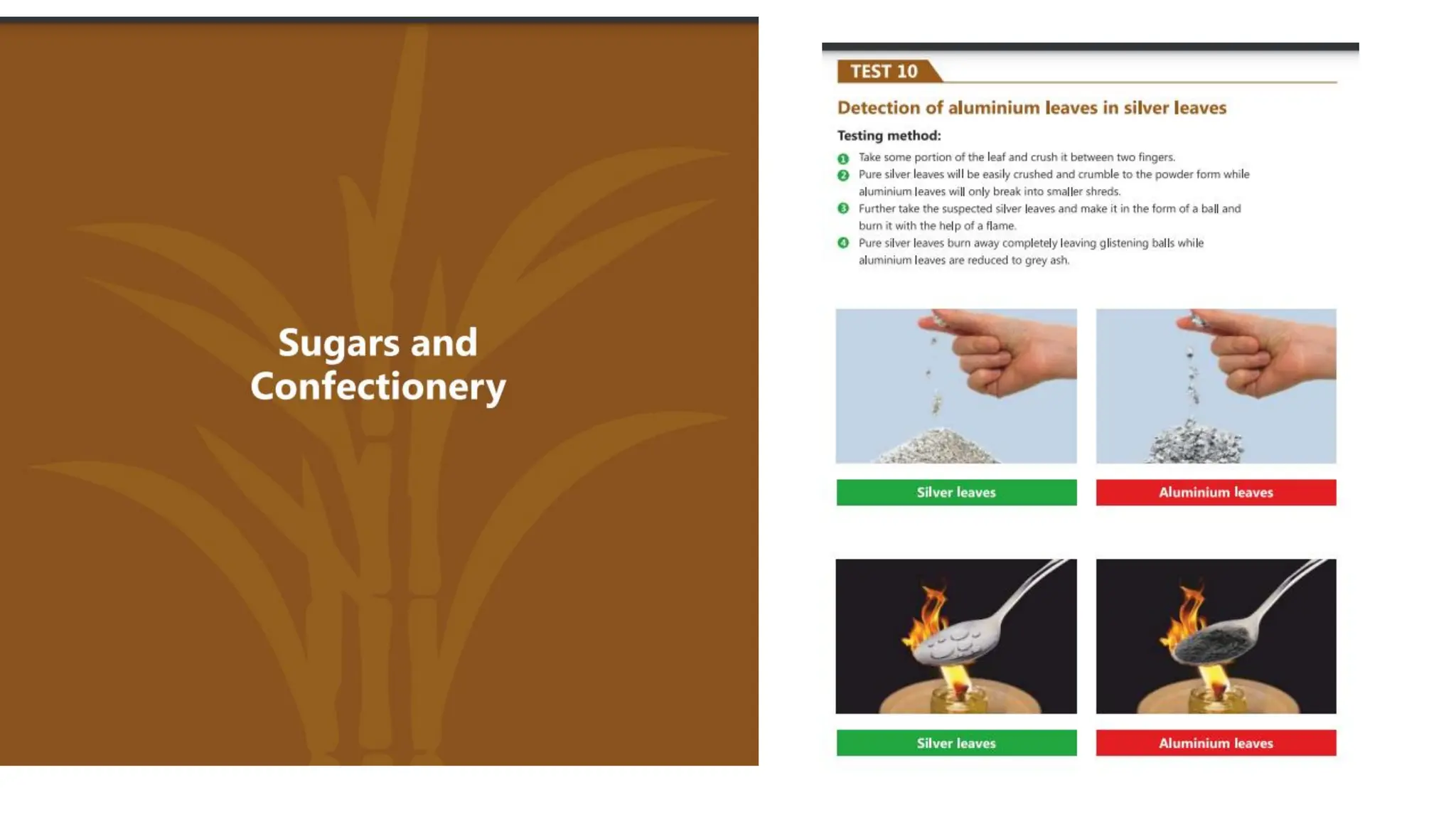
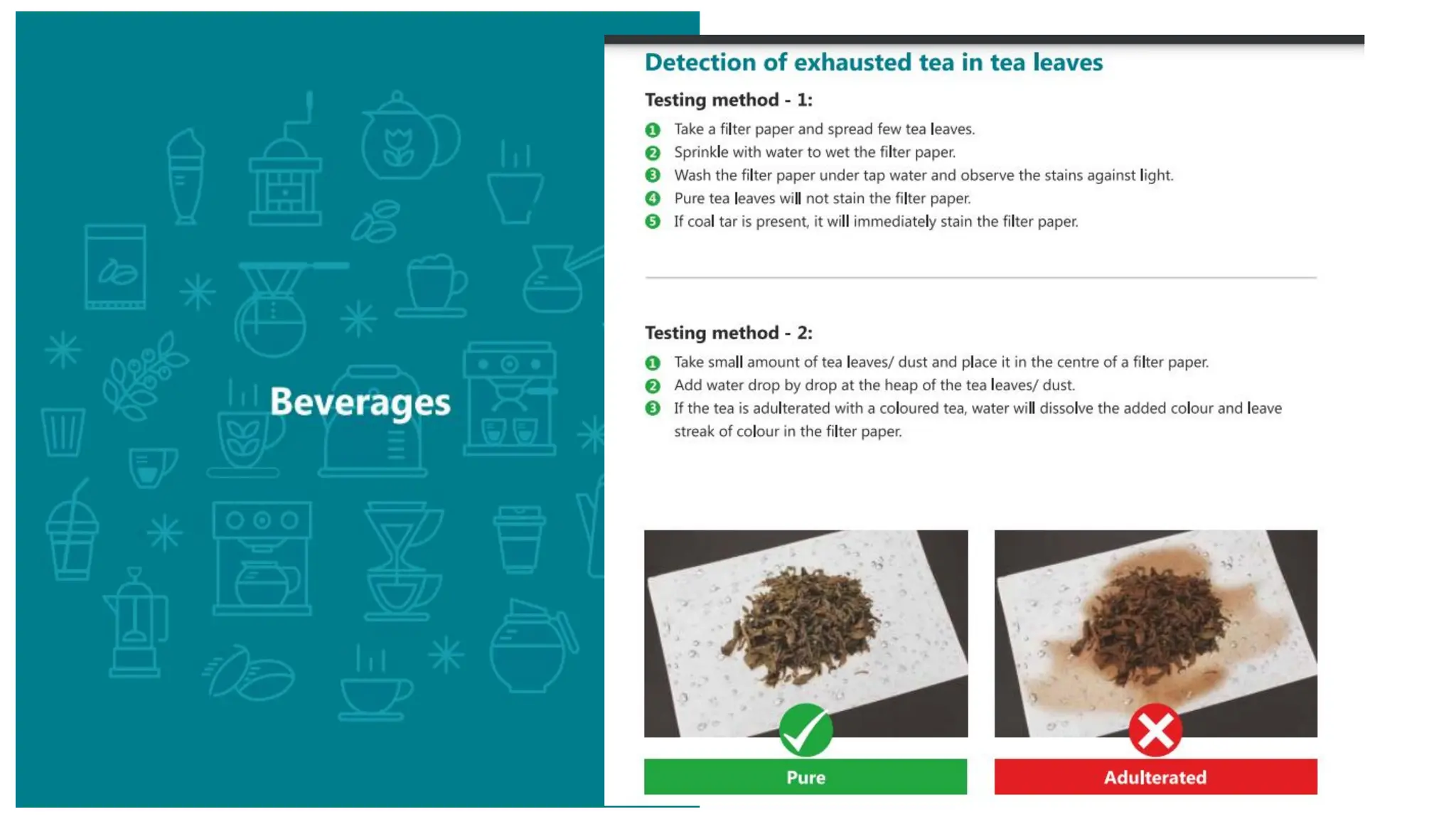
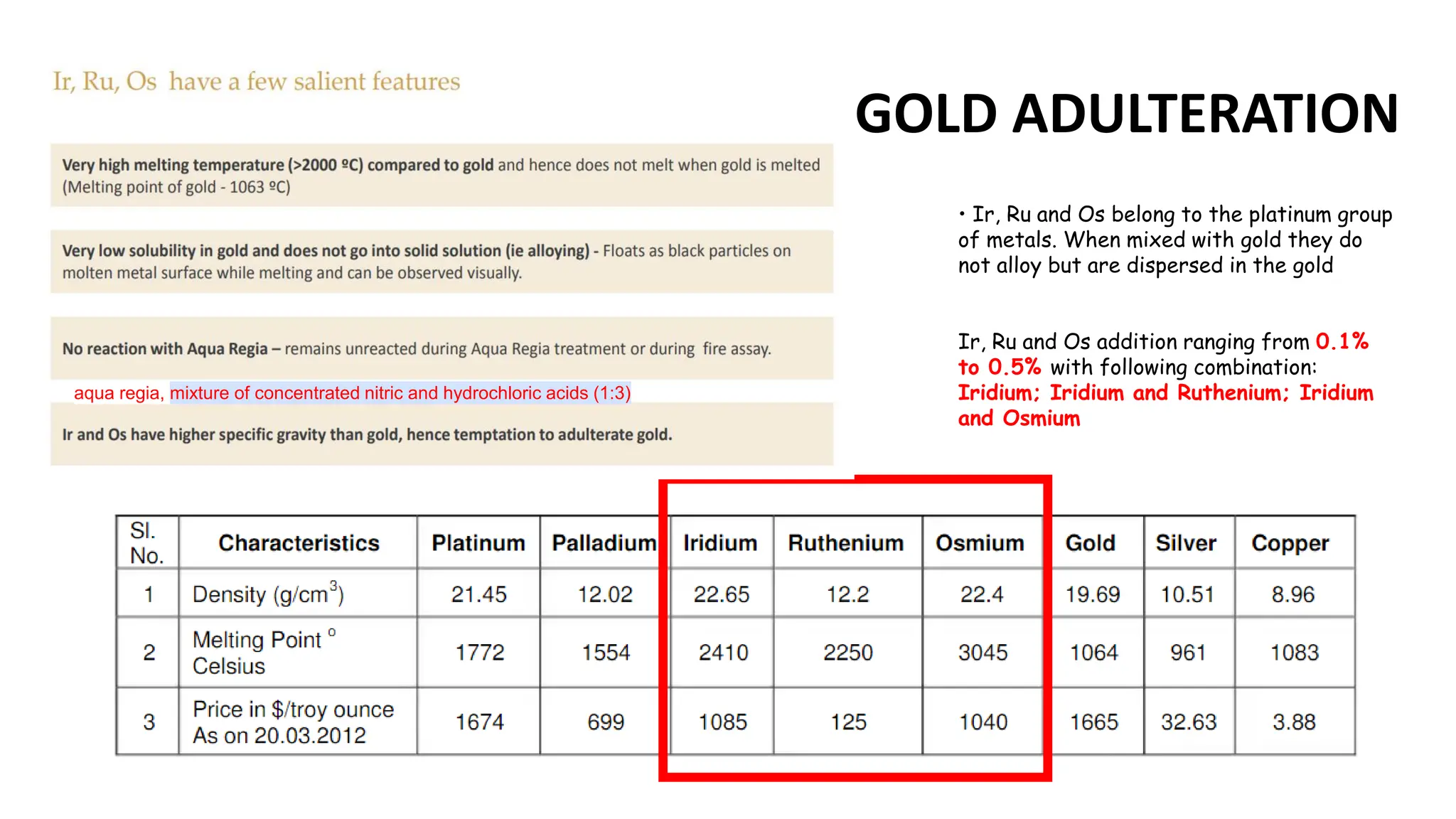
