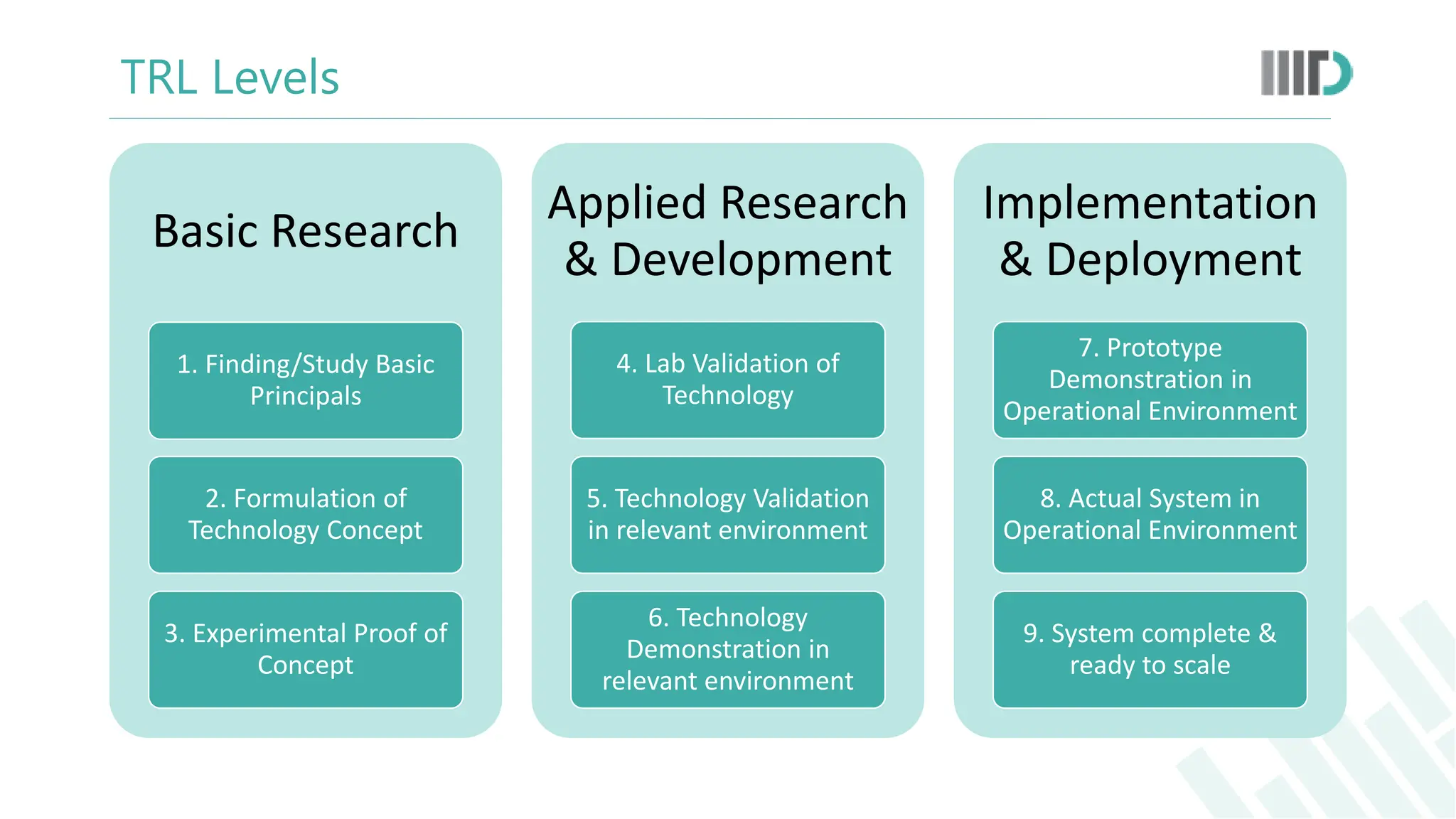
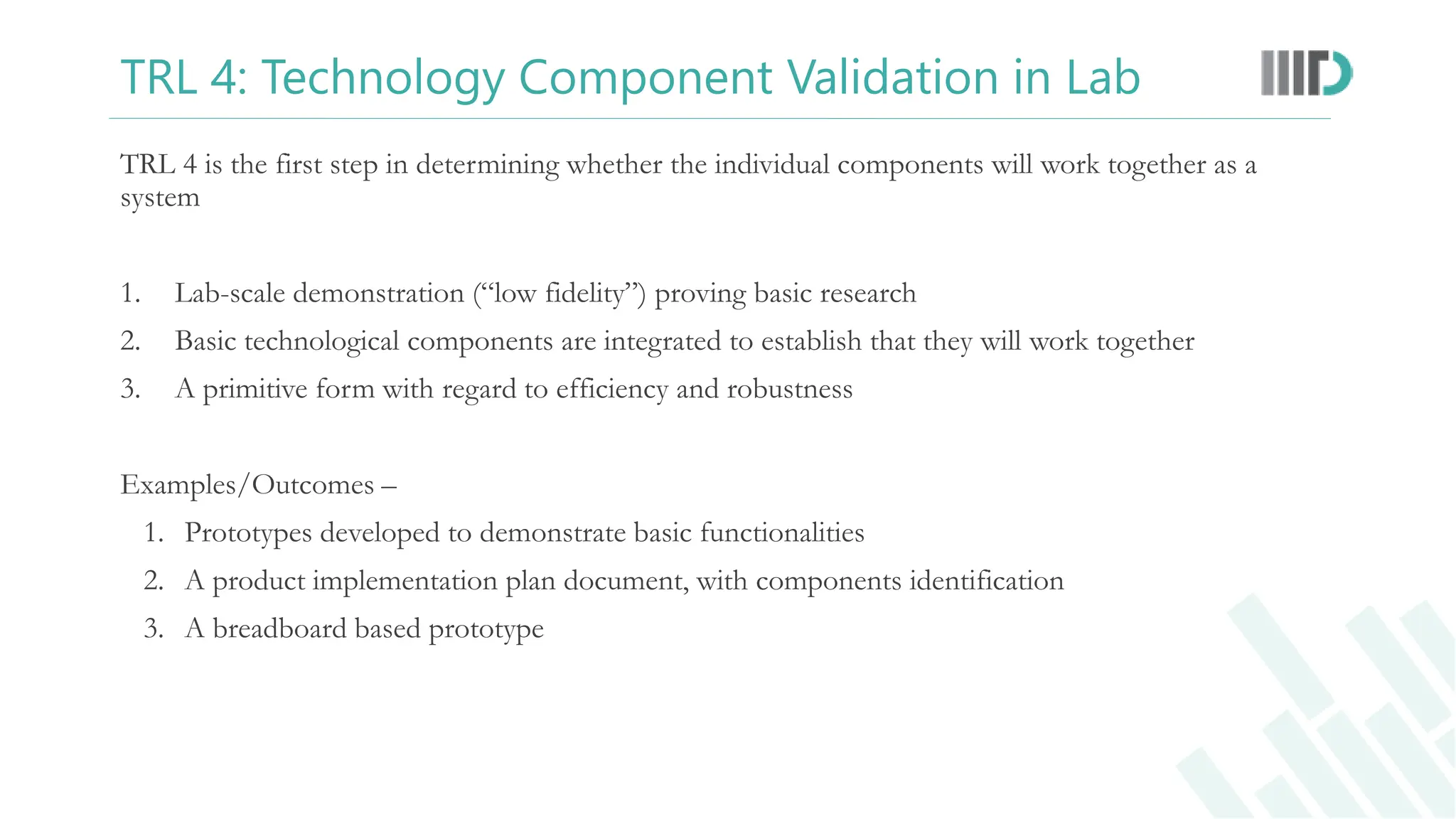
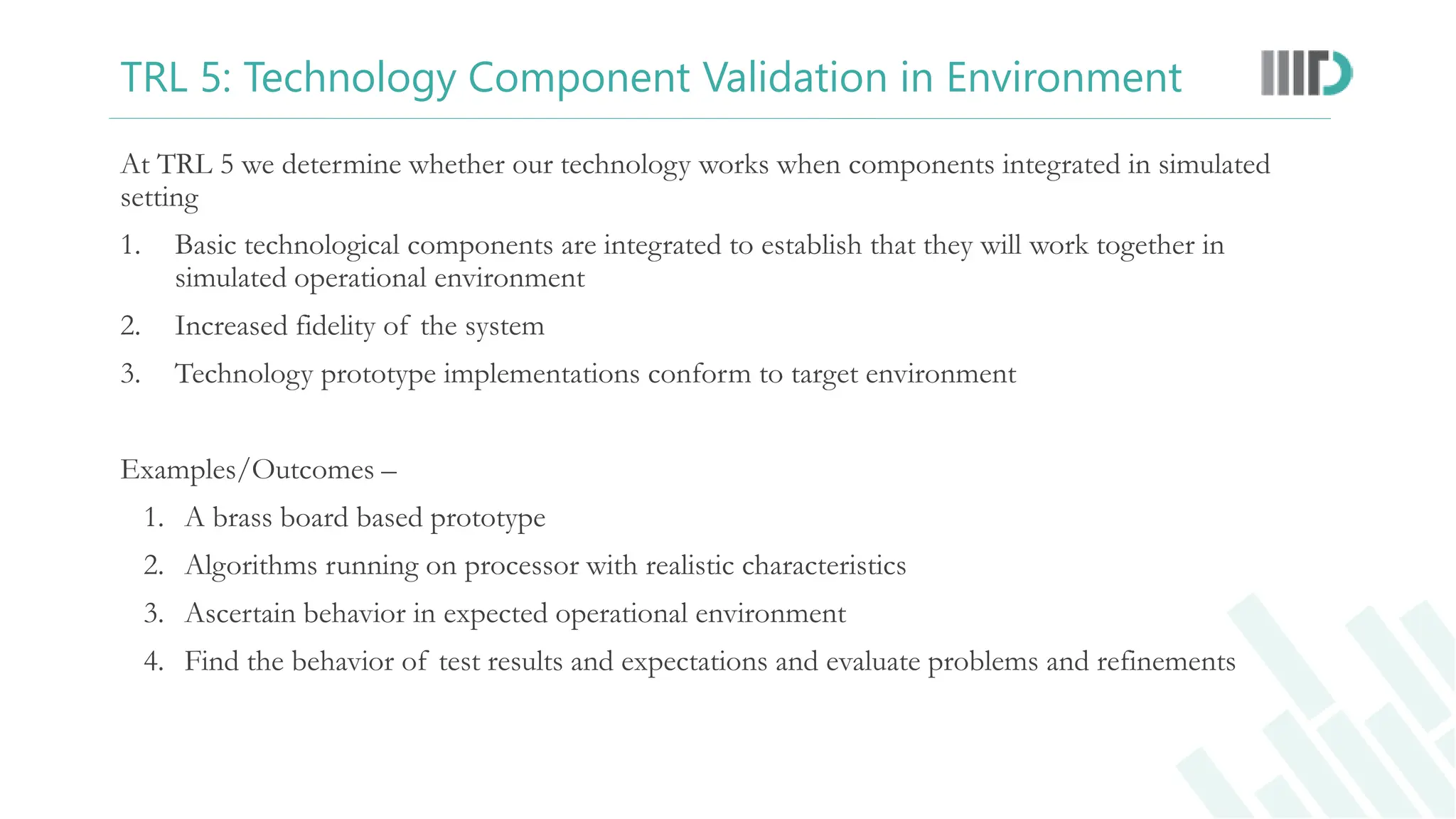
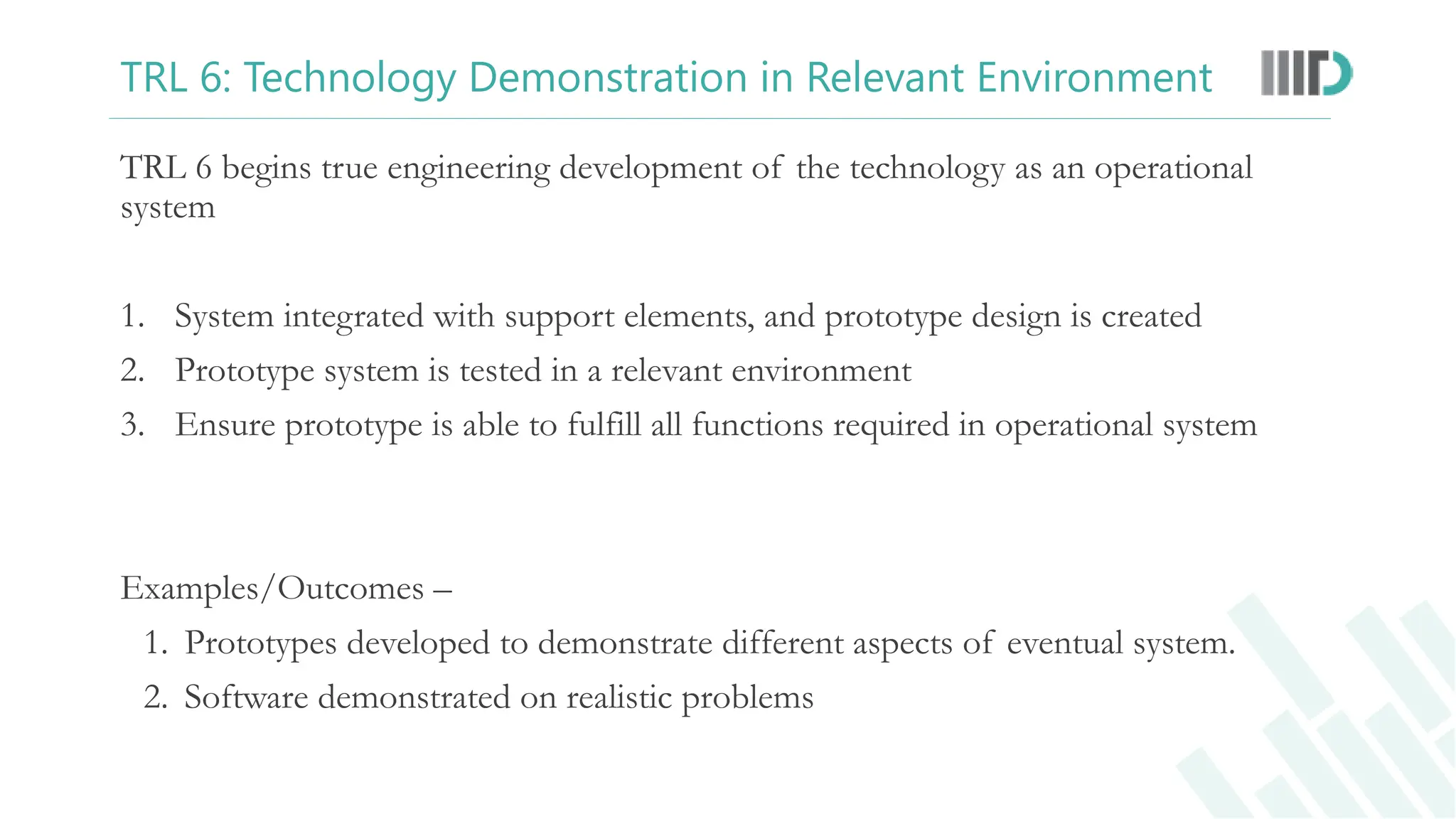
