This study assessed the diagnostic accuracy of lung comet-tail images detected by ultrasound compared to chest radiography, wedge pressure, and extravascular lung water (EVLW) measured by the PiCCO system. 20 patients undergoing cardiac surgery were examined before, immediately after, and 24 hours following surgery using ultrasound to detect comet-tail images, chest radiography, pulmonary artery catheterization, and the PiCCO system. Significant positive correlations were found between the number of comet-tail images and EVLW, wedge pressure, and radiographic lung water score, indicating ultrasound detection of comet-tail images provides reliable information about interstitial pulmonary edema.
![“Ultrasound Comet-Tail Images”:
A Marker Of Pulmonary Edema*
A Comparative Study With Wedge Pressure And
Extravascular Lung Water
Eustachio Agricola, MD; Tiziana Bove, MD; Michele Oppizzi, MD;
Giovanni Marino, MD; Alberto Zangrillo, MD; Alberto Margonato, MD; and
Eugenio Picano, MD
Background: Echographic examination of the lung surface may reveal multiple “comet-tail
images” originating from water-thickened interlobular septa. These images could be useful for
noninvasive assessment of interstitial pulmonary edema.
Study objective: The purpose of this study was to assess the diagnostic accuracy of lung comet-tail
images compared with chest radiography, wedge pressure, and extravascular lung water (EVLW)
quantified by the indicator dilution method (PiCCO System, version 4.1; Pulsion Medical Systems;
Munich, Germany).
Methods and patients: We enrolled 20 patients (mean age, 62.6 ؎ 11.5 years [؎ SD]). Patients
were studied before, immediately after, and 24 h following cardiac surgery with chest ultrasound,
chest radiography, pulmonary artery catheterization, and the PiCCO system. Performing echo
scanning (right and left hemithorax, from second to fourth intercostal space, from parasternal to
midaxillary line), an individual patient comet score was obtained by summing the number of
comets in each scanned space.
Results: A total of 60 comparisons were obtained. Significant positive linear correlations were
found between comet score and EVLW determined by the PiCCO System (r ؍ 0.42, p ؍ 0.001),
between comet score and wedge pressure (r ؍ 0.48, p ؍ 0.01), and between comet score and
radiologic lung water score (r ؍ 0.60, p ؍ 0.0001).
Conclusions: The presence and the number of comet-tail images provide reliable information on
interstitial pulmonary edema. Therefore, ultrasonography represent an attractive, easy-to-use,
bedside diagnostic tool for assessing cardiac function and pulmonary congestion.
(CHEST 2005; 127:1690–1695)
Key words: alveolar interstitial syndrome; chest ultrasound; comet-tail artifact; extravascular lung water
Abbreviations: CO ϭ cardiac output; EVLW ϭ extravascular lung water
The objective diagnosis of interstitial pulmonary
edema is traditionally based on chest radio-
graphic findings, which when performed at the
bedside may be difficult to interpret, and can have
weak correlations with extravascular lung water
(EVLW).1,2 The lung is considered poorly accessible
using ultrasound because air prevents the progres-
sion of the ultrasound beam with production of
reverberation artifacts under the lung surface.3 The
“comet-tail image” is an echographic image detect-
able with a cardiac ultrasound probe positioned over
the chest.4 This image consists of multiple comet
tails fanning out from the lung surface originating
from water-thickened interlobular septa, and could
provide useful information on EVLW.
The correlation between comet-tail images and
interstitial edema has been documented by CT
scanning,5,6 but not validated by quantitative mea-
surements of EVLW.7,8 The purpose of this study
was to assess the correlation between lung comet-tail
*From the Divisions of Non-Invasive Cardiology (Drs. Agricola,
Oppizzi, and Margonato) and Anesthesiology and Intensive Care
(Drs. Bove, Marino, and Zangrillo), Cardiothoracic Department,
San Raffaele Hospital, Istituto di Richerche e Cura a carattere
Scientifico, Milano; and Institute of Clinical Physiology (Dr.