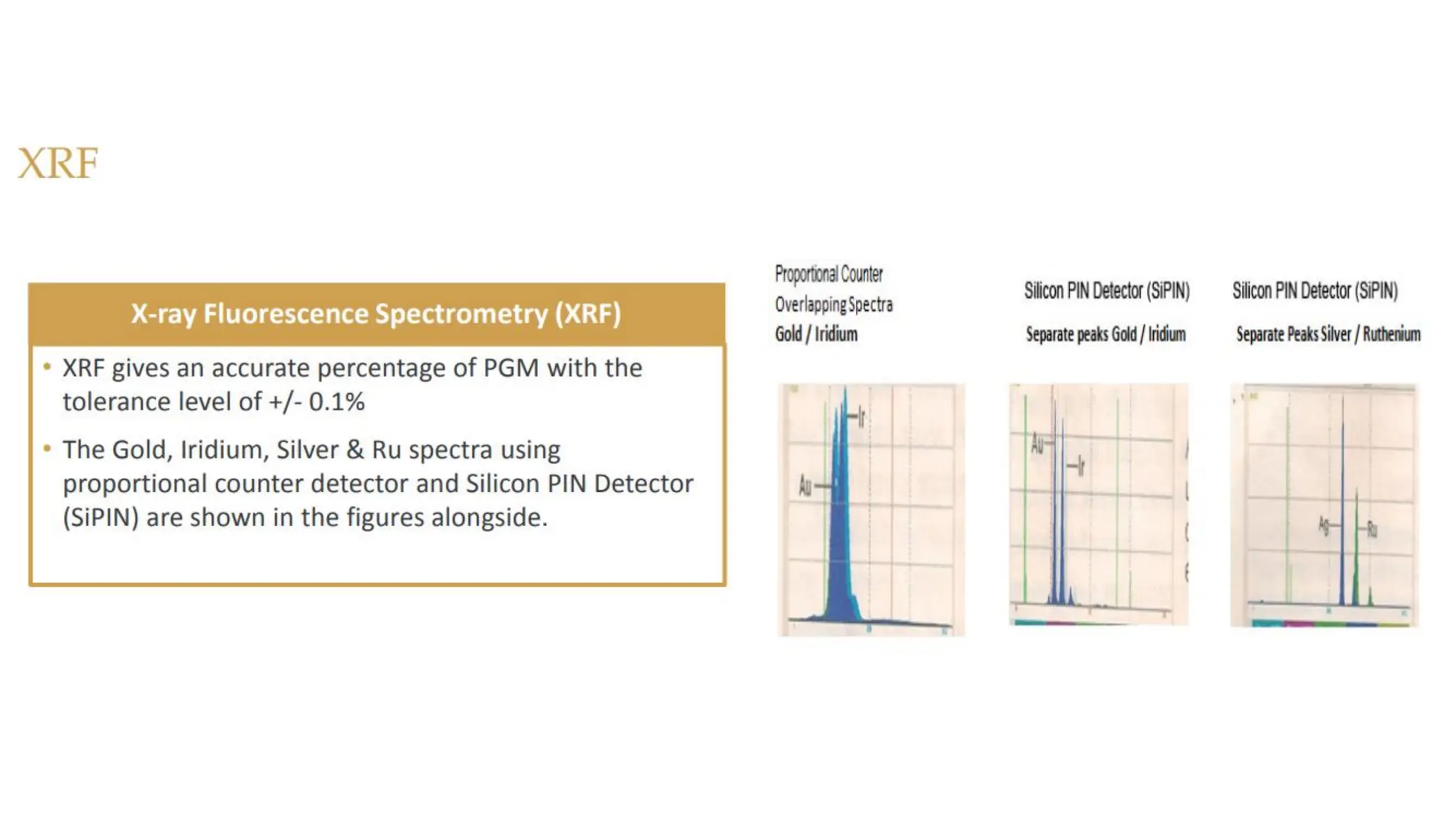
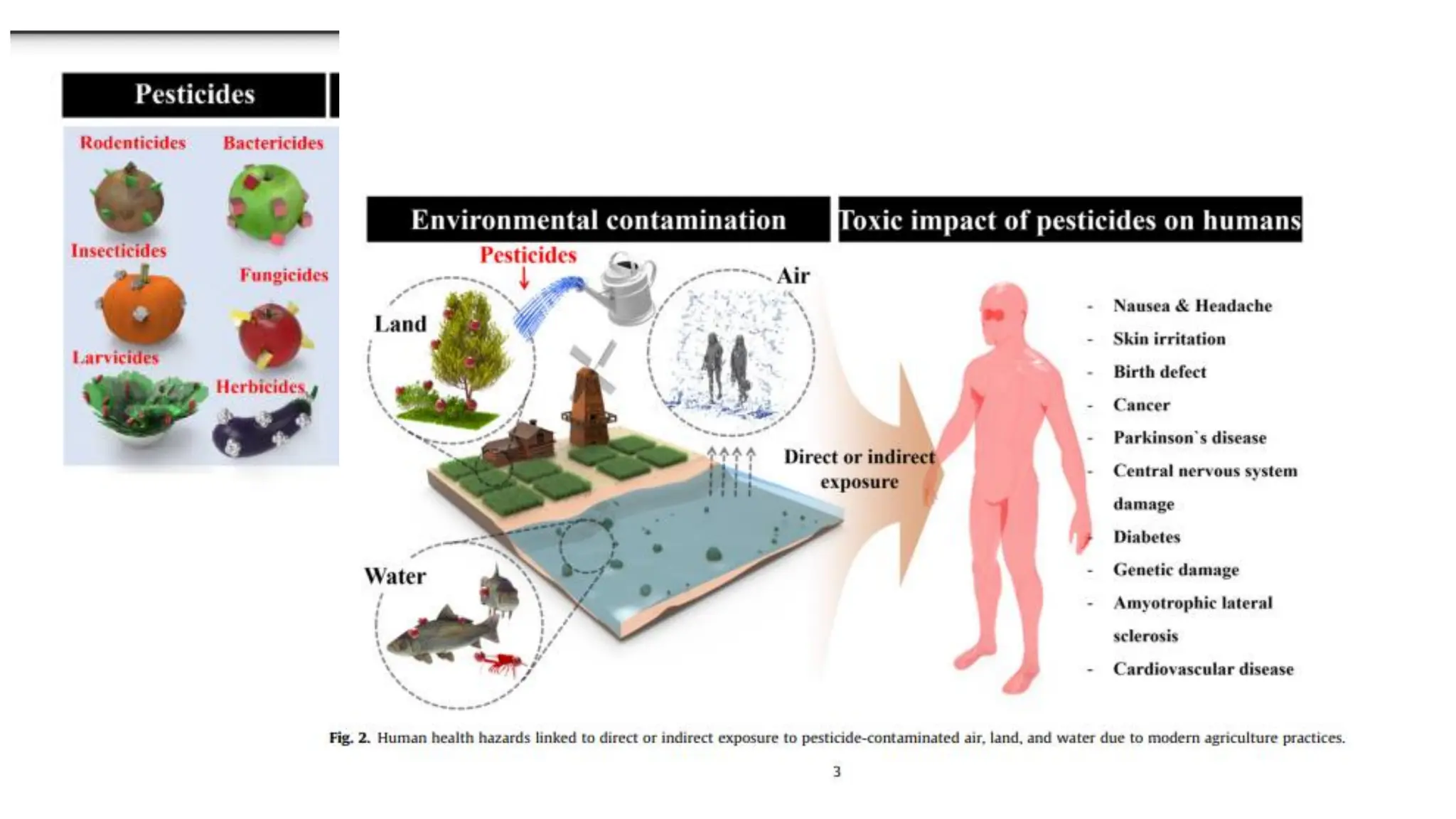