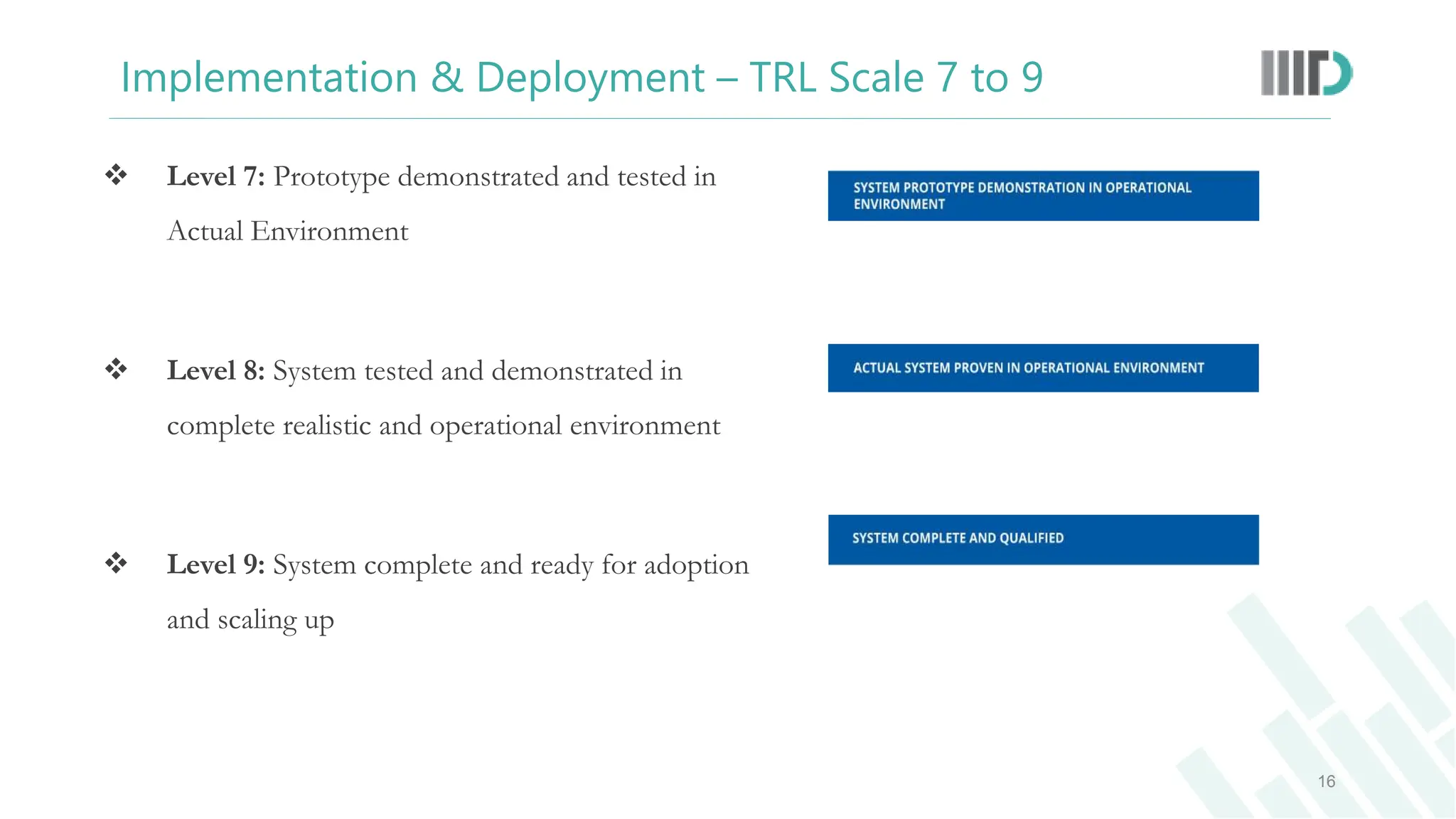
The document discusses the Technology Readiness Level (TRL) assessment framework, which measures the maturity of technology from basic research through to full-scale deployment. It outlines the nine TRL phases, providing a detailed explanation of each stage and how to evaluate the readiness of technological solutions for commercialization. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of technology transfer and the potential benefits for researchers, including patent opportunities and startup development.