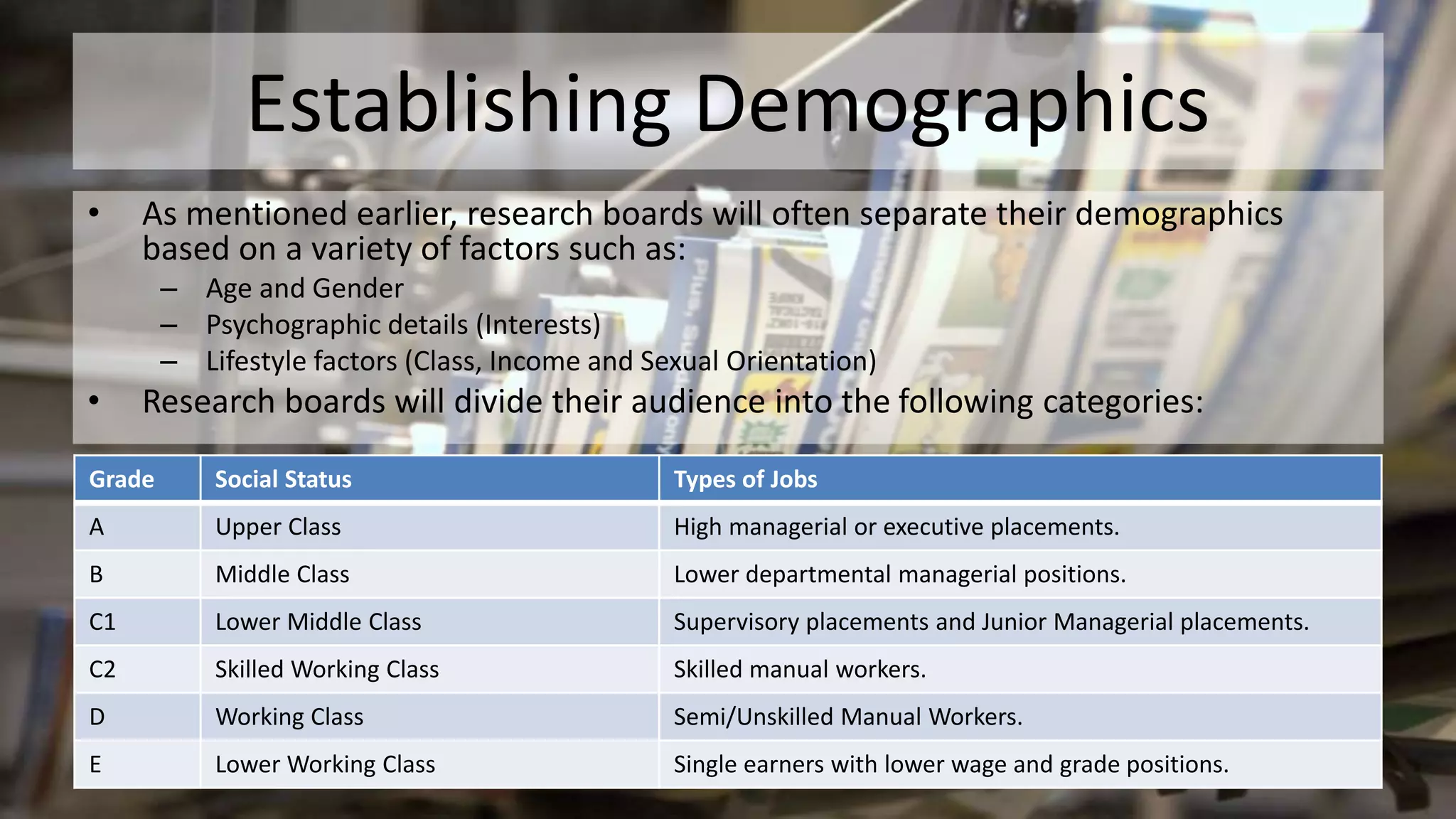
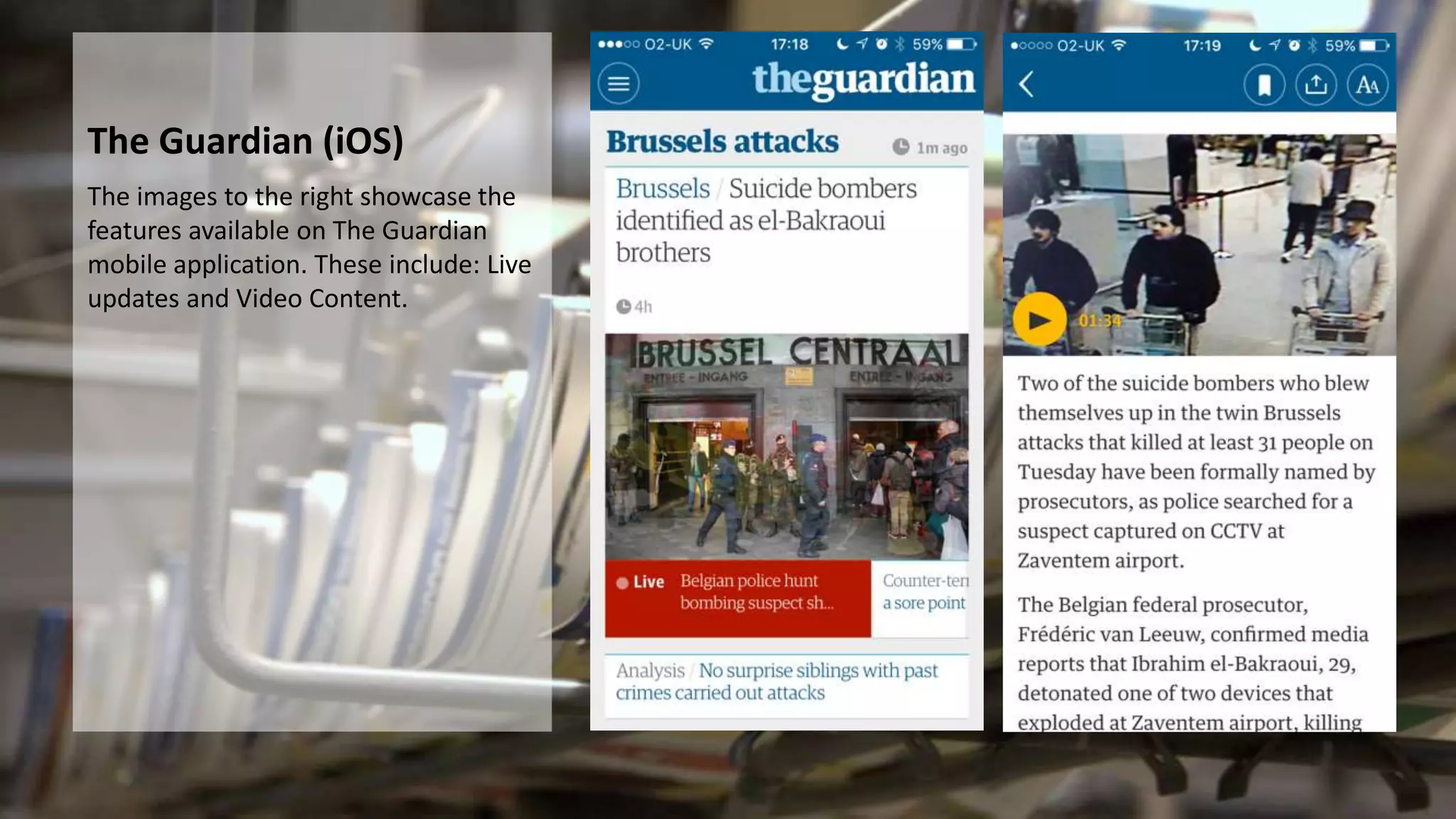
The document discusses various aspects of publishing, including audience research methods, the impact of new media technologies, and the roles within the publishing industry. It highlights how understanding demographics and audience needs is crucial for successful publications, as well as the regulatory frameworks guiding the industry. Additionally, it addresses challenges in publishing, such as bias, media imperialism, and the influence of technology on traditional media consumption.