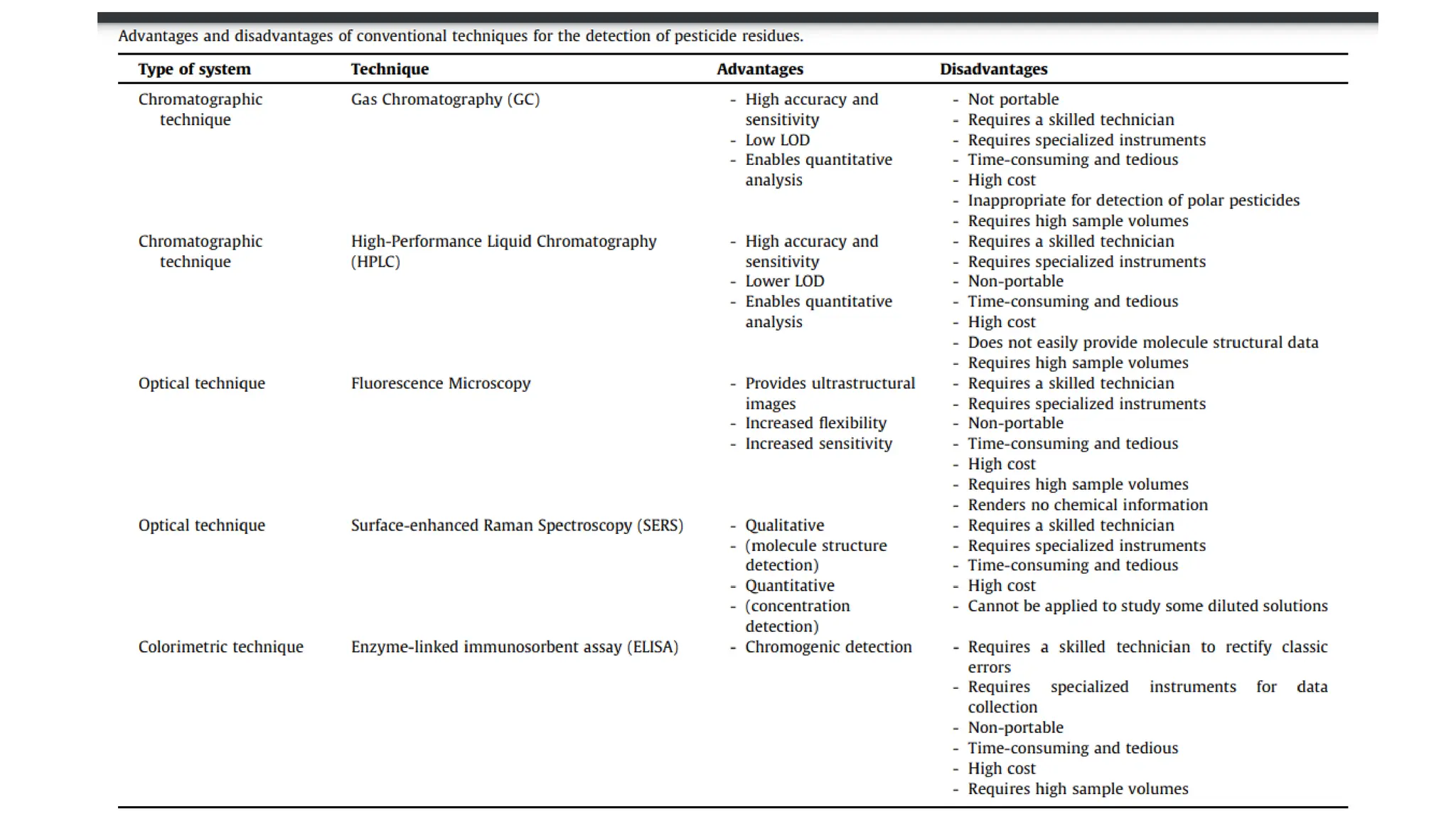
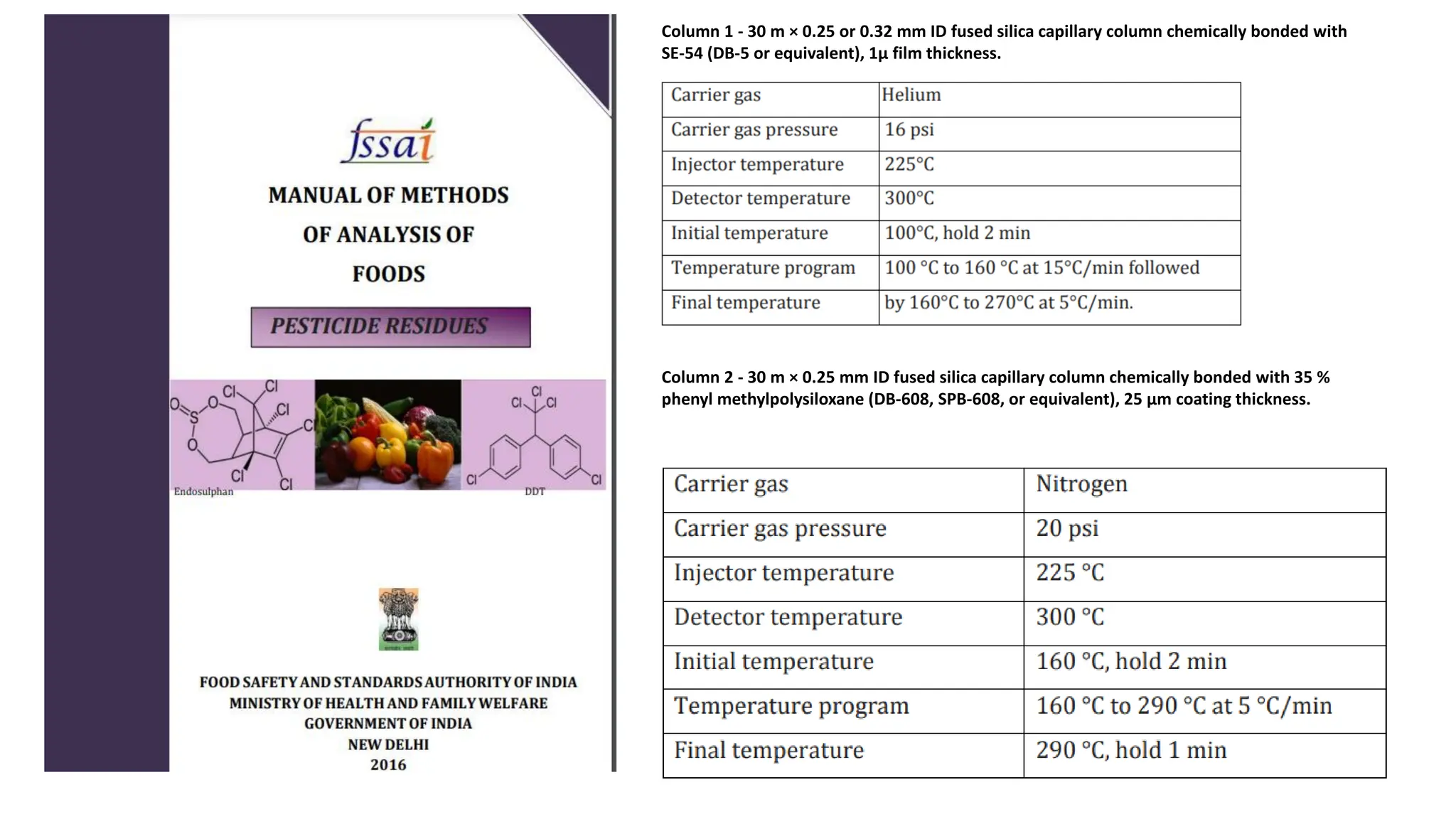
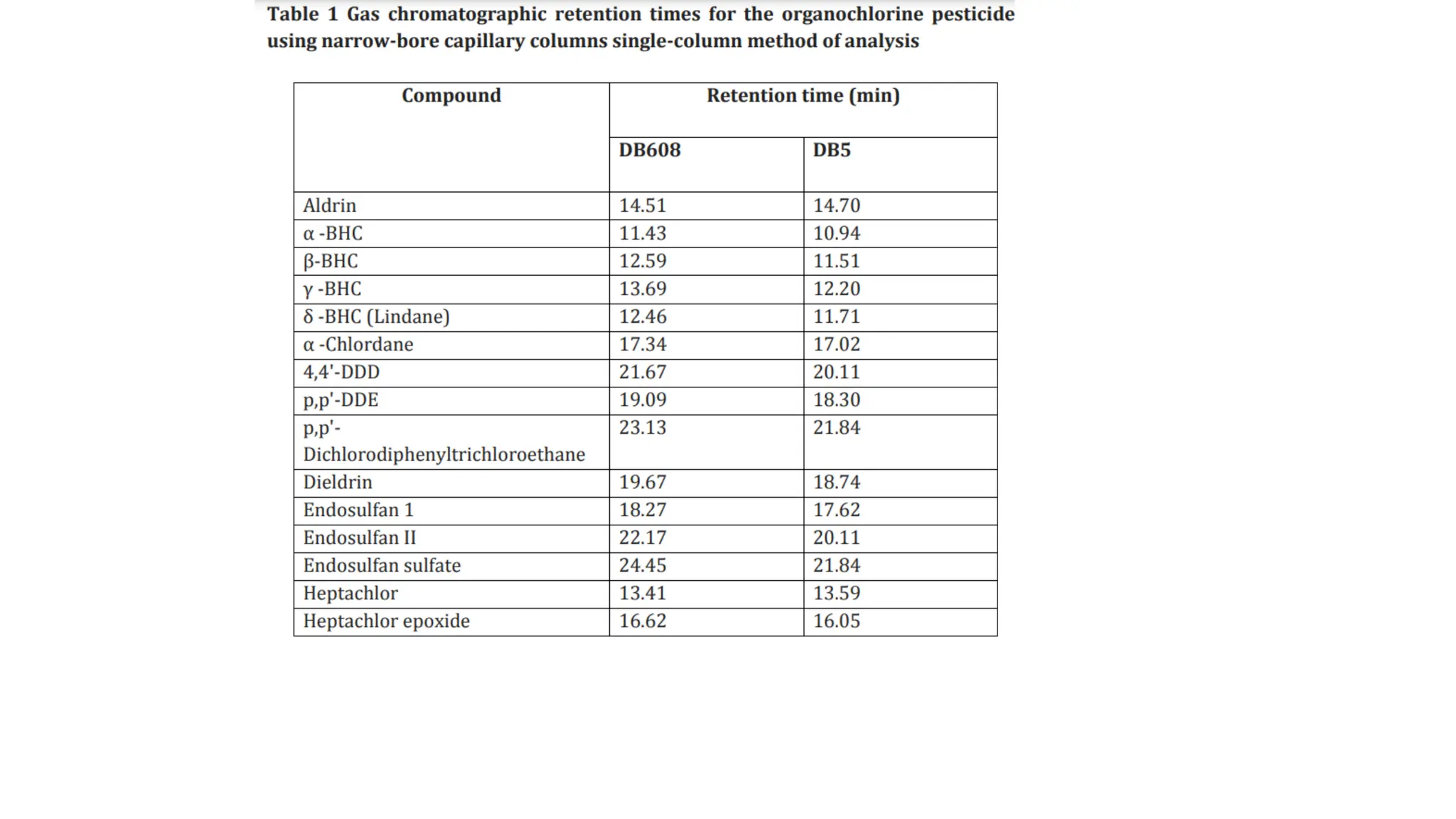