Picano), Consiglio Nazionale delle Richerche, Pisa, Italy.
Manuscript received May 11, 2004; revision accepted September
15, 2004.
Reproduction of this article is prohibited without written permission
from the American College of Chest Physicians (www.chestjournal.
org/misc/reprints.shtml).
Correspondence to: Eustachio Agricola, MD, Division of Non-
Invasive Cardiology, Cardiothoracic Department, San Raffaele
Hospital, IRCCS, Via Olgettina 60, 20132 Milano, Italy; e-mail:
agricola.eustachio@hsr.it
1690 Clinical Investigations
Downloaded From: http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/ on 11/28/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ultrasound-comet-tail-image-160210064221/75/Ultrasound-comet-tail-image-1-2048.jpg)
![images with chest radiographic findings, wedge pres-
sure, and EVLW measured by the indicator dilution
method (PiCCO System, version 4.1; Pulsion Medi-
cal Systems; Munich, Germany).
Materials and Methods
Patients
We enrolled 20 patients (16 men and 4 women; mean age,
62.6 Ϯ 11.5 years) who underwent cardiac surgery with cardio-
pulmonary bypass (Table 1). Patients with lung diseases were
excluded. The patients were assessed with chest ultrasonography,
chest radiography, pulmonary artery catheterization, and the
PiCCO System at baseline, immediately after surgical operation,
and after 24 h. All examinations were performed within a few
minutes and were read by independent operators unaware of the
results of the other tests. All patients gave their informed
consent.
Chest Ultrasound
The echographic examinations were performed with patients in
the supine position. The ultrasound scanning of the anterior and
lateral chest was obtained on both the right and left hemithorax,
the second to fourth (on the right side to the fifth) intercostal
space, and the parasternal to midaxillary line. In each intercostal
space, the number of comet-tail images was registered at the
parasternal, midclavear, anterior, and middle axillary lines as
previously described.9 The sum of the comet-tail images was
provided as an echo comet score of the extravascular fluid of the
lung. Zero was defined as a complete absence of comet-tail
images on the investigated area. The intraobserver and interob-
server variabilities of the echo comet score were assessed by two
independent observers (E.A. and T.B.) in a set of 10 consecutive
cases, and were 3.1% and 4.4%, respectively. The comet-tail
image was defined as a hyperechogenic, coherent bundle with
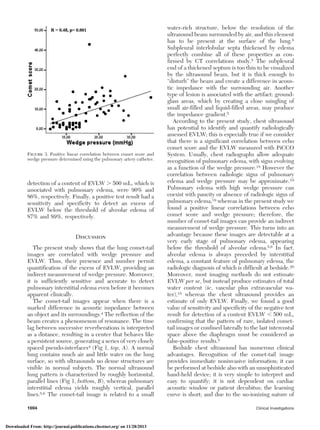
narrow basis spreading from the transducer to the further border
of the screen.5,6 The comet-tail image described here extends to
the edge of the screen (whereas short comet-tail artifacts may
exist in other regions), and arises only from the pleural line.6
Comet-tail images arising from the pleural line can be localized
or disseminated to the whole lung surface, or again isolated or
multiple (when at least three artifacts are visible in a frozen image
in one longitudinal scan), with a distance Յ 7 mm between two
artifacts) [Fig 1, top, A].6 A positive (or pathologic) test result was
defined as bilateral multiple comet-tail images, either dissemi-
nated (defined as all over the anterolateral lung surface) or lateral
(defined as limited to the lateral lung surface). A negative test
result was defined as an absence of comet-tail images, replaced
by the horizontal artifact (Fig 1, bottom, B), or when rare, isolated
comet-tail images were visible or when multiple comet-tail
images were confined laterally to the last intercostal space above
the diaphragm.6 The examinations were performed using an
ultrasound system (Sonos 5500; Phillips Medical Systems; An-
dover, MA) equipped with 1.8- to 3.6-MHz probe.
