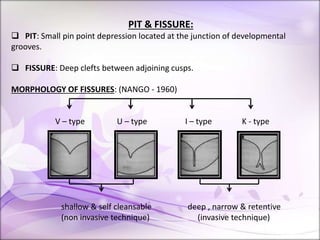
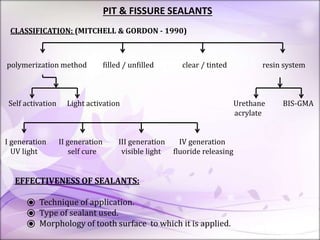
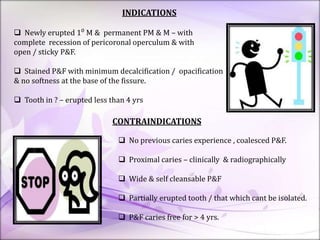
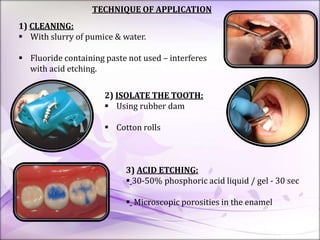
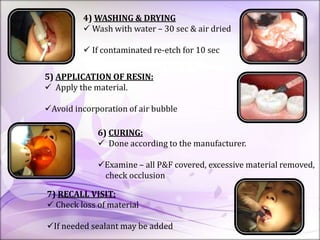
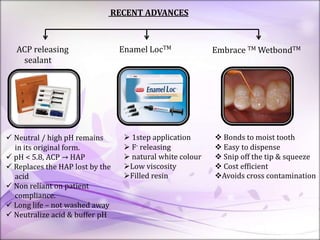
This document discusses pit and fissure sealants. It begins by noting that pit and fissure areas are highly susceptible to dental caries, accounting for 50% of caries. It then reviews the caries process in pits and fissures. Several milestones in pit and fissure sealant development are outlined, from early filling techniques to modern resin-based sealants. The document discusses the classification, effectiveness, requirements, case selection criteria, and application technique for pit and fissure sealants. Recent advances including acid-releasing and wet-bonding sealants are also summarized.