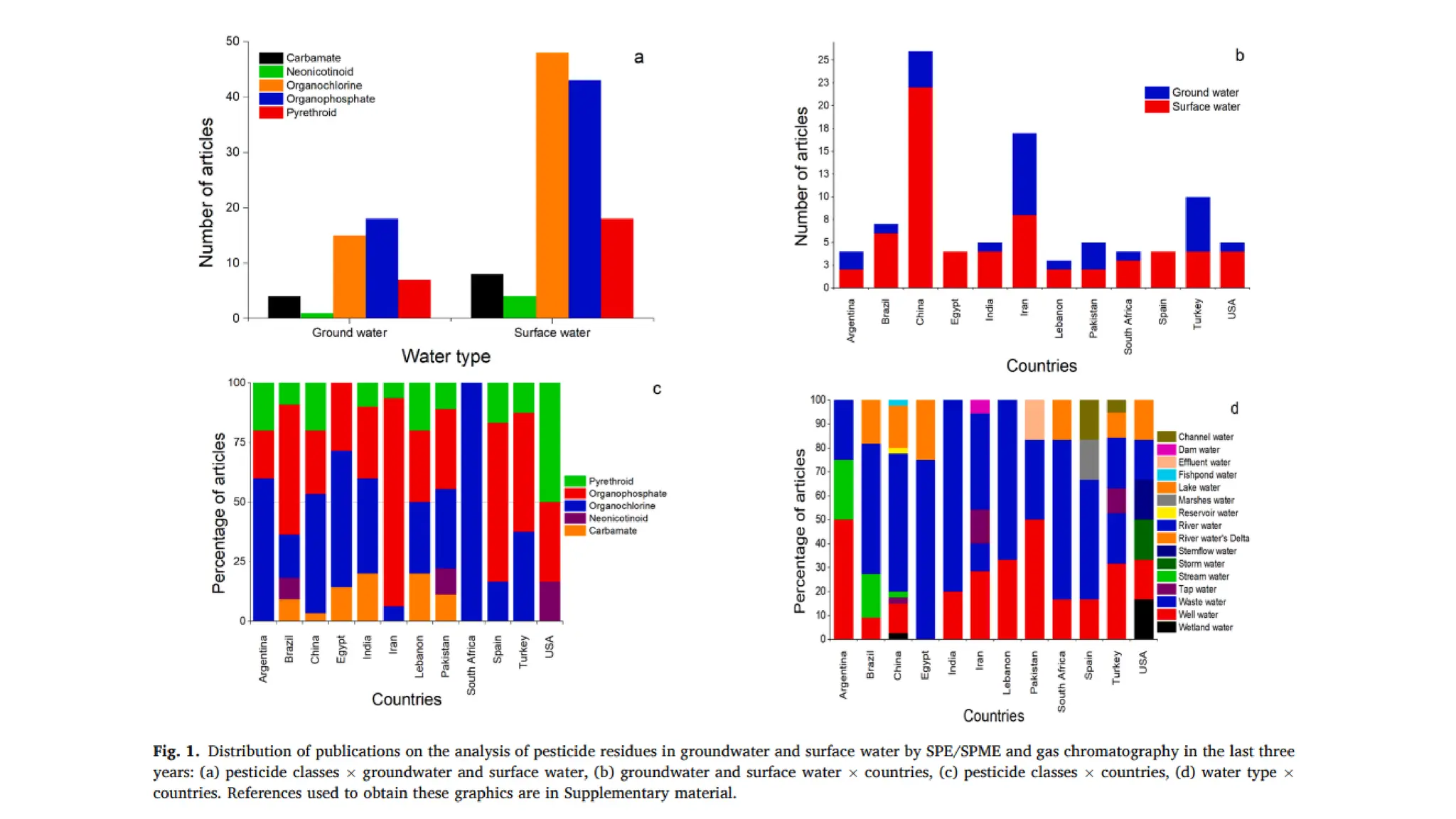
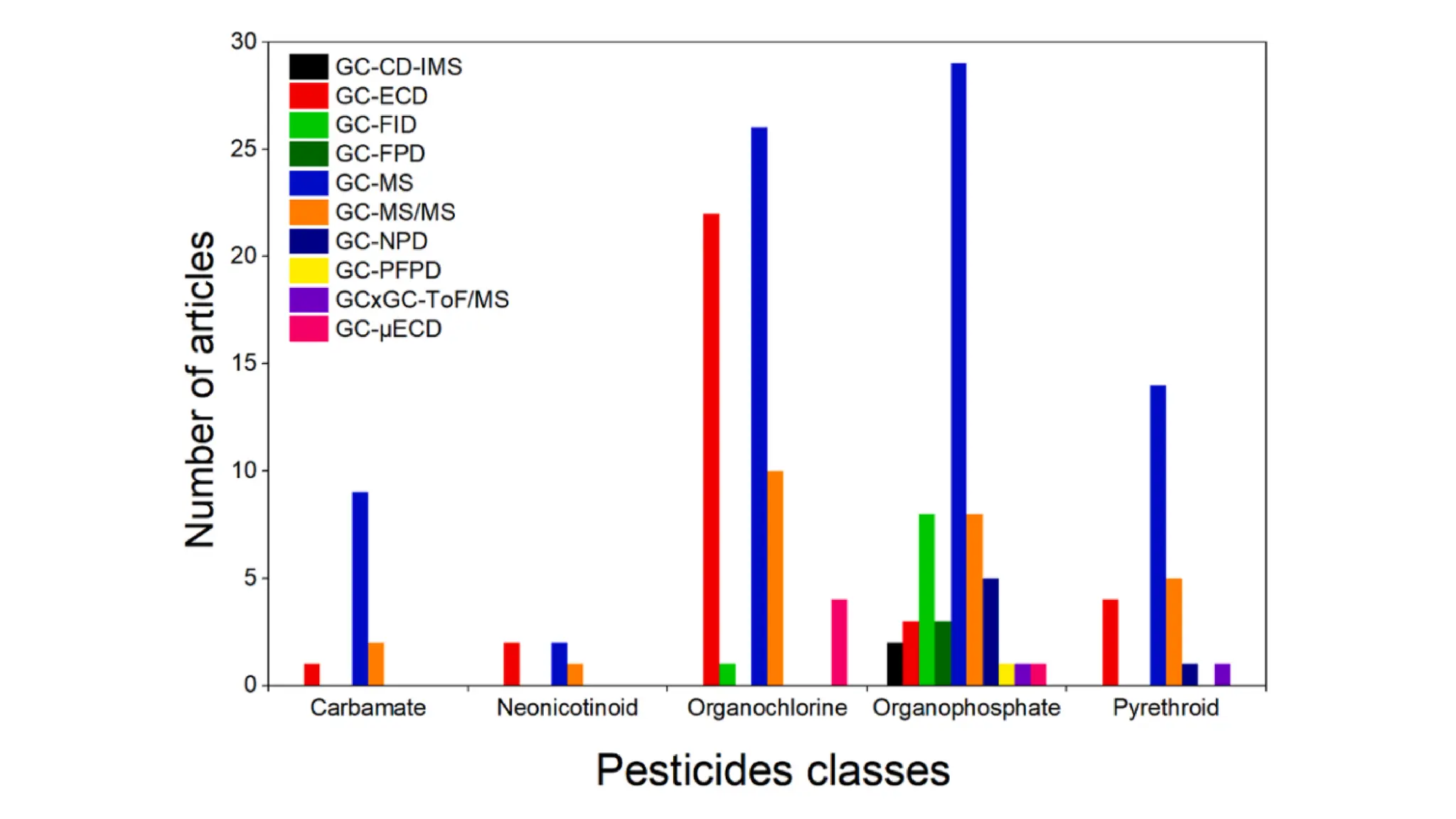
The document provides an extensive overview of forensic chemistry relevant to arson, toxicology, and analysis of adulteration in various materials. It details methodologies for sampling, testing, and analysis of substances like cement, cosmetics, and edible oils, utilizing techniques such as gas chromatography and titration. Additionally, it covers detection of contaminants and adulterants, emphasizing the importance of analytical methods in forensic investigations.