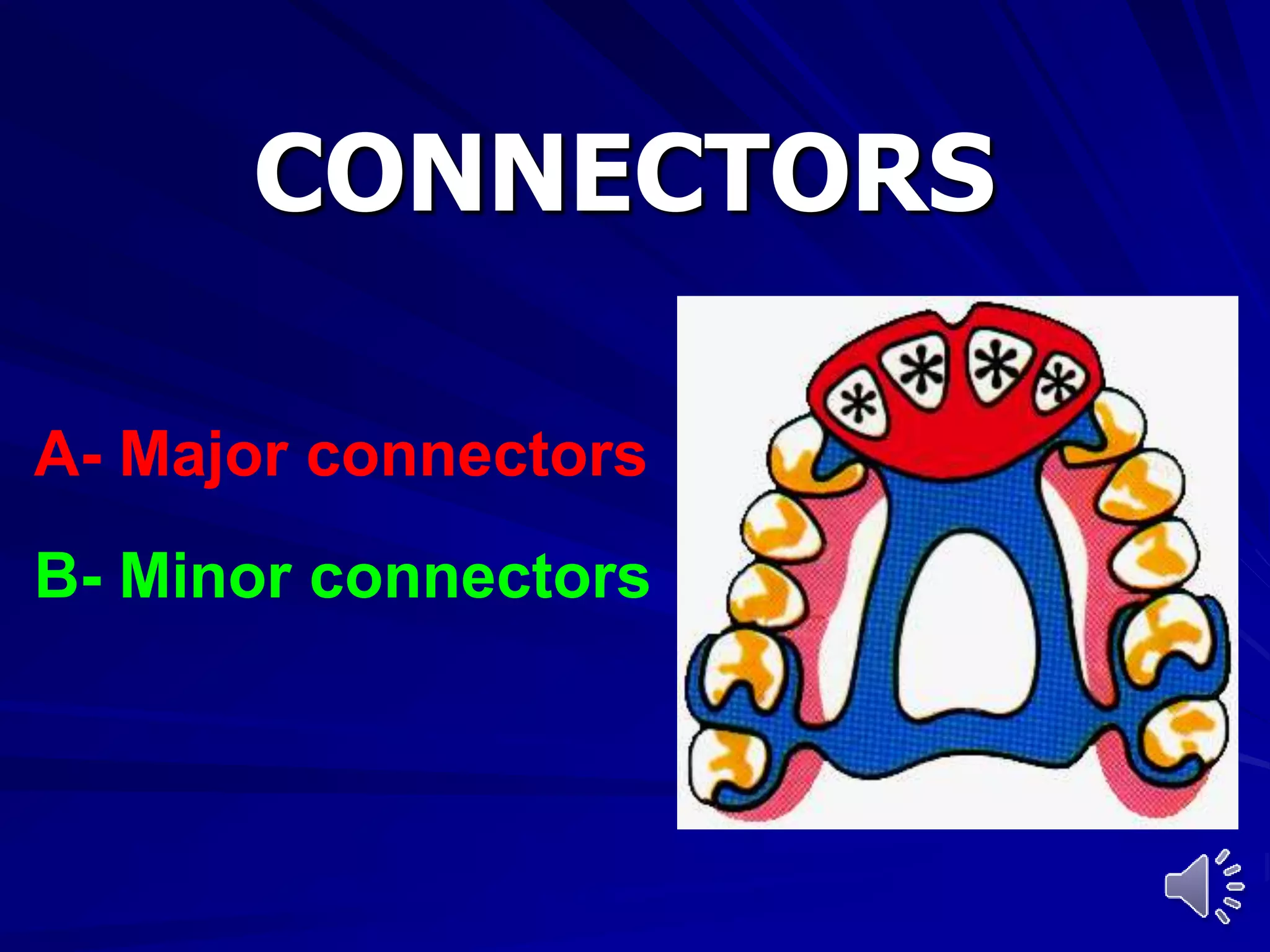
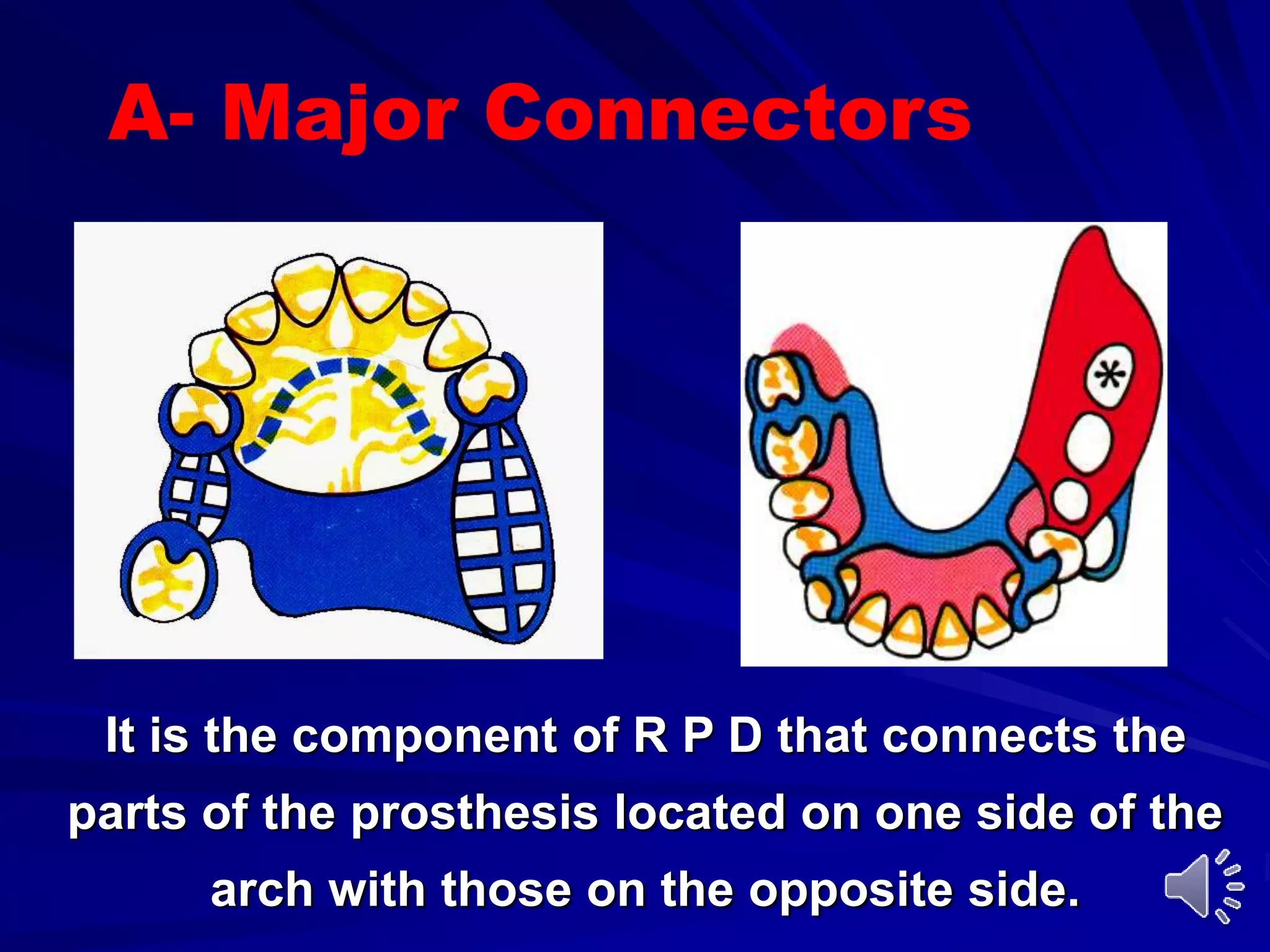
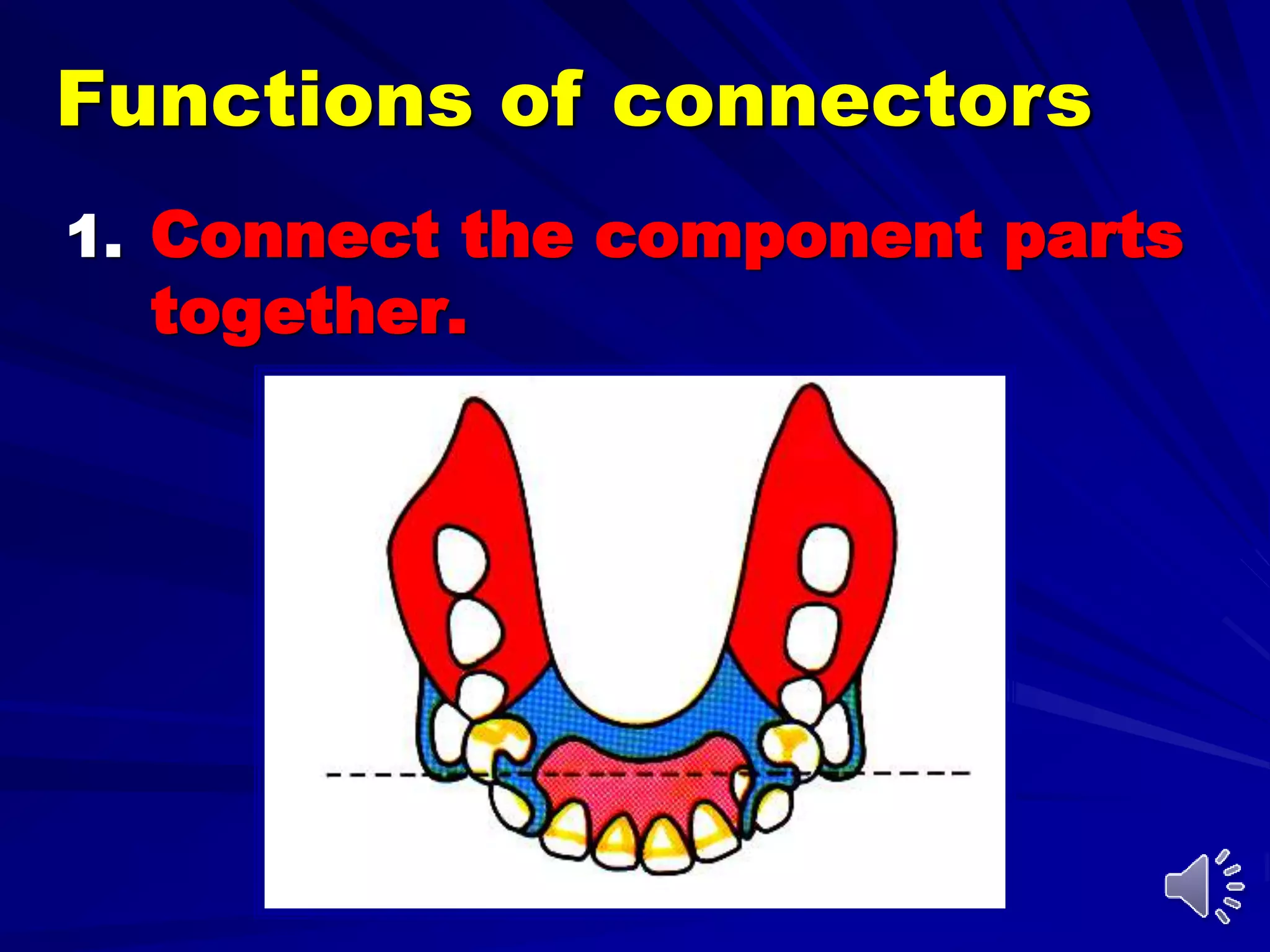
