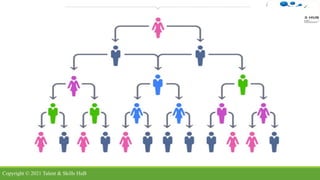
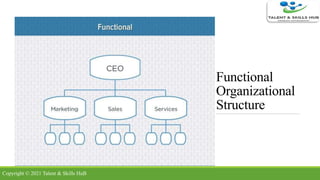
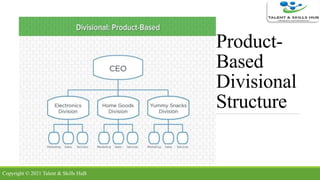
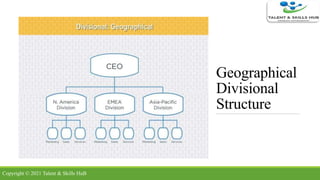
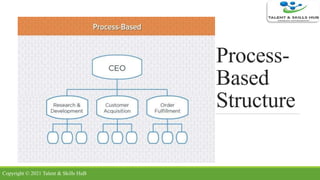
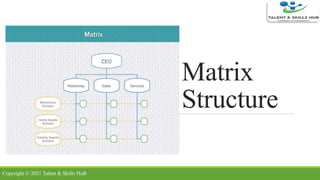
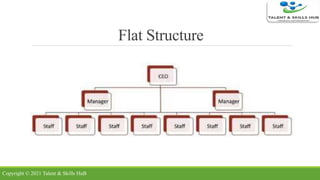
The document discusses different types of organizational structures. It describes mechanistic and organic structures, as well as functional, product-based divisional, geographical divisional, process-based, matrix, and flat structures. Each structure is explained in terms of how roles are coordinated, advantages, and disadvantages. The document aims to provide an overview of common organizational structure models.