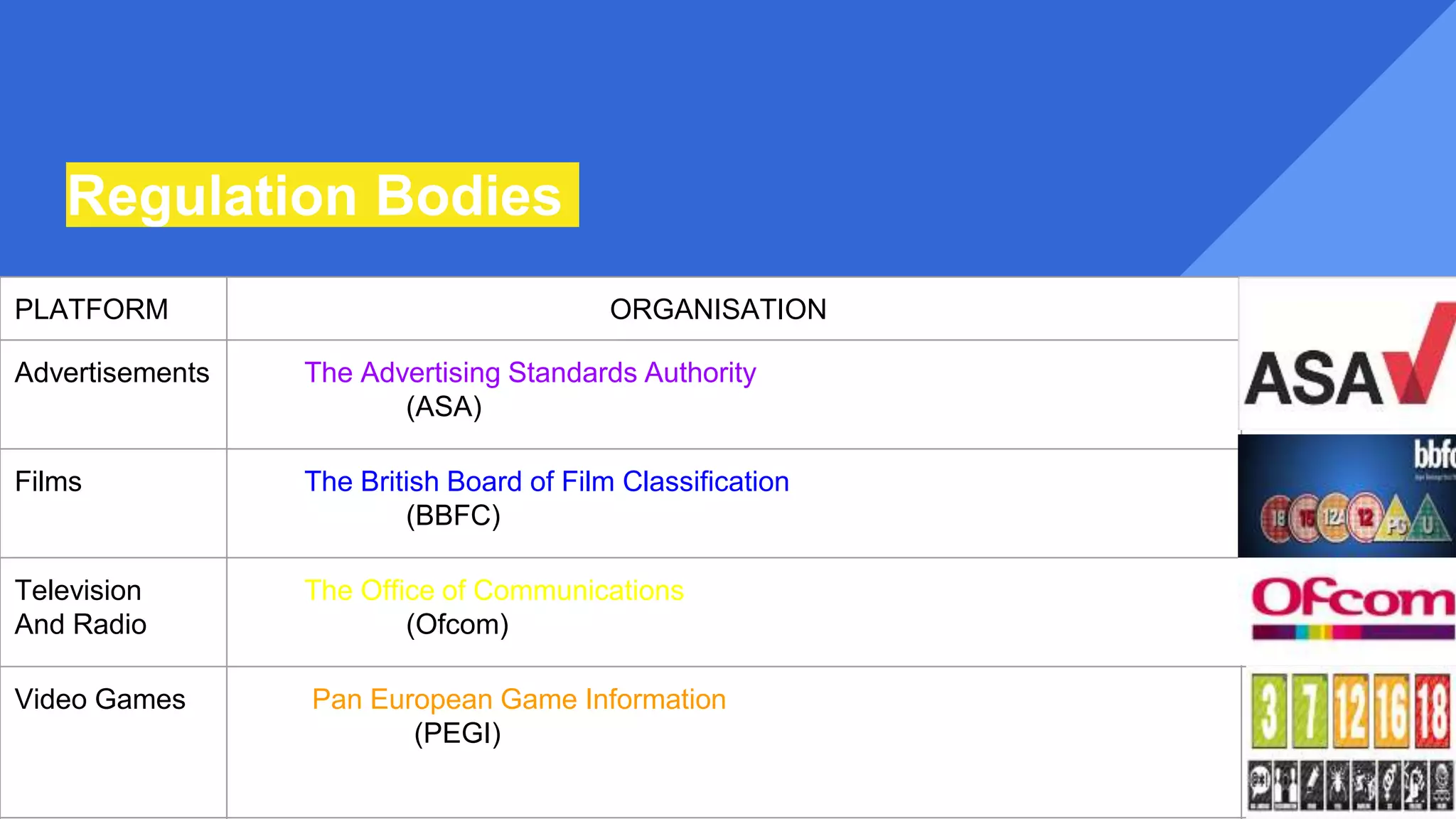
This document provides an overview of different digital media sectors and audiences. It discusses sectors such as film, video games, magazines, music, newspapers, television, radio, and the web. It also covers analogue vs digital platforms, the media text production process, convergence, and different types of audiences. Key concepts explained include primary and secondary audiences, active and passive consumers, personalization and interaction, and audience theories like hypodermic theory and uses and gratifications. The document also briefly mentions regulation bodies and the watershed for television broadcasting.