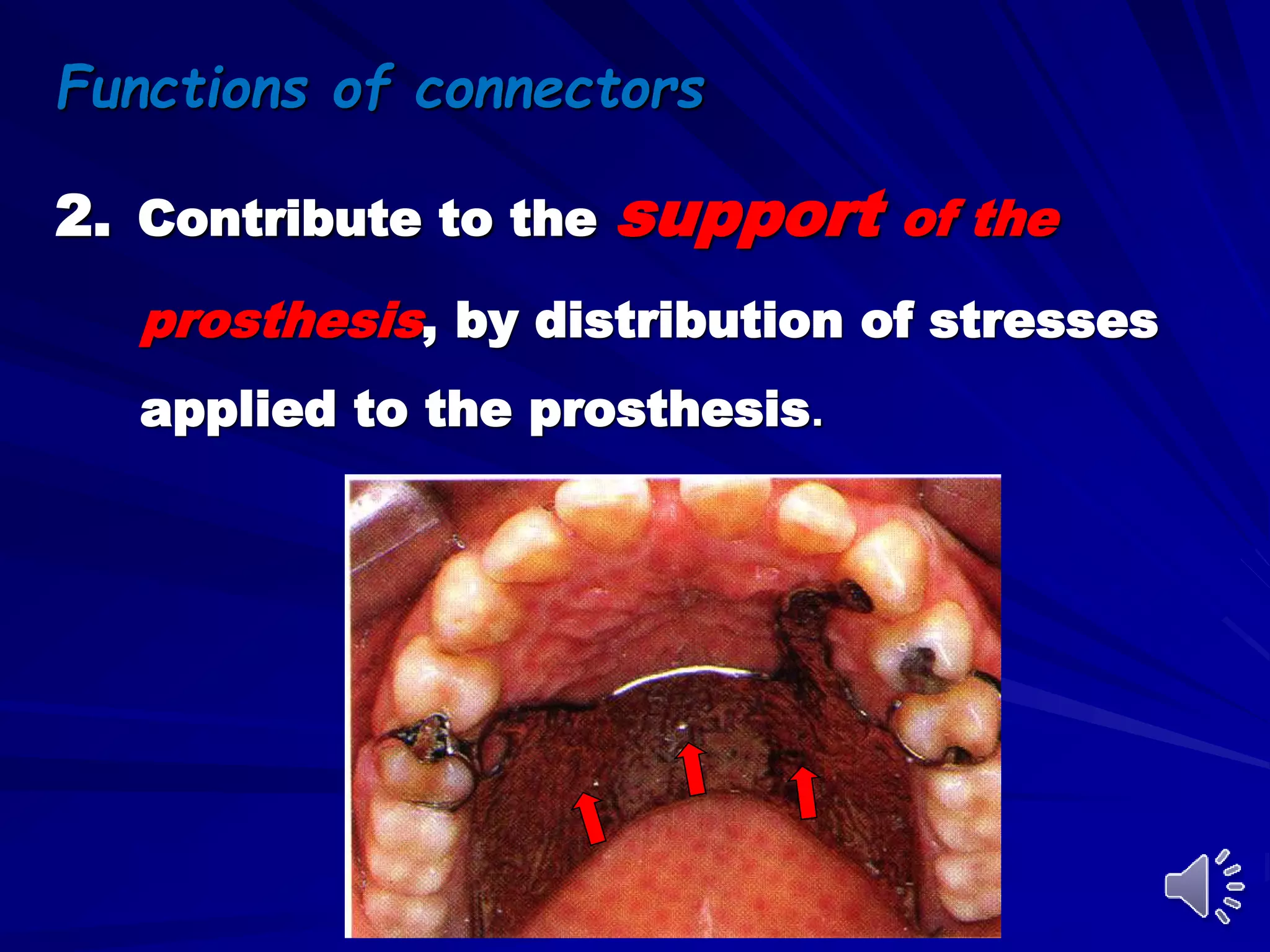
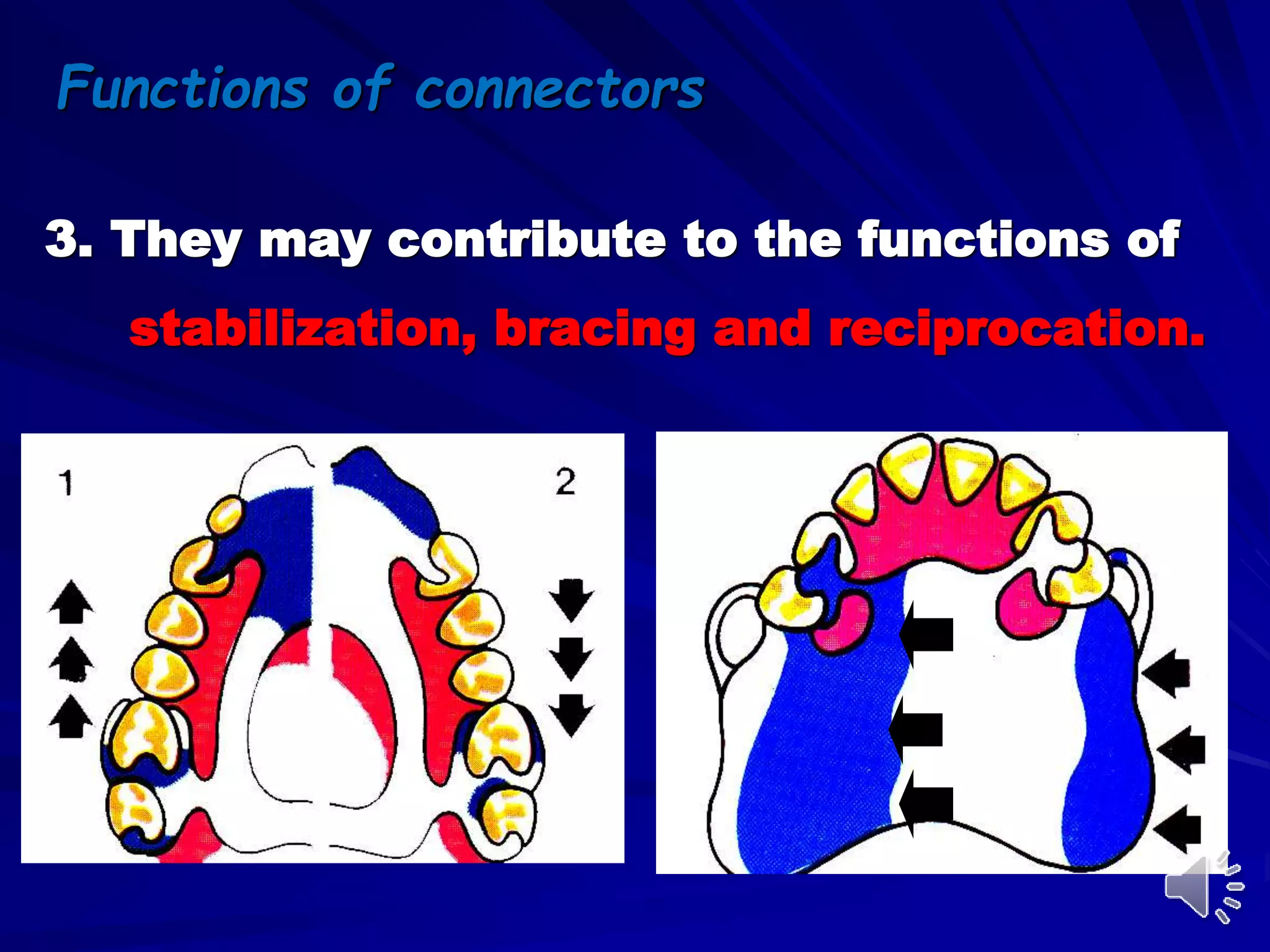
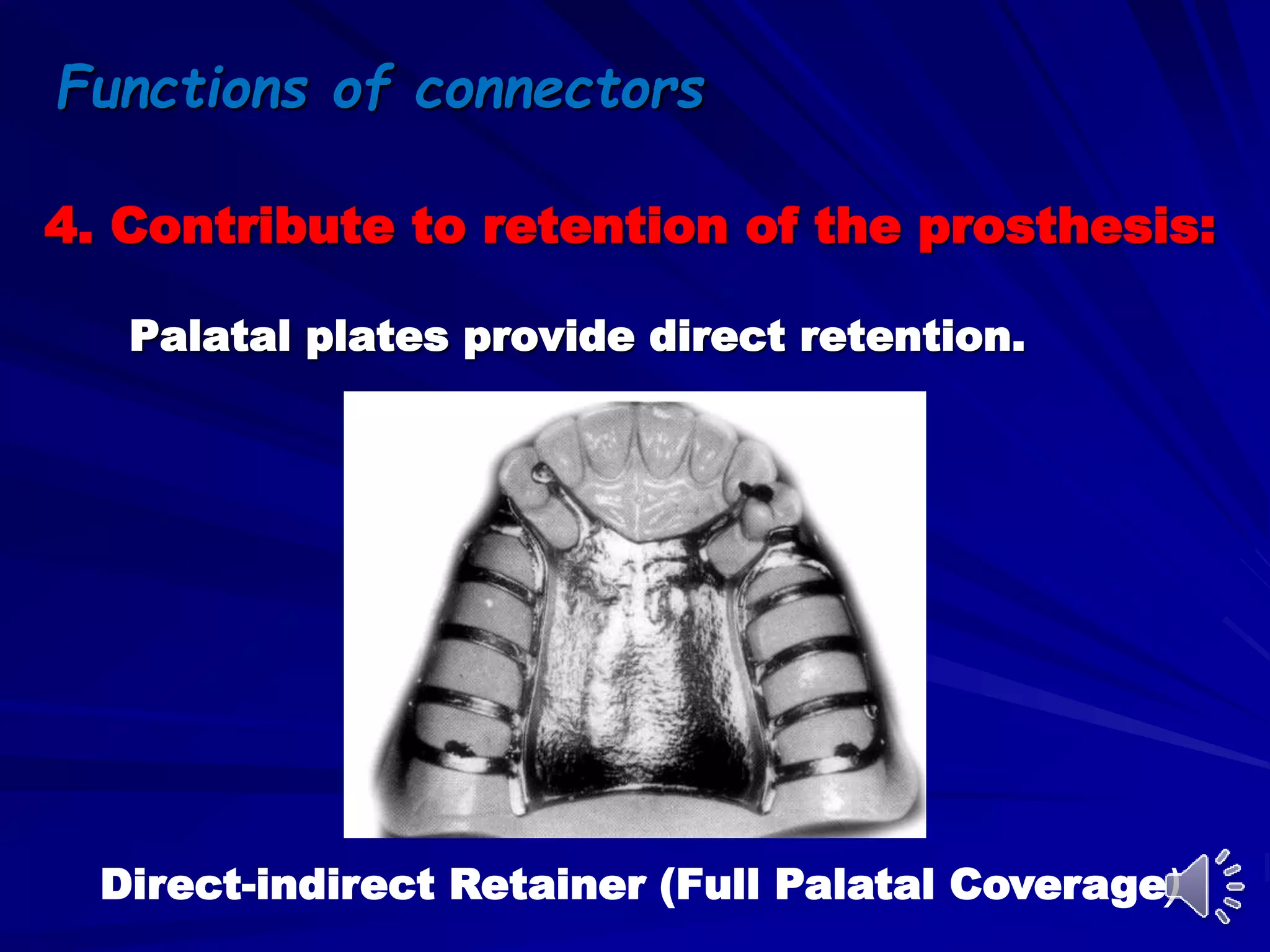
