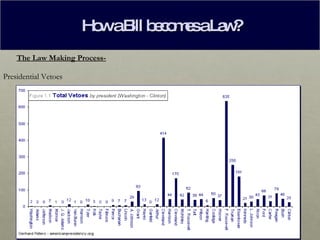
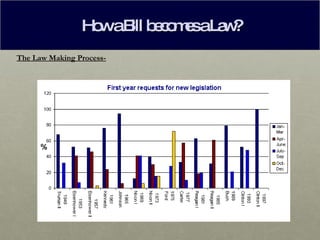
A bill becomes a law through a multi-step legislative process. It begins by being introduced in either the House of Representatives or the Senate by a member of Congress. If the bill passes through committee and floor votes in one chamber, it then moves to the other chamber to repeat the process. If the bill is approved by both chambers in identical form, it is sent to the President, who can sign it into law, veto it, or take no action and allow it to become law automatically.


![How a Bill becomes a Law? The Law Making Process- The Bill will start in either the House or the Senate (all revenue bill must start in the House) STEP 1: Bill is placed in the hopper (box), read titled and numbered. EX: H.R.0157 = “House Resolution” 1057 S.4556 = “Senate” 4556 STEP 2: Bill is sent to the proper Standing Committee. EX: H.R.4185 : To direct the Consumer Product Safety Commission to strengthen regulations concerning the flammability of children's clothing. Sponsor: Rep Andrews, Robert E. [NJ-1] (introduced 11/1/2007) Cosponsors (None) Committees: House Energy and Commerce Latest Major Action: 11/1/2007 Referred to House committee. Status: Referred to the House Committee on Energy and Commerce](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/congress-1228788313373437-9/85/How-a-Bill-becomes-a-Law-3-320.jpg)