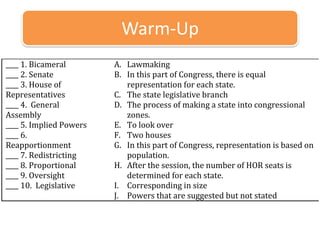
This document outlines the process of how a bill becomes a law in the United States. It discusses how bills are introduced in Congress and assigned to committees for review. Committees hold hearings on bills and can amend them before sending them to a full House or Senate vote. If passed, bills go to the other body and may end up in a conference committee if versions differ. An agreed upon bill then goes to the President to be signed into law or vetoed. The document provides examples and checks for student understanding of the lawmaking process.