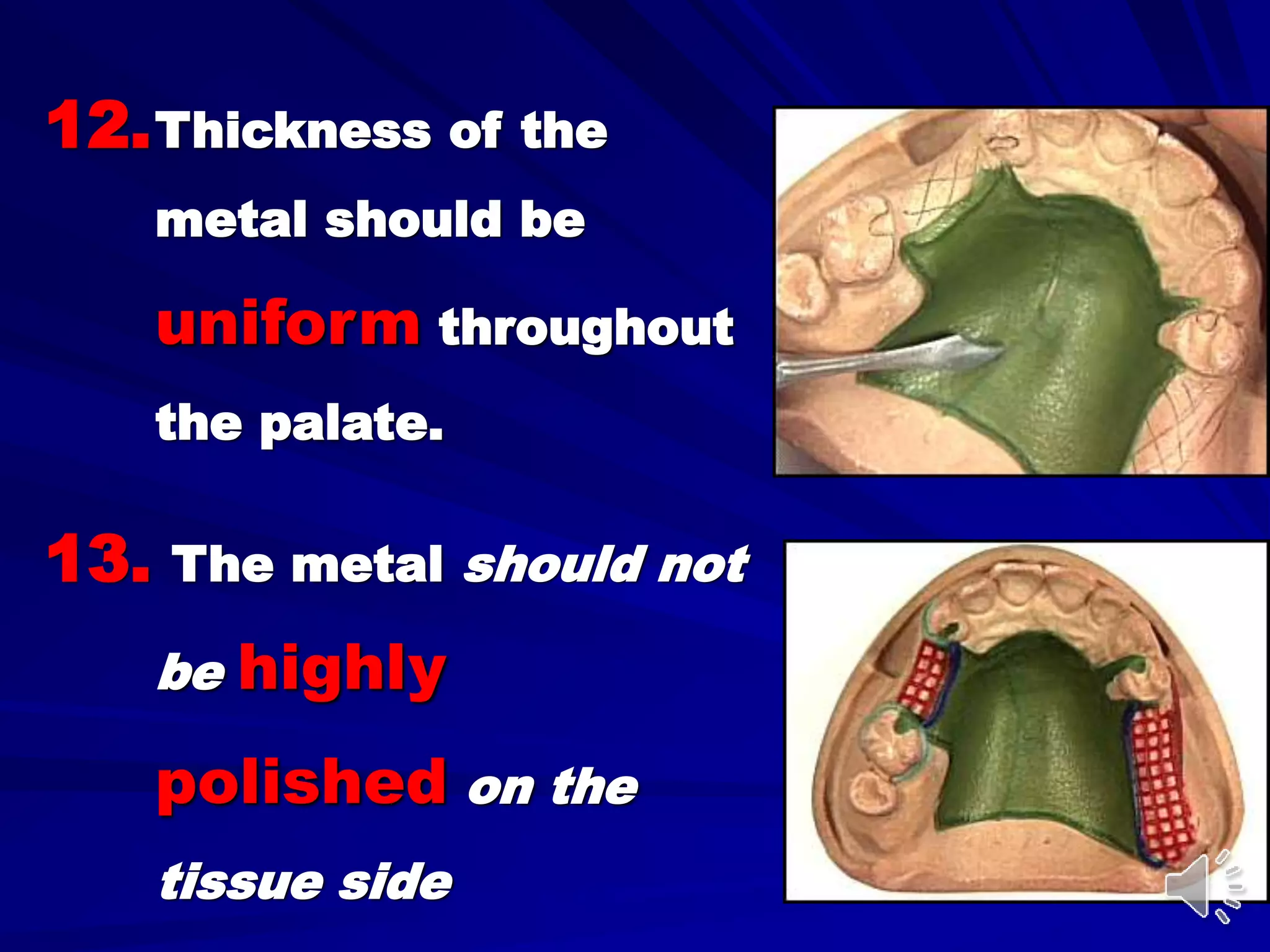
1. Major connectors join the component parts of a removable partial denture together and contribute to its support, bracing, retention, and stabilization functions.
