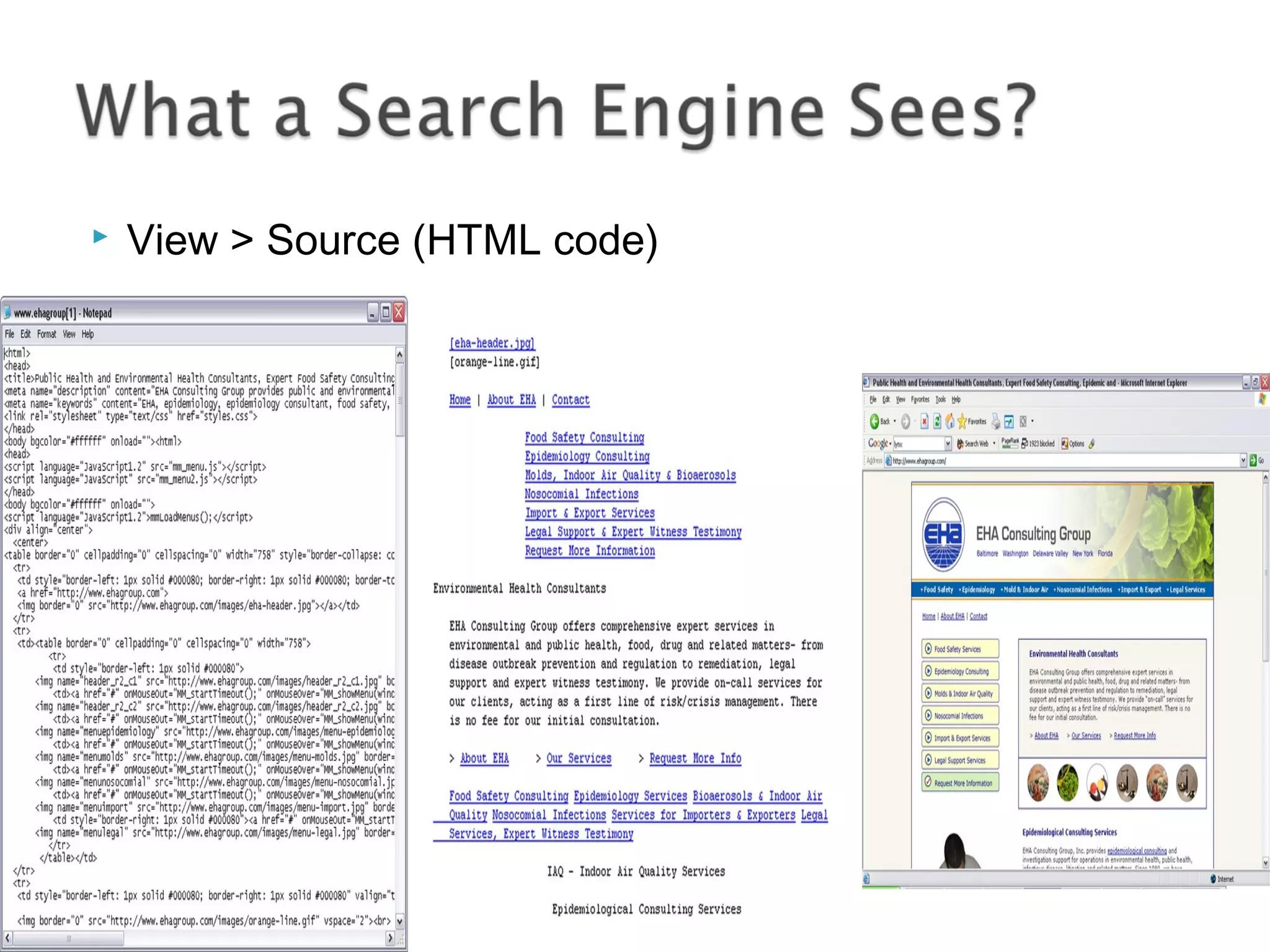
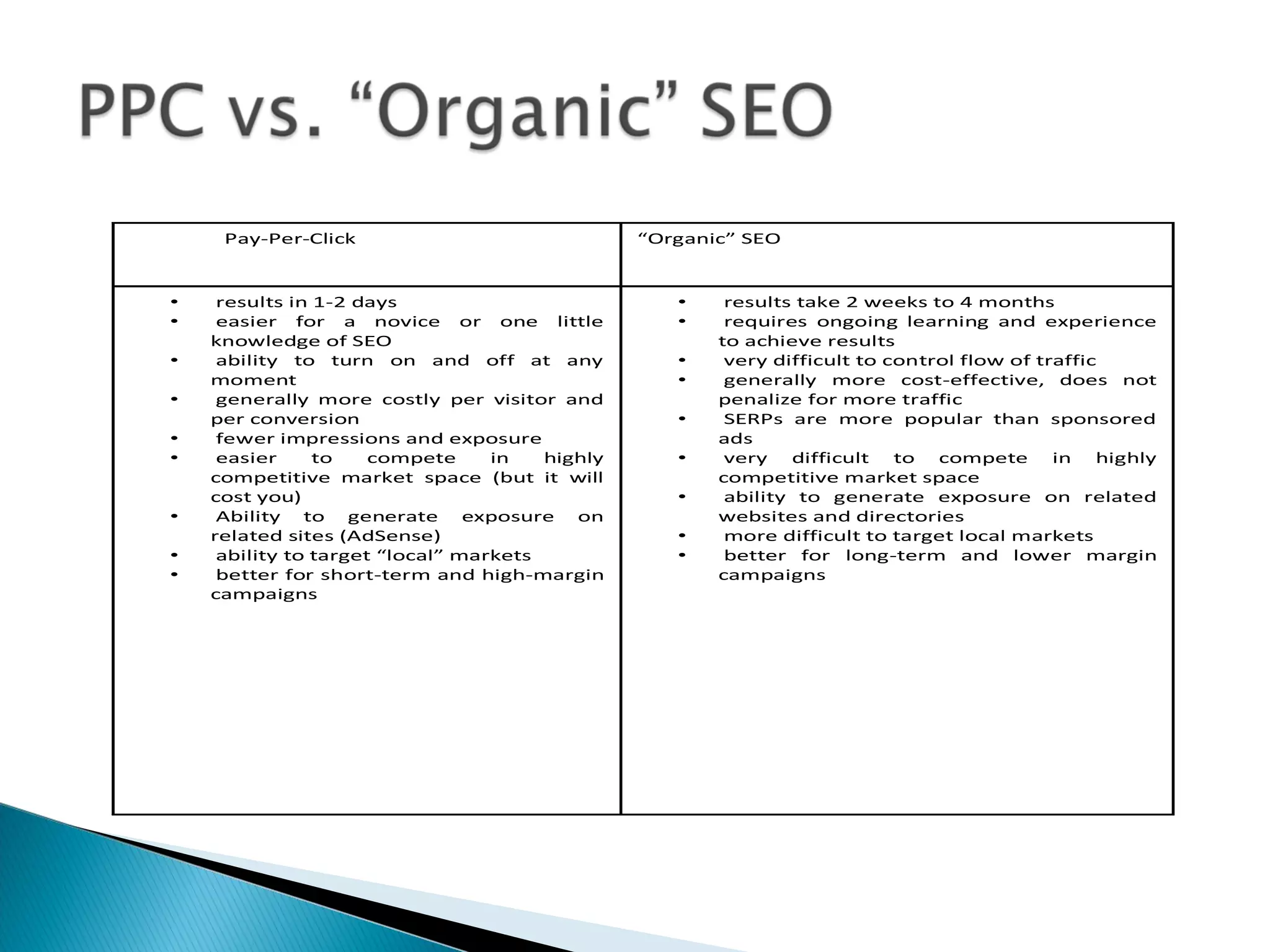
This document defines a search engine as an internet-based tool that searches an index of documents for terms specified by users. It searches billions of web pages. Search engines work by using spiders to crawl the web and index page content, then search this database in response to user queries. Results are ranked algorithmically based on relevance. The document outlines common search engine components and processes, as well as how search engine optimization (SEO) aims to improve rankings through on-page and off-page optimization strategies.