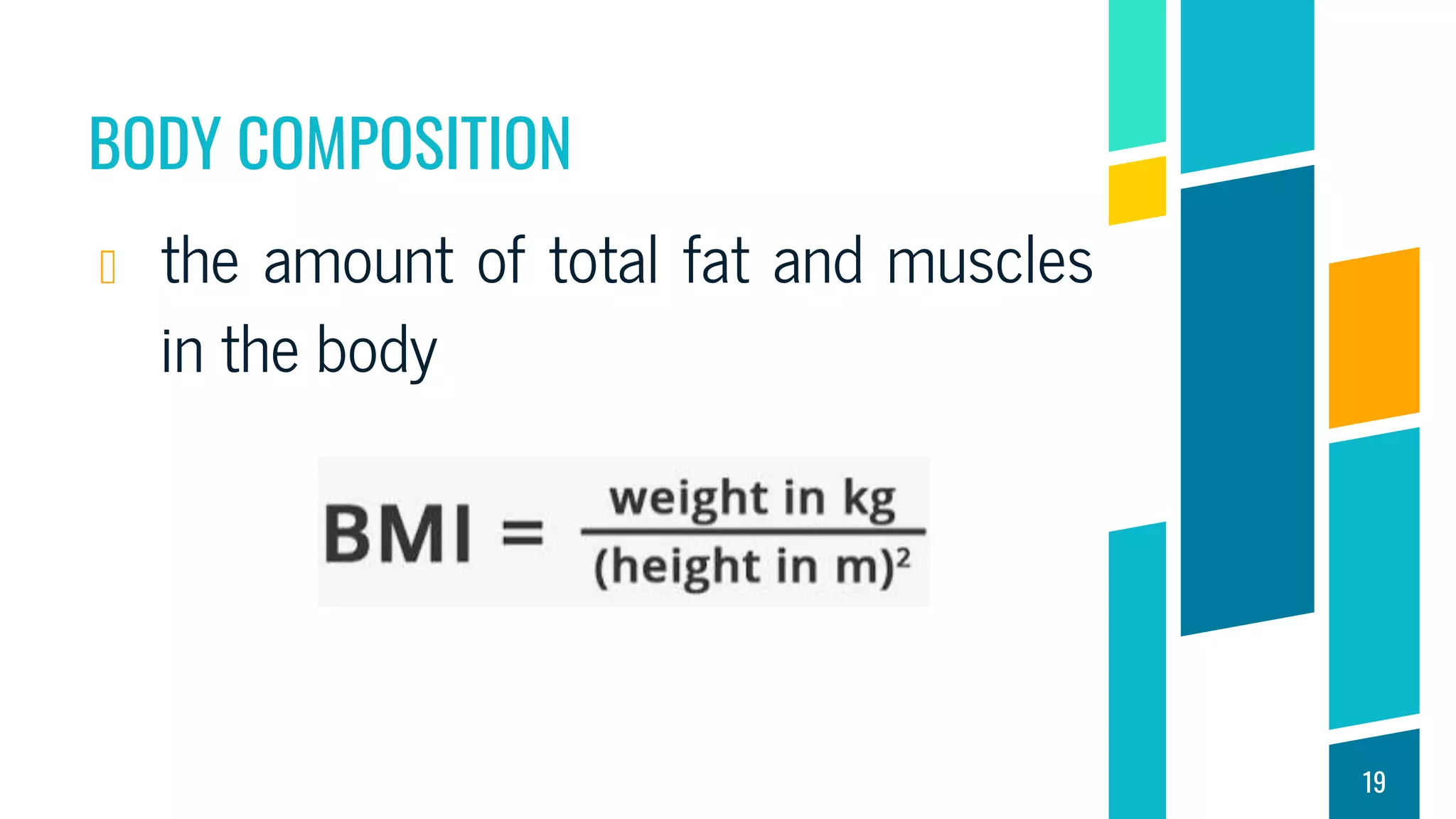
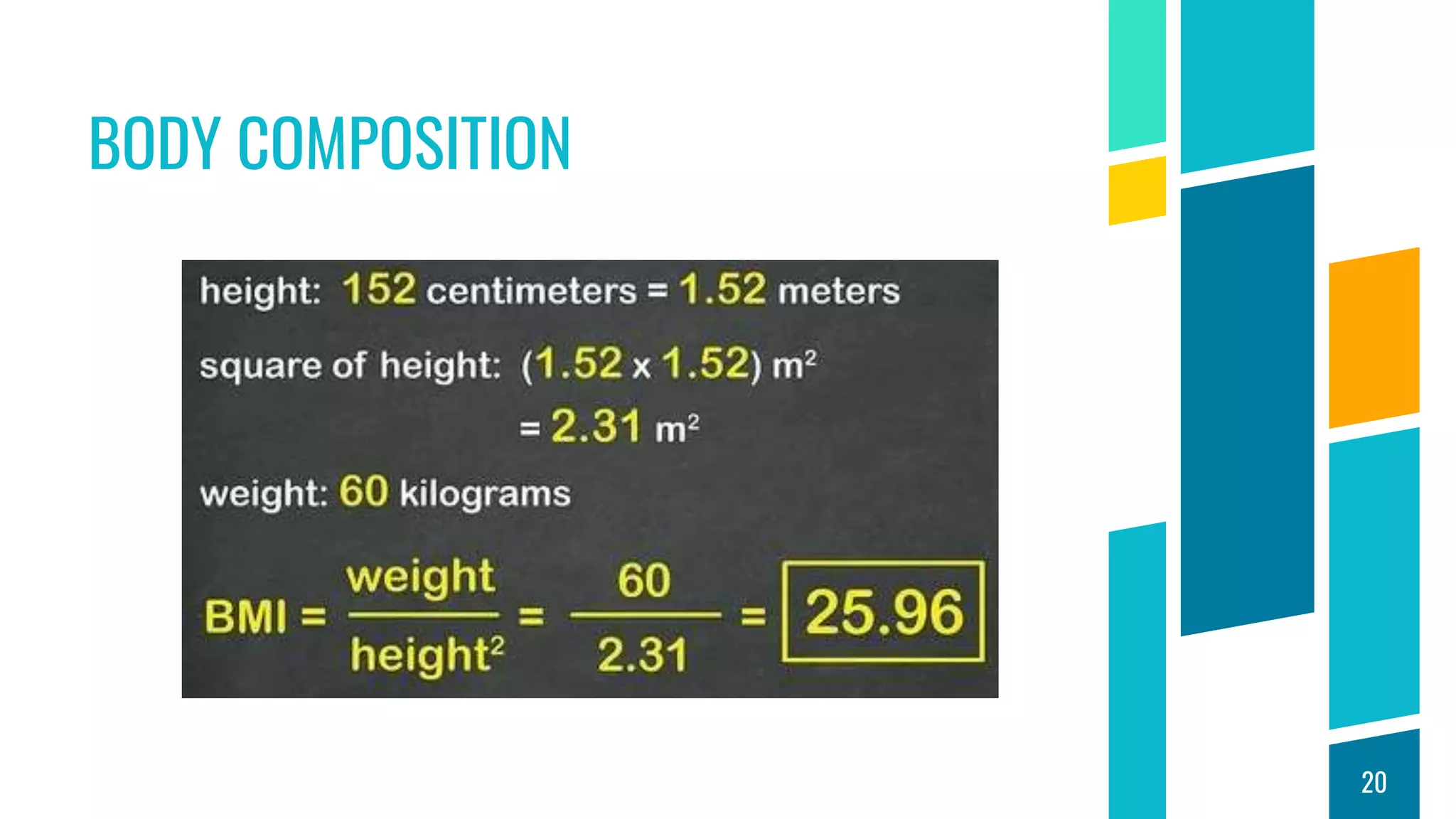
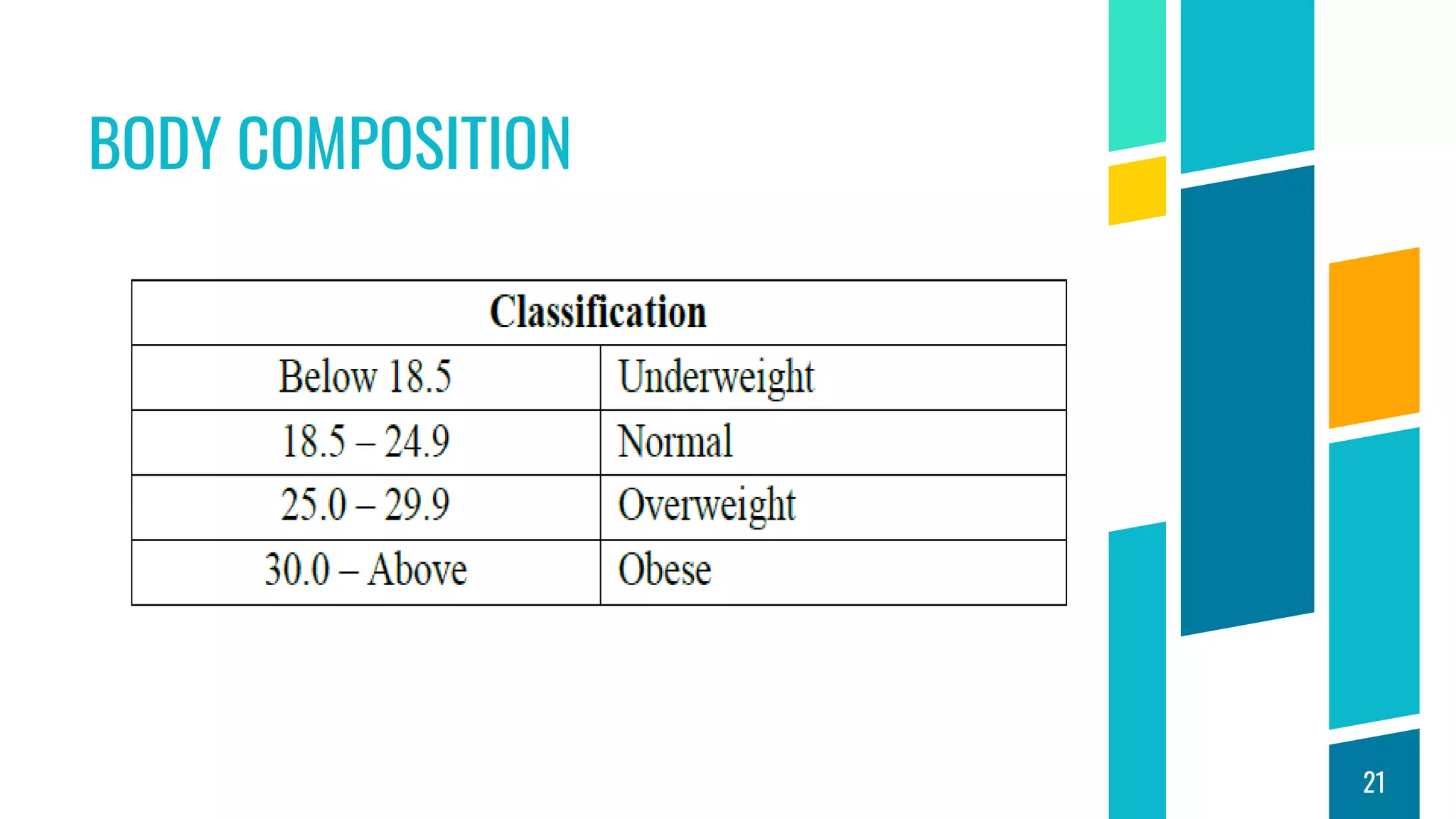
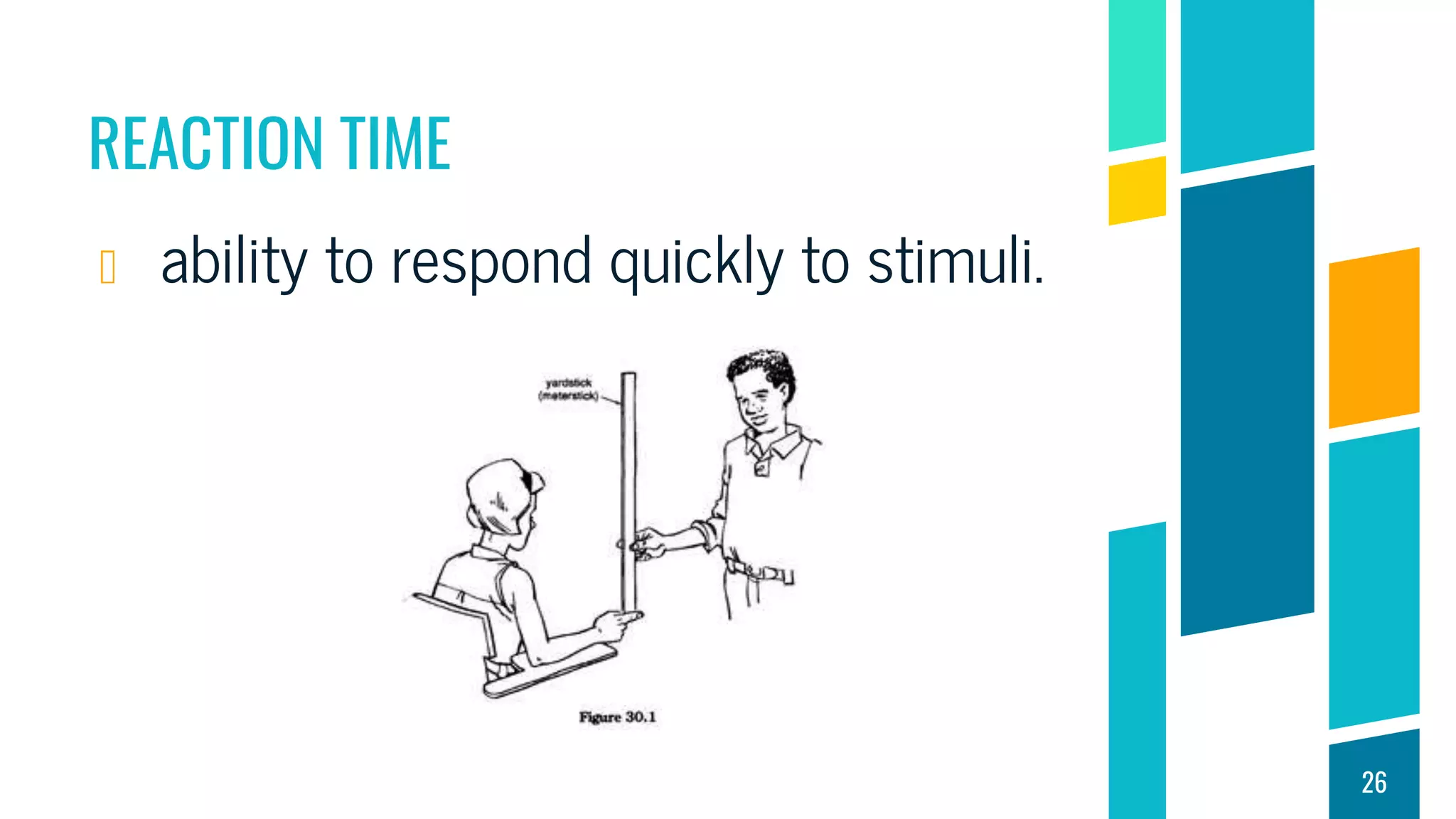