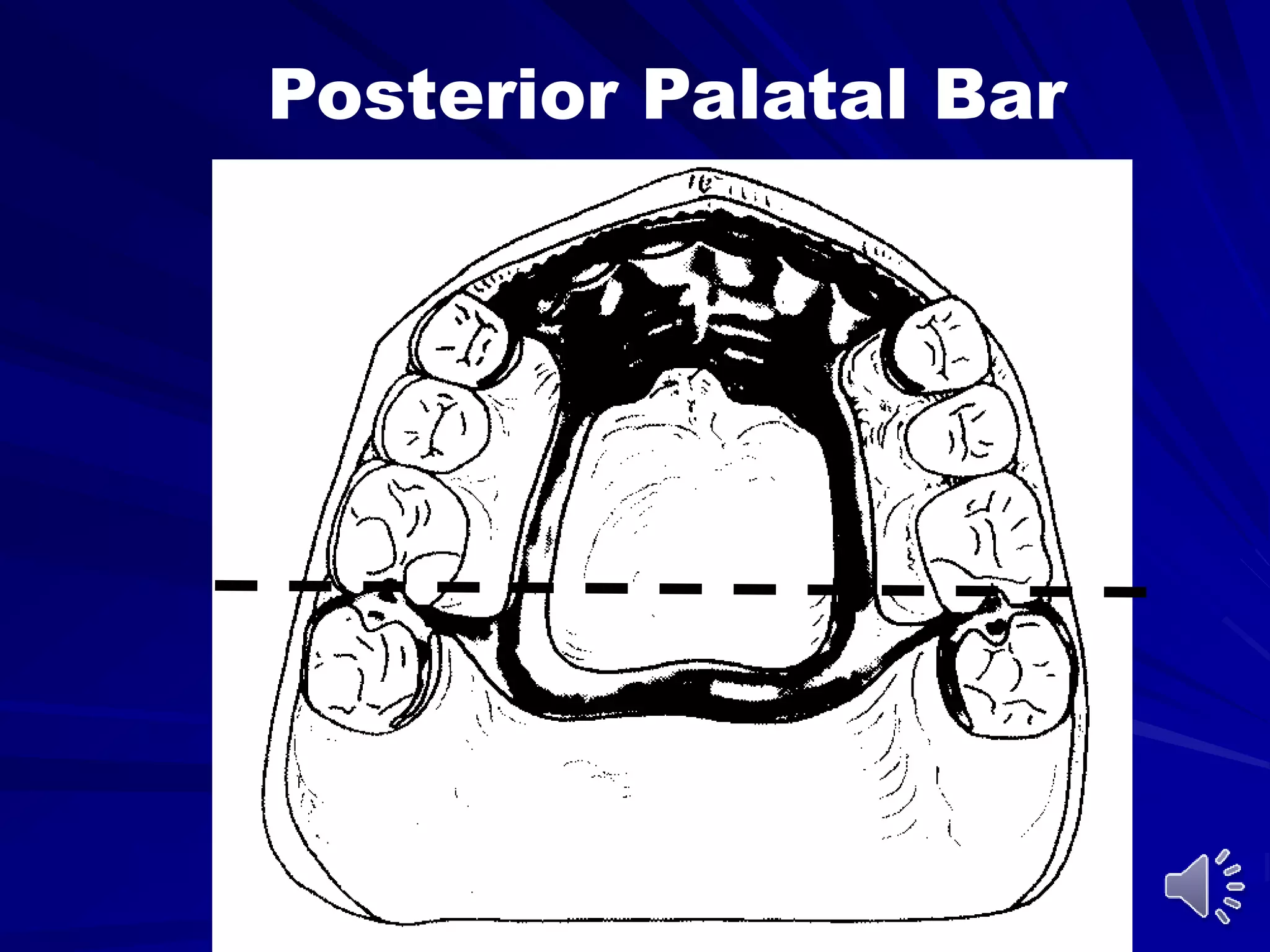
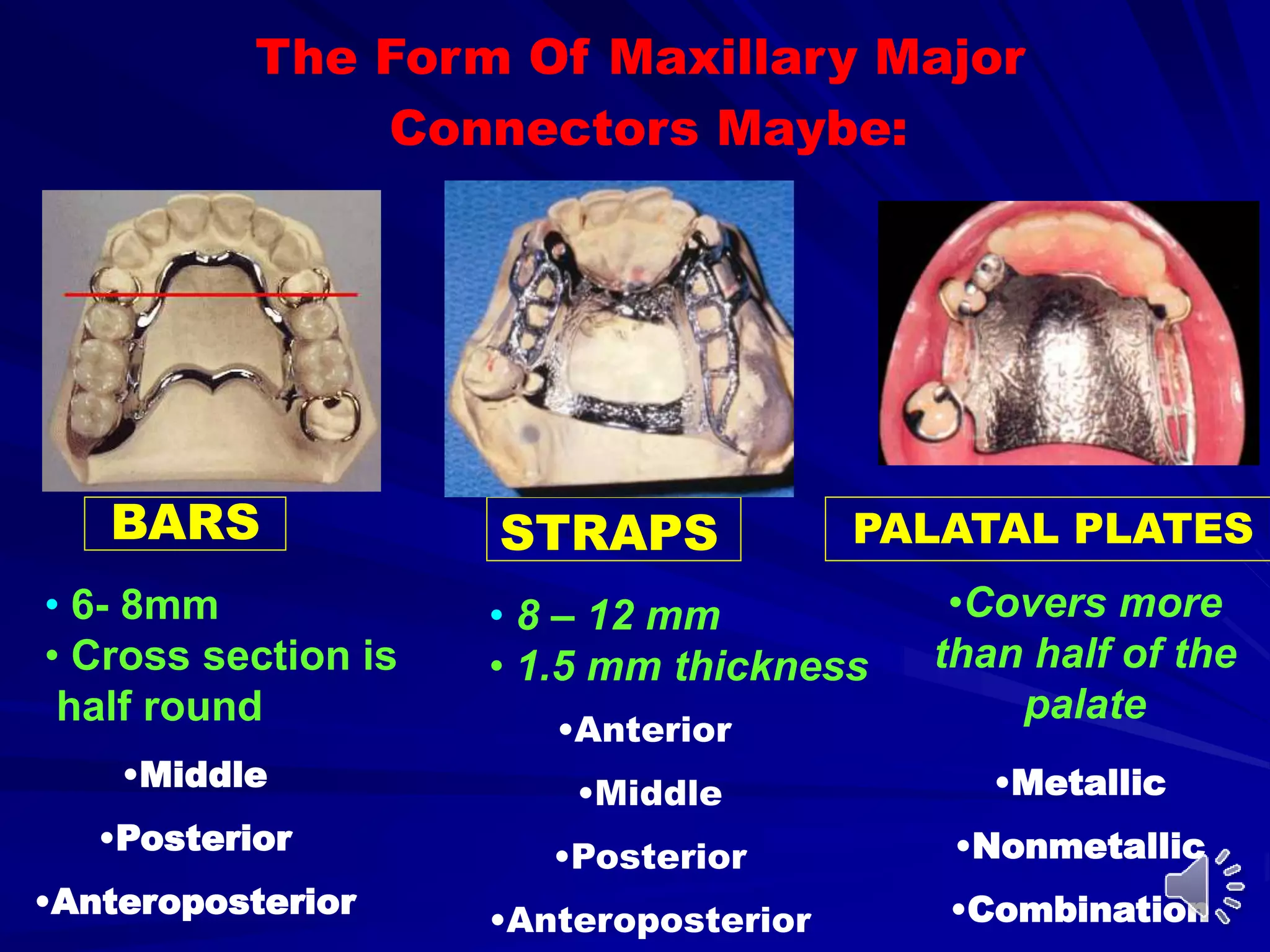
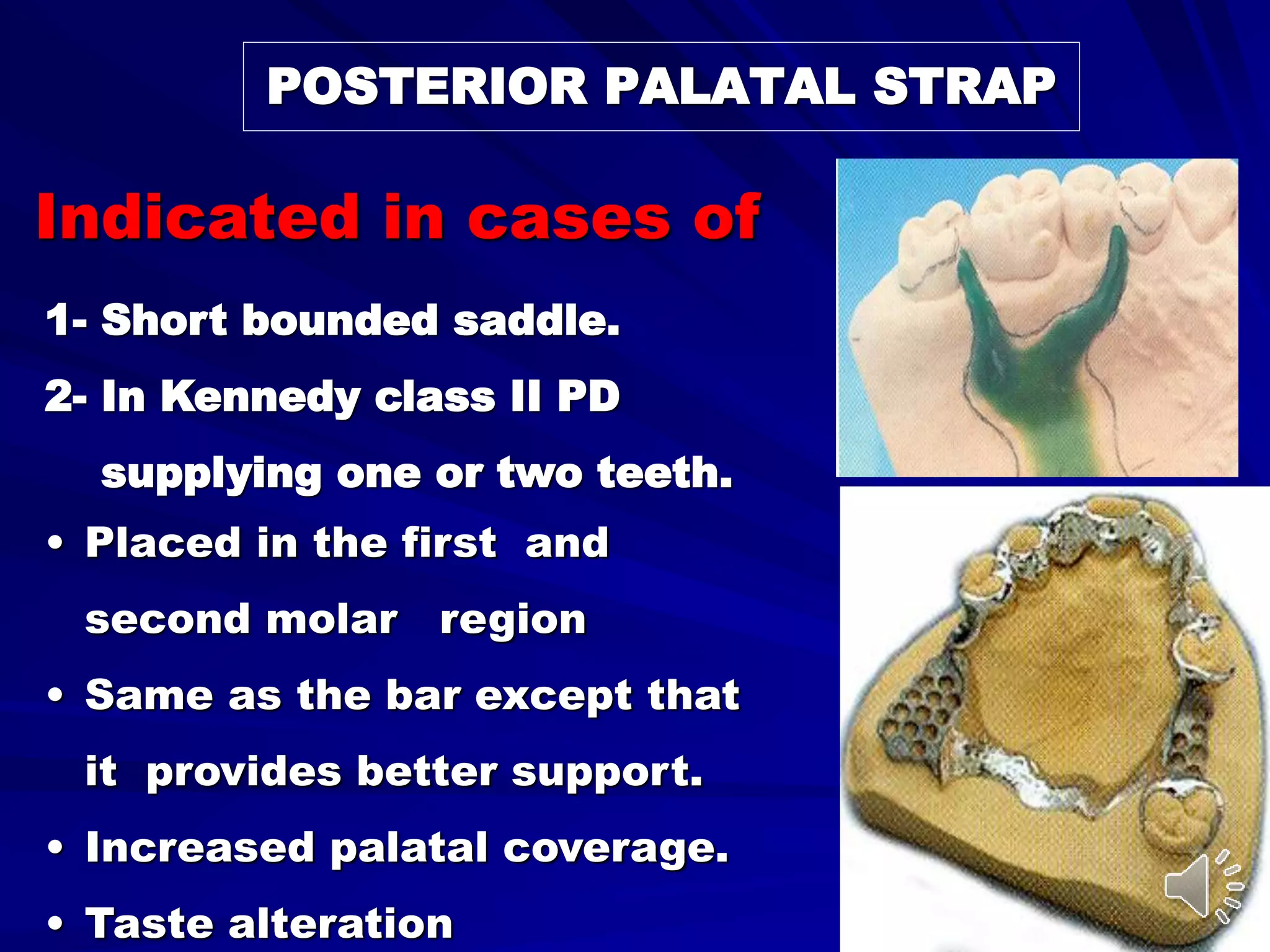
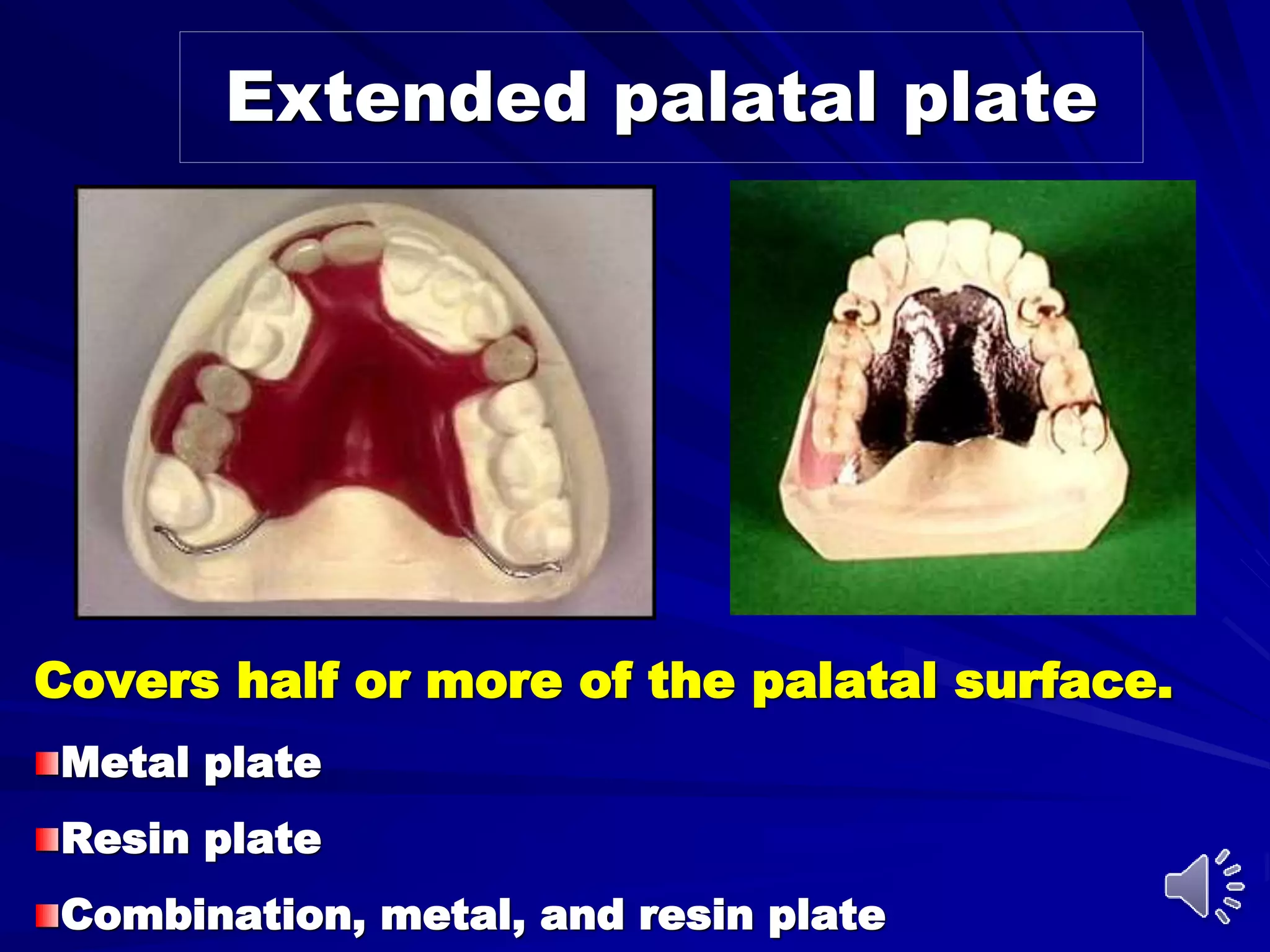
