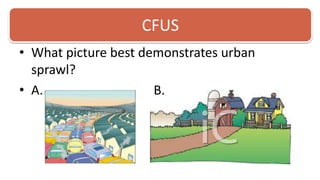
This document contains information about zoning laws and smart growth planning. It defines zoning as local governments regulating land use and development. Common zoning designations include residential, commercial, and agricultural areas. Smart growth is presented as an alternative to uncontrolled urban sprawl that aims to limit growth, preserve open spaces, and reduce taxpayer costs. Students are tasked with analyzing local zoning decisions using smart growth principles and writing arguments for or against them.