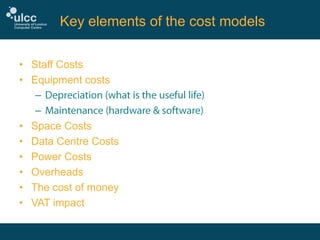
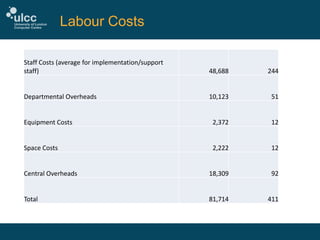
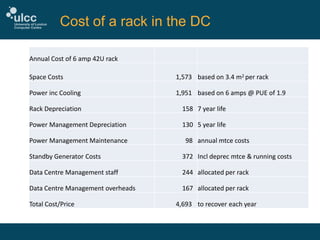
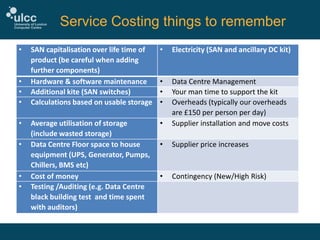
The document discusses the challenges and strategies at ULCC regarding IT spend and costing, highlighting the need for better financial data to inform decision-making. It outlines key cost components, such as staff, equipment, and space costs, and emphasizes the importance of comprehensive data collection and continuous model improvement. Additionally, it suggests internal communication and an understanding of data centre costs as crucial for effective management and recovery of expenses.