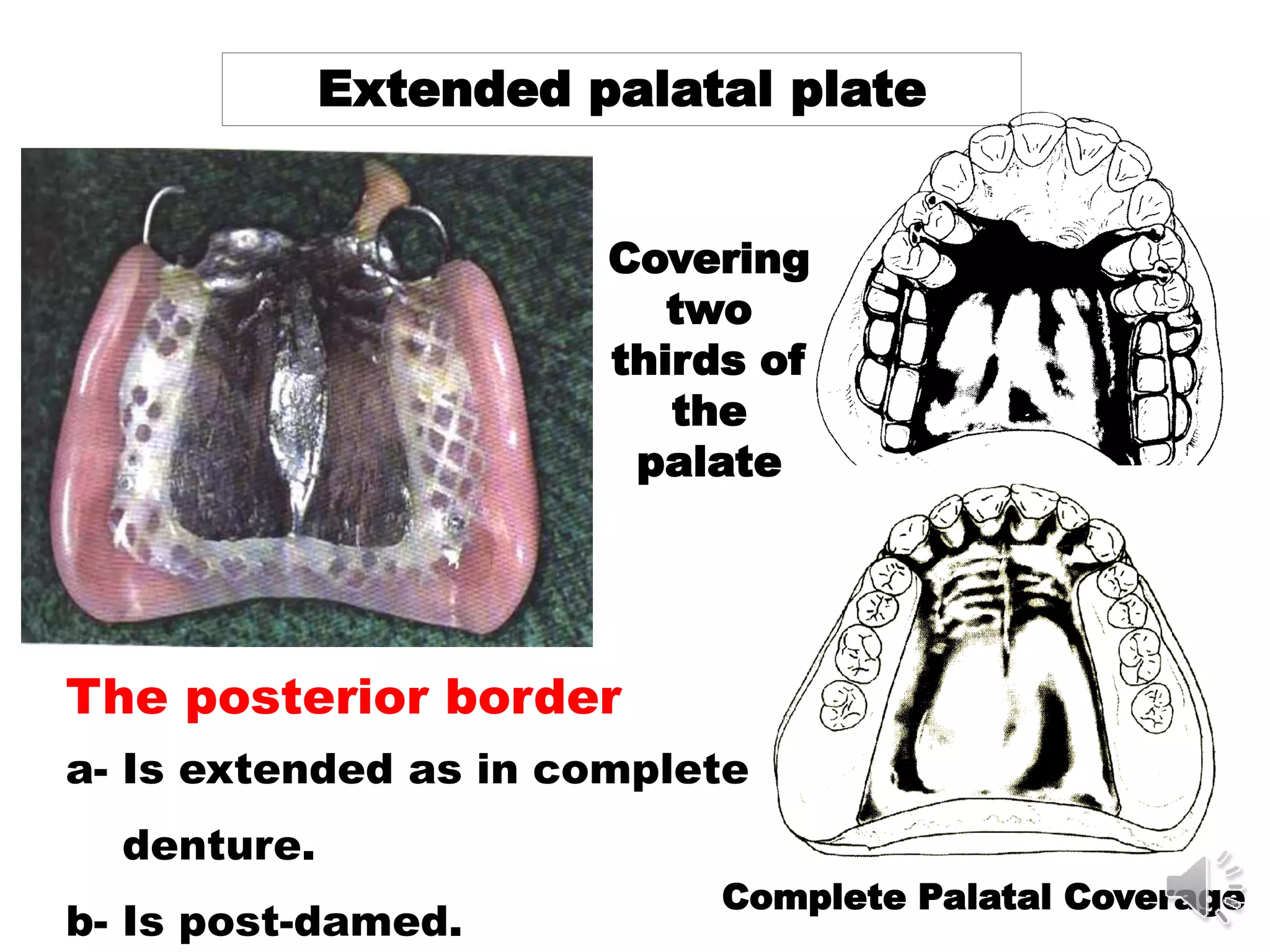
2. The most common types of major connectors include palatal straps and plates. Palatal straps are preferred as they are