Chest Radiography
The patients underwent chest radiography in the supine
position with specific assessment of EVLW using a commercially
available radiograph machine and a standard technique. A pre-
viously validated radiologic score of EVLW was used incorporat-
ing assessment of hilar vessels (dimension, density, blurring),
Kerley lines (A, B, and C), micronoduli, widening of interlobar
fissures, peribronchial and perivascular cuffs, subpleural effusion,
and diffuse increase in density (Table 2).10–12 The intraobserver
and interobserver reproducibility of radiologic scoring of EVLW
among experienced observers was very high, as previously de-
scribed.10–12
PiCCO System
The PiCCO System is a device for cardiac output (CO)
measurement combined with cardiac preload volume and lung
water monitoring. It computes the CO utilizing an arterial pulse
contour analysis algorithm after calibration by means of a
transpulmonary thermodilution method.
In all patients, a 5F thermistor-tipped catheter (Pulsiocath
PV8115; Pulsion Medical Systems) was placed into the right
femoral artery, and connected to the PiCCO System for moni-
toring. To calibrate this system, individual arterial input imped-
ance to arterial pressure is calculated by simultaneously deter-
mining the area under the systolic portion of the arterial pulse
wave. A 10-mL bolus of cold 5% dextrose solution is injected
through central venous catheter, and the thermodilution curve is
evaluated with arterial catheter inserted in the femoral artery.
The mean of three consecutive boluses was used. If an injection
had to be rejected, more injections were made to obtain three
measurements after rejecting the lowest and the highest value.
From the CO we can obtain the intrathoracic thermal volume
and the intrathoracic blood volume; from the difference of these
two parameters, we can obtain the value of EVLW. Normally,
EVLW is Ͻ 500 mL13–15; the alveolar flooding appears usually
when the EVLW is Ͼ 75% above normal limit.15,16
Pulmonary Artery Pressure
A pulmonary artery catheter was introduced via the right
internal jugular vein for conventional pulmonary artery thermodi-
lution CO measurements. Pulmonary wedge pressure, and sys-
tolic, diastolic, and mean pulmonary pressures were also mea-
sured.
Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as the mean value Ϯ SD or percentages.
The correlations between echo comet score, EVLW, radiologic
Table 1—Clinical Features
Variables Data*
Age, yr 62.6 Ϯ 11.5
Male/female gender, No. 16/4
Disease, No. (%)
Mitral regurgitation 9 (45)
Coronary artery disease 4 (20)
Aortic regurgitation 1 (5)
Coronary artery disease plus aortic stenosis 1 (5)
Mitral stenosis 1 (5)
Mitral regurgitation plus atrial septal defect 1 (5)
Mitral regurgitation plus coronary artery
disease
1 (5)
Aortic regurgitation plus ascending aortic
aneurysm
1 (5)
Aortic regurgitation plus mitral regurgitation 1 (5)
End-diastolic volume, mL 121.6 Ϯ 45
End-systolic volume, mL 44 Ϯ 19
Ejection fraction, % 63.5 Ϯ 5.5
*Data are presented as mean Ϯ SD unless otherwise indicated.
www.chestjournal.org CHEST / 127 / 5 / MAY, 2005 1691
Downloaded From: http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/ on 11/28/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ultrasound-comet-tail-image-160210064221/85/Ultrasound-comet-tail-image-2-320.jpg)
![lung water score, and data obtained by pulmonary artery catheter
monitoring were analyzed by the Pearson two-tailed method.
