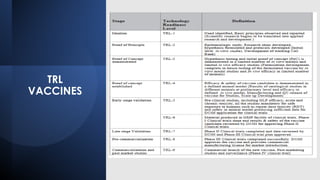
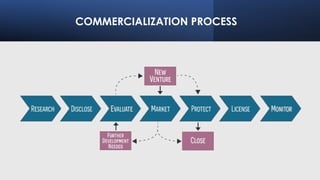
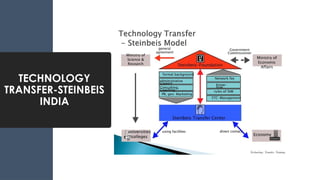
The document discusses Technology Readiness Levels (TRL) and their significance in assessing the maturity of technologies during the commercialization process, originally developed by NASA in 1974. It highlights the roles of various committees and organizations, like BIRAC, in evaluating and guiding technology projects while emphasizing the importance of technology transfer for innovation, economic growth, and job creation. Furthermore, it outlines the phases of technology transfer and stresses how it enables effective movement of innovations from research labs to market applications.