thinner, cover less tissue, and interfere less with speech and comfort.
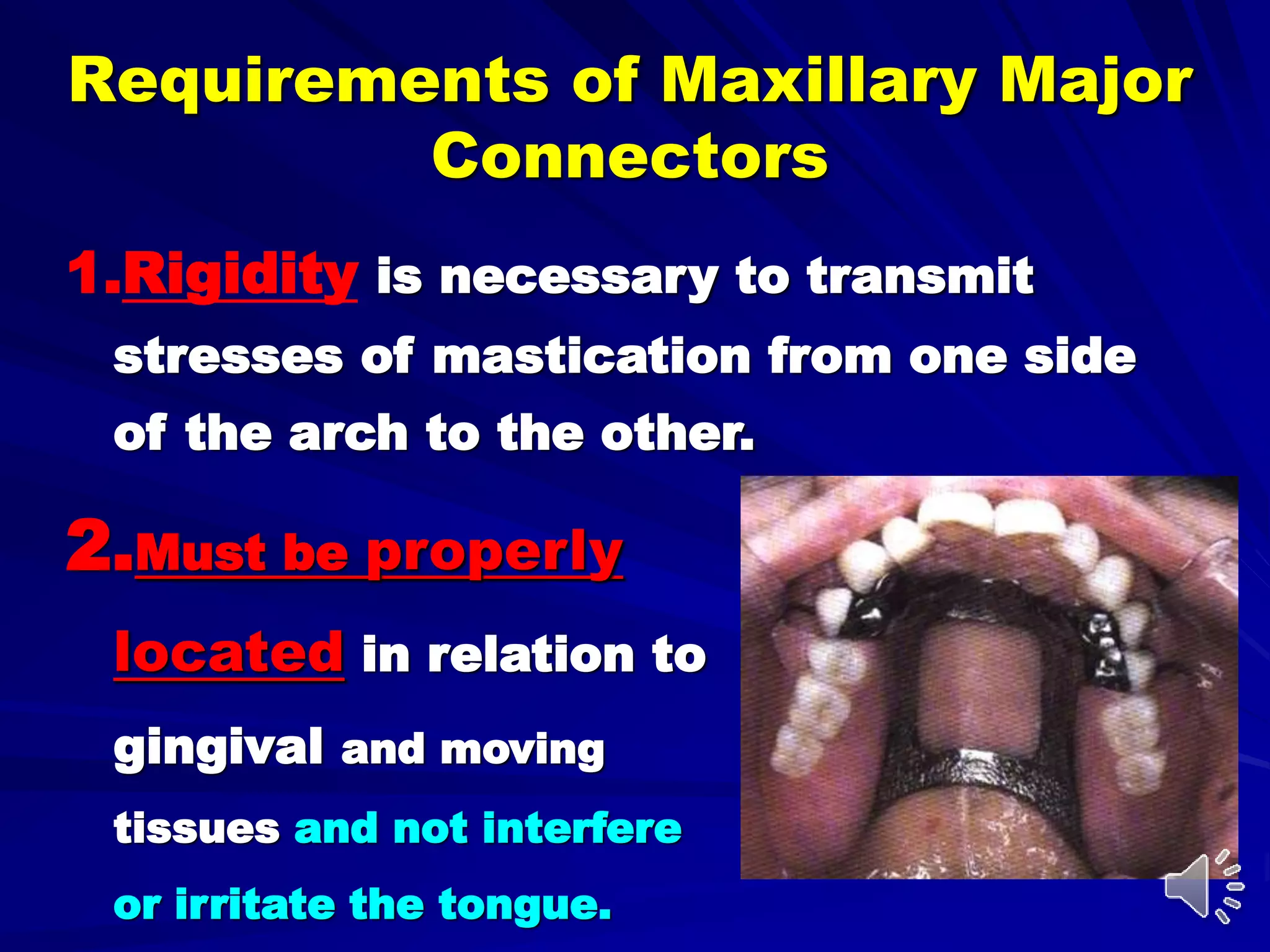
3. The design of a major connector depends on factors like the locations of edentulous areas, the need for rigidity and indirect retention, and patient comfort. A middle palatal strap is often the most versatile option.