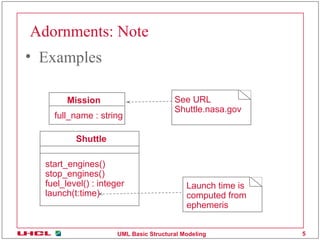
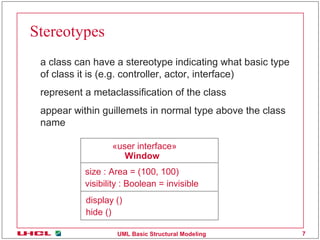
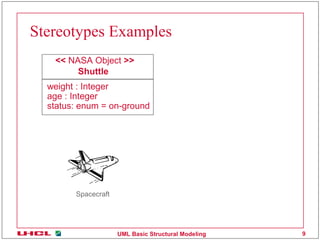
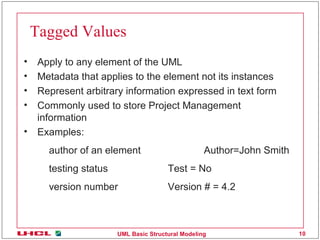
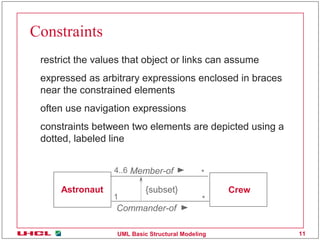
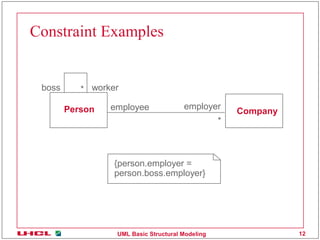
This document discusses various common mechanisms in UML structural modeling including specifications, adornments, common divisions, extensibility mechanisms, stereotypes, tagged values, and constraints. It provides examples of how to use notes, stereotypes, tagged values, and constraints in UML class diagrams to annotate elements with additional information.