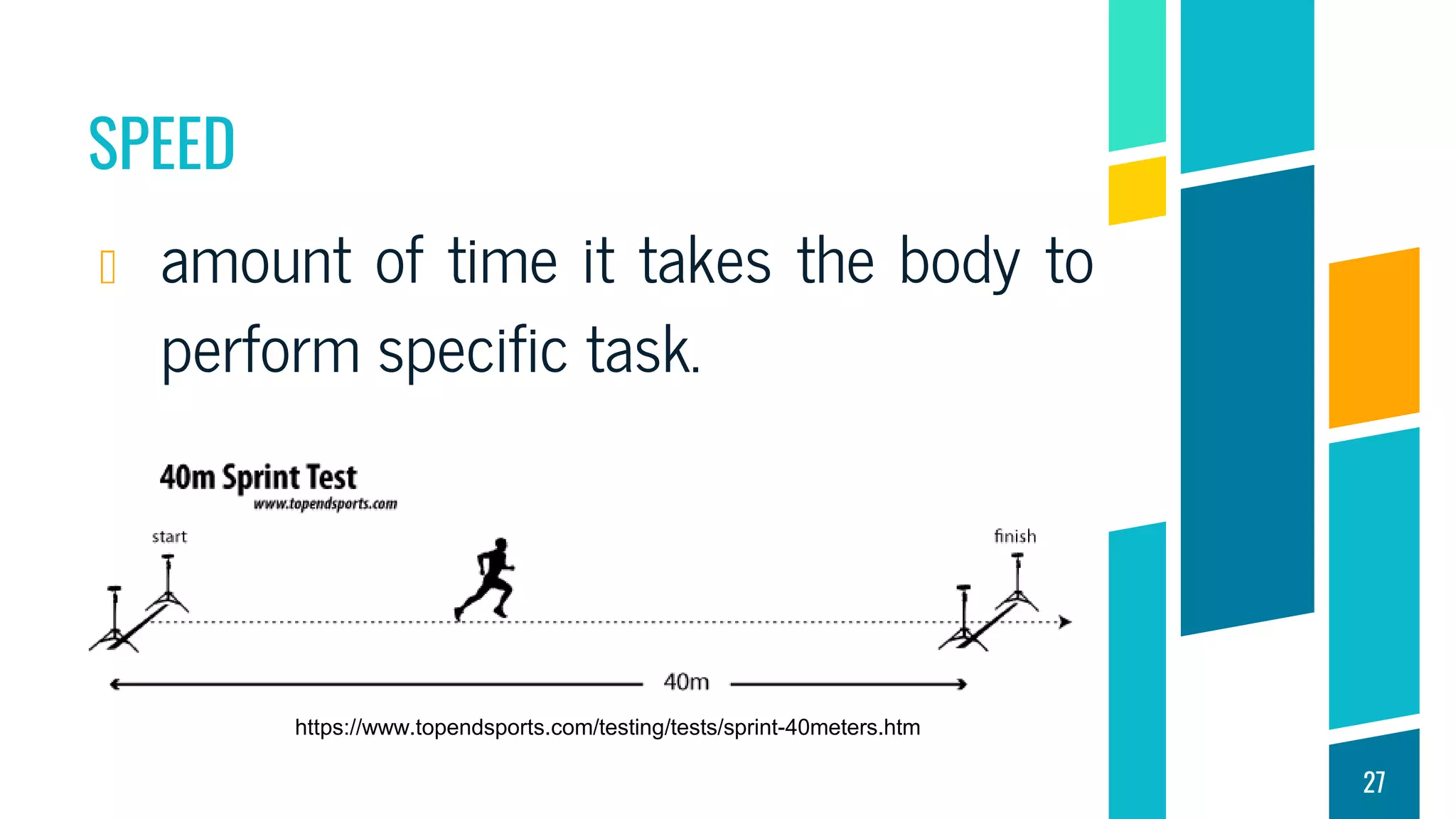
This document discusses physical fitness assessments and components of health-related and skill-related physical fitness. It describes five groups of health-related fitness: muscular strength, flexibility, muscular endurance, cardiovascular endurance, and body composition. It also describes six components of skill-related fitness: agility, balance, coordination, power, reaction time, and speed. For each component, it provides a brief definition and examples of how it can be measured or developed through exercise. The overall purpose is to help individuals understand different aspects of physical fitness and how to assess their own levels of fitness.