Moreover, the agreement between chest ultrasound and radio-
graph methods was analyzed using the Bland and Altman meth-
od.17 Bias between the methods was calculated as the mean
difference between echo comet score and radiograph score. The
upper and the lower limits of agreement were calculated as bias
(2 SD), and defined the range in which 95% of the differences
between the methods were expected to lie. The precision of the
bias analysis and limits of agreement was assessed using 95%
confidence intervals. Bias between comet score and radiograph
score was analyzed using the paired Student t test. The difference
in the mean content of EVLW between positive and negative
comet test results was evaluated with an independent Student t
test. Moreover, we calculated the sensitivity and specificity of a
negative test result for detection of EVLW content Ͻ 500 mL,
the sensitivity and specificity of a positive test for detection of
EVLW content Ͼ 500 mL, and finally the sensitivity and speci-
ficity of a positive test result for detection an excess of EVLW
below the threshold of alveolar flooding. A p value Ͻ 0.05 was
considered statistically significant. The statistical analysis was
performed using software (version 8.0; SPSS; Chicago, IL).
Results
The determinations with the different methods
were obtained in all patients. No data were rejected.
A total of 60 comparative measurements were per-
formed between the methods.
Comparison Between Chest Ultrasound, Chest
Radiograph Findings, and EVLW
The feasibility of the chest ultrasound examination
for the diagnosis of EVLW was 100%. The time
needed for the echo lung examination was Ͻ 5 min
in all cases (mean, 4.3 Ϯ 1 min). The mean number
of comets per person (comet score) was 7.6 Ϯ 9.3,
the mean radiologic score was 12 Ϯ 7, and the mean
EVLW was 643.7 Ϯ 603.6 mL.
A significant positive linear correlation was found
between echo comet score and radiologic score
(r ϭ 0.60, p Ͻ 0.0001), and no significant difference
in the mean difference between these two scores was
observed (bias, 4.7; 95% limits of agreement, Ϫ 9.9
to 19.3). There was a significant positive linear
correlation between echo comet score and EVLW
(r ϭ 0.42, p ϭ 0.001) [Fig 2].
Comparison Between Chest Ultrasound and
Hemodynamic Parameters
Positive linear correlations were found between
echo comet score and wedge pressure (r ϭ 0.48,
p Ͻ 0.0001) and systolic pulmonary pressure
(r ϭ 0.53, p ϭ 0.007) determined using pulmonary
artery catheterization (Fig 3). No significant correla-
tions between echo comet score and CO and cardiac
index were observed.
Positive vs Negative Comet Test Results
Thirty-two examination results were considered
positive and 28 were negative. When we compared
the group of test results considered positive vs
negative, a significant difference in mean EVLW was
found (742 Ϯ 277 mL vs 392 Ϯ 92 mL, p ϭ 0.0001).
The mean content of EVLW in negative test result
was below the normal limit of EVLW (Ͻ 500 mL).
The sensitivity and specificity of the negative test
result for detection of a content of EVLW Ͻ 500 mL
were 90% and 89% respectively, whereas the sensi-
tivity and specificity of the positive test result for
Table 2—Radiologic Scoring of EVLW
Variables Score*
Hilar vessels
Enlarged 1 2 3
Increased in density 2 4 6
Blurred 3 6 9
Kerley lines
A 4 8
B 4 8
C 4 8
Micronoduli 4 8
Widening of interlobar fissures 4 8 12
Peribronchial and perivascular cuffs 4 8 12
Extensive perihilar haze 4 8 12
Subpleural effusion 5 10
Diffuse increase in density 5 10 15
*The score assigned to each variable depends on the severity of
involvement: ie, Hilary vessels enlarged: 1, normal mild enlarge-
ment; 2, moderate enlargement; 3, severe enlargement.
Figure 2. Significant positive linear correlation between comet
score and EVLW determined with the indicator thermodilution
method (PiCCO System).
www.chestjournal.org CHEST / 127 / 5 / MAY, 2005 1693
Downloaded From: http://journal.publications.chestnet.org/ on 11/28/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ultrasound-comet-tail-image-160210064221/85/Ultrasound-comet-tail-image-4-320.jpg)