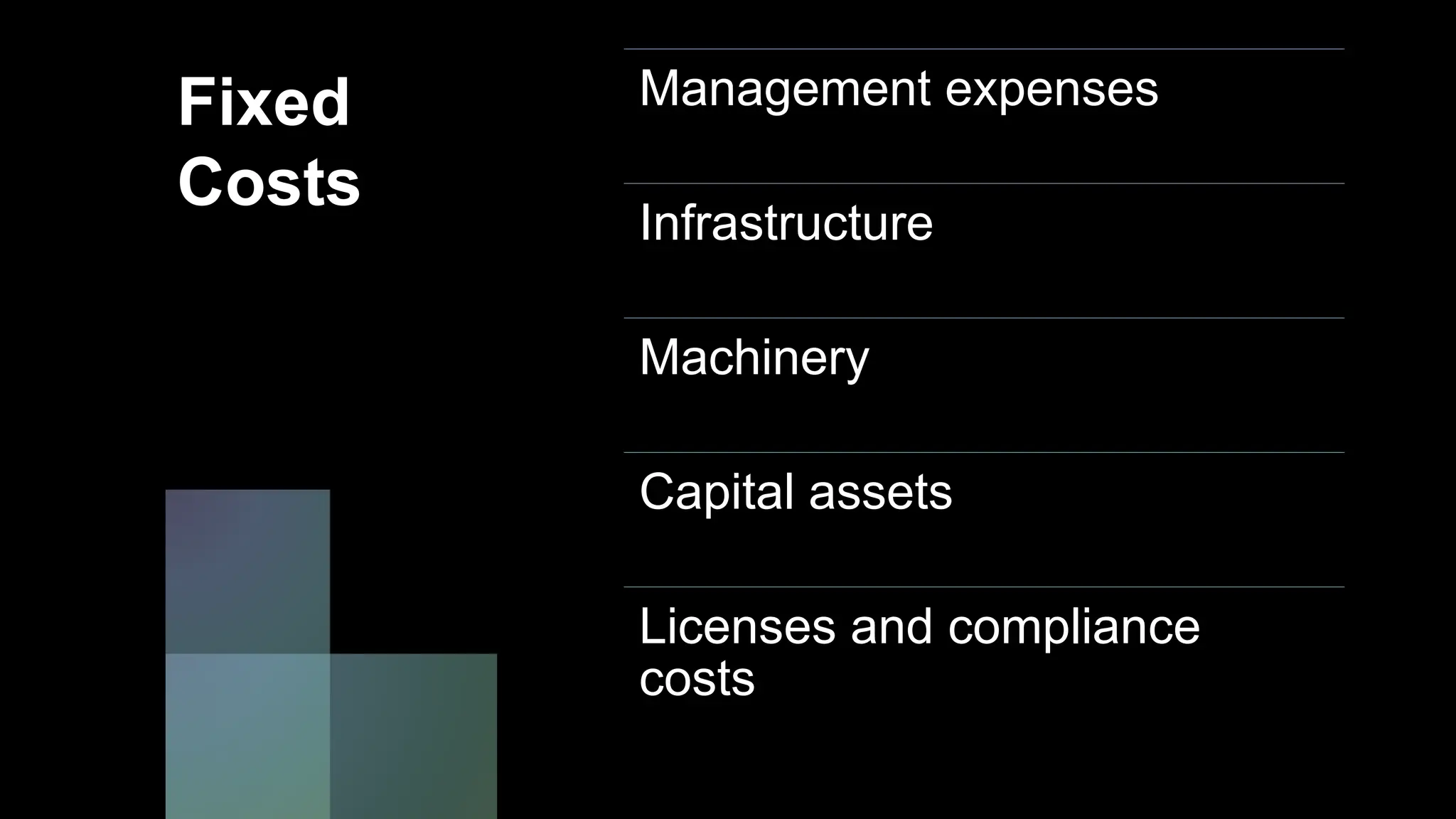
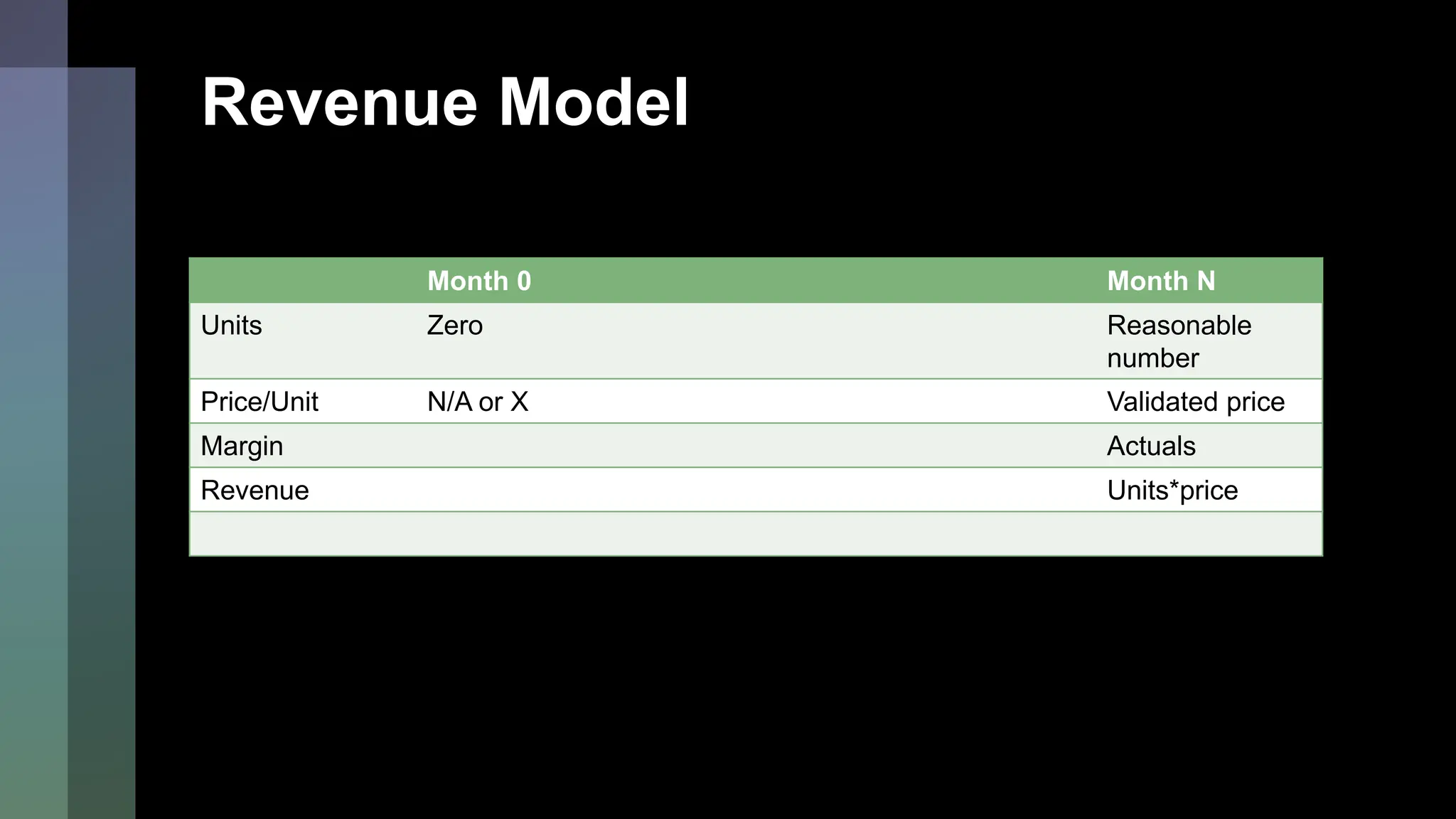
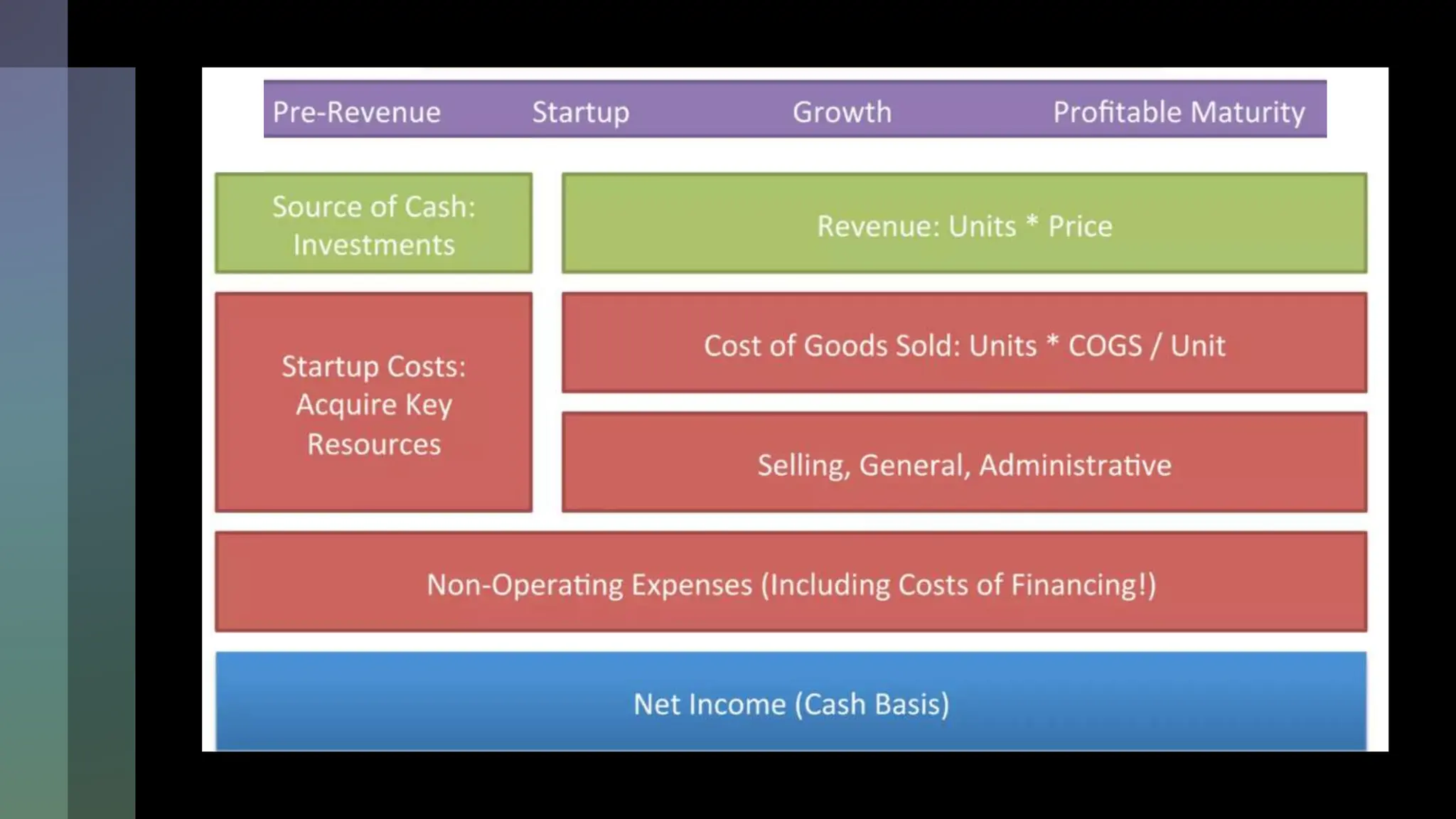
This document emphasizes the importance of financial planning for startups, covering key aspects such as understanding market potential, estimating costs, and identifying necessary resources. It outlines various components of a financial plan, including cost models, revenue streams, and the cost of goods sold. Additionally, it stresses the need for reasonable sales projections and the evaluation of profitability as the business matures.